Plum (Prunus) belongs to the genus of arborescent plants and is a member of the pink family. This genus unites about 250 species that are naturally found in the Northern Hemisphere. Plum is a natural hybrid of blackthorn and cherry plum. Already in Ancient Egypt, this plant was grown, in the 5-6th century BC. At the same time, long before our era, the Syrians learned to make prunes from the fruits of plums, while they traded them with other countries. There is a legend that it was the Roman general Pompey who brought the plum from Damascus to Europe. Damascus plum and walnut plum were the best varieties in Rome. During the Crusades, other excellent varieties of this culture were also brought to the lands of Europe, for example, Renclode, which got its name in honor of Claude, who was the daughter of Louis XII. Below, it will be described in detail about such a home plum, whose homeland is the Caucasus.
Content
Plum features
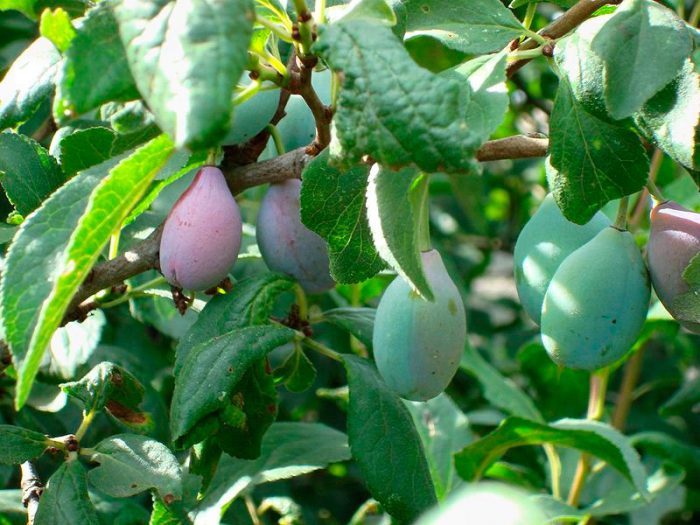
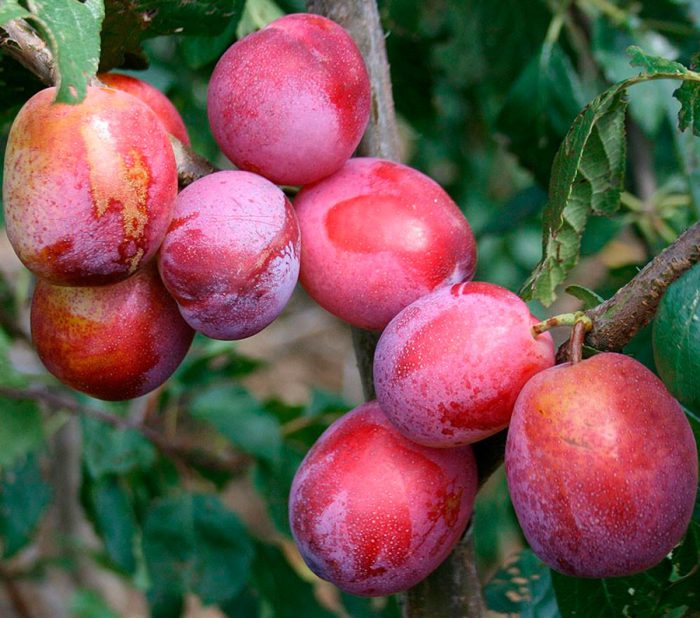
Plum is a tree that reaches a height of about 15 meters. The shape of the crown is ovoid. The life expectancy of this culture is approximately 25 years, while it actively bears fruit from 10 to 15 years. The beginning of fruiting in early-growing varieties is observed 2–3 years after planting, while in late-fruited varieties - only 6–7 years. Such a tree has a core system of roots. Moreover, most of the roots are located at a depth of 0.2 to 0.4 m.Simple alternate leaf plates have short petioles and an elliptical or obovate shape. The edge of the leaves can be crenate or serrate, on the seamy surface of the plate there is pubescence. The length of the leaf plates is 4–10 centimeters, and their width is 2–5 centimeters. From a flower bud, from 1 to 3 white flowers appear, which reach 15–20 mm in diameter. The fruit is a drupe, inside of which there is a flattened bone, which has sharp edges on both sides. It can be colored yellow, red, purple, greenish or bluish-black, with a bluish bloom on the surface. The hearths can be elongated or rounded. This genus also includes such plants as: cherry, sweet cherry, bird cherry, almond, apricot and peach.
Planting plums in open ground
What time to plant
If the climate in your region is cool enough, then planting plums in open ground should be done in spring, or rather, in April, before bud break. If the climate is mild and warm, then this procedure can be carried out in the autumn in mid-September, in this case the seedling will be able to take root well before the onset of frost. However, if you have a plum sapling in October or November, then planting should be postponed until next spring. In this case, the seedling must be dug in the garden area, and then covered with spruce branches, placing the needles upward, which will not allow the mice to get to the planting material. After the snow falls, it should be thrown over the shelter in a thick layer. In spring, during the period of bud opening, the seedlings need to be pulled out and planted in holes, the preparation of which should be done in the fall.
Plum planting in autumn
If the winter in your region is mild and relatively warm, then you can start planting plums in autumn, but you need to prepare the site for this in advance. Despite the fact that a self-fertile variety of plums will be used for planting, experts advise planting a couple of bushes of a different variety nearby, in this case, their consistently high fruiting will be guaranteed.
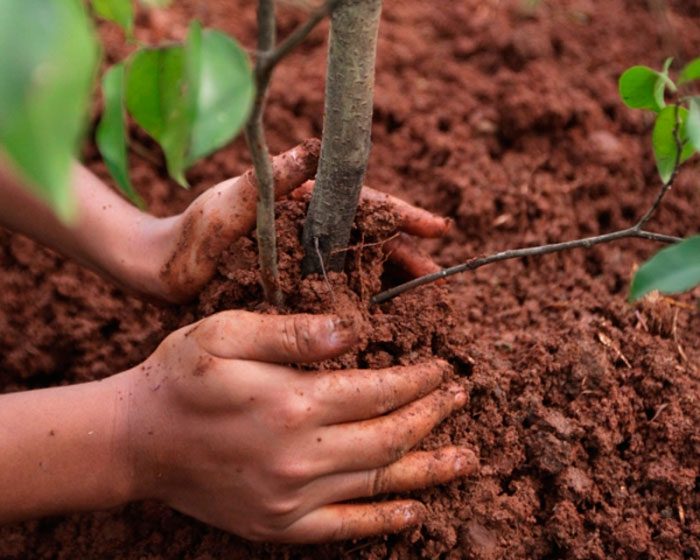
The preparation of the landing pit should be done half a month before the day of disembarkation. The soil on the site can be anything, just not sour. But the depth of the groundwater should be more than 1.5 m. The site should be located in the southwestern, southern or western part of the garden. It should be well lit and protected from cold winds and drafts. The site should be dug to the depth of the shovel bayonet. If the soil is acidic, then one of the deoxidizers is introduced into it for digging, for example, wood ash or dolomite flour (per 1 square meter of the site from 0.6 to 0.8 kg). After that, it is necessary to make a pit, the diameter of which should be about 0.7 m, and the depth should be at least 0.6 m. When digging a hole, the upper nutrient layer of the soil must be thrown away separately from the lower one. A long stake should be installed in the center of the bottom of the pit so that it rises above the surface of the site by at least 50 cm. The nutrient soil must be combined with peat or humus in a 1: 1 ratio. The resulting soil mixture must be poured onto the bottom of the pit with a mound.
It is also very important to choose the right seedling. The root system of a good seedling should be fresh, not dry. A slightly weathered root system must be placed in a container of water a few hours before planting. The bark must be intact, not damaged. Examine the bole carefully, it should be in very good condition. There should be no bifurcations at the trunk of the seedling.
The sequence of planting plums in autumn is as follows: a one-year-old seedling should be placed on a mound that was previously poured around the peg, then when the roots are very carefully straightened, the pit is filled with nutritious soil, which is combined with organic matter in advance.You need to fill up the hole gradually, trying not to leave voids in the soil. In a planted plant, the root collar should rise above the surface of the site by 30–40 mm. The planted plum needs watering; for this, 20-30 liters of water are poured under the bush. After the liquid is completely absorbed and the soil has settled, the root collar of the plant should be flush with the soil surface. Then the surface of the trunk circle must be covered with a layer of mulch (peat).


Watch this video on YouTube
Spring planting
Plum planting in spring and autumn has only slight differences. So, in the springtime, a nutritious soil mixture must be mixed with both organic and mineral fertilizers. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are also added, which cannot be used in autumn. Nutrient soil must be combined with organic matter (compost or humus) in a 1: 1 ratio, then 40 to 60 grams of potassium salt, 200 to 300 grams of superphosphate and 300 to 400 grams of wood ash are poured into it and everything is mixed well. The resulting soil mixture will need to be filled with the root system of the seedling during planting. A distance of at least 3-4 m should be kept between seedlings. Experts recommend planting two plums not far from each other, while choosing varieties that bloom at the same time. The cherry plum growing not far from the plum tree can become its pollinator. Do not forget that you need to have time to plant the plum before the sap flow begins.
Plum care
Taking care of a plum tree is not at all difficult, but only if you know certain rules and tricks, which will be discussed below.
Plum care in spring
To greatly facilitate pest control, it is necessary to attract as many birds as possible to your garden plot in early spring. To do this, birdhouses are hung in the garden. The plum tree will need to be pruned in mid-March. In April, the soil should be dug in the near-trunk circles and between the rows, while nitrogen fertilizers are applied to it. For 1 adult tree, which has already begun to bear fruit, take from 300 to 400 grams of urea or calcium nitrate, while for a young plant that is more than one year old, 100-200 grams will be enough. You need to dig up the soil carefully, as you can injure the roots of the plant. Therefore, soil can be dug around the trunk to a depth not exceeding 5-10 centimeters. In spring, this crop should be treated for prophylaxis in order to destroy pests and pathogenic microorganisms that have settled down for the winter in the upper soil layer and in the bark of the plant. If the air temperature drops to 1 degree, then every night it will be necessary to burn smoke heaps, while smoking can only be stopped a couple of hours after the sun rises. If there is no rain in spring, then the plum will need to be watered, while the water consumption per plant for 1 watering is from 30 to 60 liters. In the last days of May, plums should be fertilized with organic fertilizers, then the surface of the trunk circle should be covered with a layer of mulch (peat or sawdust). The surface of the trunk circle must always be clean, so weeds and root shoots must be pulled out in a timely manner.
Plum care in summer
In the summer, when the plum has faded, it must be fed in the same way as in the spring, while using the same fertilizers in the same proportions. If there is a drought, then the plant will need watering. The beginning of fruiting occurs, as a rule, in the last summer weeks, in this regard, you need to be ready to collect and process ripe fruits on time.
Plum care in autumn
Fruit collection continues in September. When the entire crop is harvested, the plant will need water-charging podzimny watering.If the soil on the site is under black steam, then you must first rake and destroy all the leaves that have flown around, and then dig the soil between the rows and in the near-trunk circles. What fertilizers do experts advise to use for feeding plums in autumn? Mineral fertilizers, as well as organic matter (described in more detail below) are applied to each trunk circle. All mosses, lichens and dead bark must be removed from the surface of the base of the skeletal branches and the trunk. The wounds found are cleaned, then treated with a solution of iron or copper sulfate, and after all they are coated with garden varnish. The base of the branches and trunks must be whitened with lime, to which copper sulfate is added. Then plum trees need to be prepared for winter.
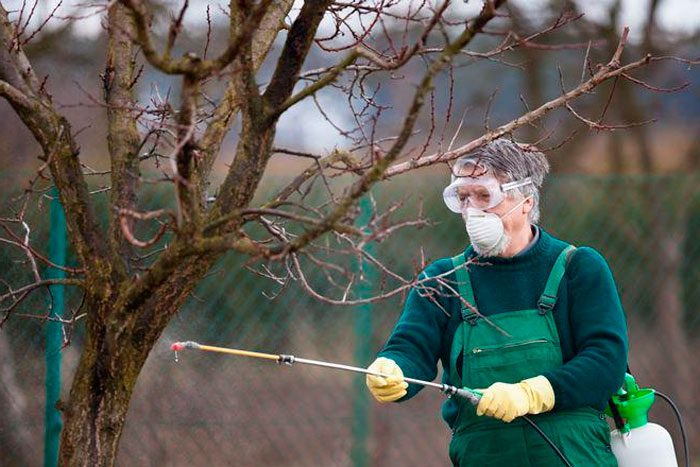
Plum processing
For the first time in a season, for the purpose of prevention, the plant is sprayed in the spring before the sap flow begins, as a rule, this time falls on the last days of March or the first days of April. Then the plant is sprayed with a urea solution (0.7 kg of substance per bucket of water). This will exterminate all pests and pathogenic microorganisms that overwintered in the bark of the plant or in the trunk circle, while the urea solution will become a source of nitrogen for the plant. However, this treatment needs to be done before the kidneys open, if you missed the moment, then urea must be replaced with Agravertin, Iskra-bio, Fitoverm, Akarin or another means of similar action. In order for the plum to become more resistant to diseases and adverse weather conditions, after the first treatment, it is necessary to spray it with a solution of Zircon or Ekoberin. Repeated preventive spraying is carried out in October, the plum is treated before starting to prepare it for winter.


Watch this video on YouTube
Watering the plum
When watering a plum tree, make sure that the soil is necessarily soaked to a depth of about 0.4 m. The amount of rainfall affects the number of irrigations throughout the growing season. On average, a plant is watered 3-5 times per season, while about 100 liters of water are poured under 1 fruit-bearing tree for 1 watering, and 40–60 liters under a young plant. In the autumn, it is necessary to water the plums with water charging, in addition to the fact that as a result of this, the soil is saturated with liquid, which is enough for the plant for the whole winter, the winter hardiness of the tree will also increase.
Plum dressing
Fertilizers are applied to the soil of the trunk circle, while simultaneously loosening it. The introduction of organic matter into the soil is carried out 1 time in 3 or 4 years (per 1 square meter from 10 to 12 kilograms). Mineral fertilizers are applied once every 2 or 3 years, while it should be borne in mind that plants need nitrogen only in spring, and potassium and phosphorus - in autumn. In the first and fourth year after planting the plum in open ground, 40 to 50 grams of potassium salt, 120 to 180 grams of superphosphate and 60 to 90 grams of ammonium nitrate are added to the soil. For 5–8 years of fertilizers for feeding, you need to take 2 times more.
Plum wintering
You do not need to cover a mature plum tree for the winter. However, the surface of the trunk circle must be covered with a layer of mulch (humus or peat). While the plant is young, it needs shelter for the winter, for this it should be wrapped in burlap or tied with spruce branches. It is not recommended to use artificial covering material, since the plant can resist under it.
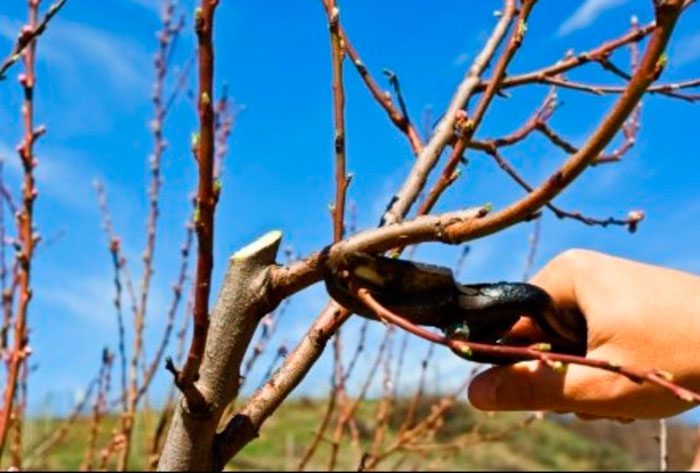
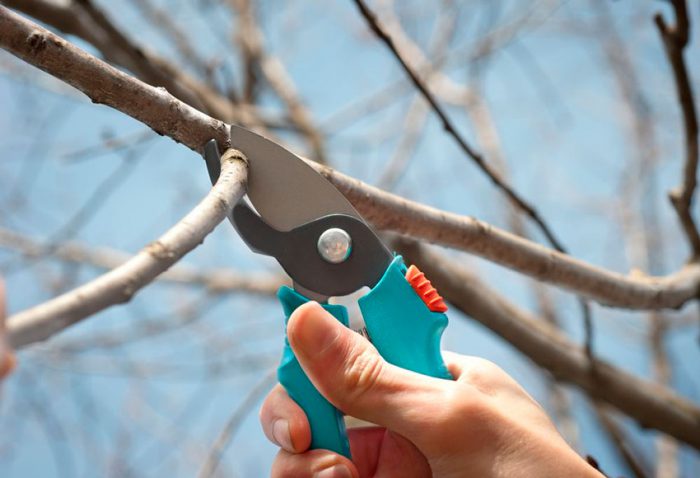
Pruning plum
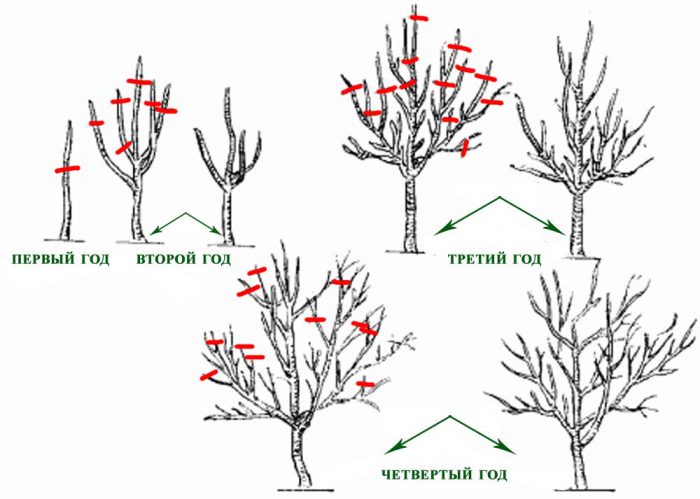
It is recommended to carry out formative pruning in spring before sap flow begins. The most popular is the shape of the crown, called a sparse-tiered, while the height of the trunk should be at least 0.4 m. They begin formative pruning 1 year after planting, the fact is that in the first years of life this culture is distinguished by the most active growth. Crown formation lasts 5 years.
How to prune a plum
Formative pruning should be started in the second year after planting the plum. In spring, a lower tier should be formed on it, which consists of 5–7 skeletal branches spaced at an equal distance from each other, and they should also be directed in different directions with an angle of departure from the trunk equal to 45 degrees. It is necessary to form this tier at the height of the trunk from 0.45 to 0.5 m (it is necessary to measure it from the surface of the site). The branches growing below this tier must be cut out. Branches located above the stem and growing at an angle of less than 40 degrees must also be removed, because they break off easily during the fruiting period. Skeletal branches must be shortened by 1/3 of the length, and the remaining ones must be cut into a ring, while there should be no stumps. The conductor must be shortened so that the annual plum height reaches 150 to 180 cm.
In the third year of growth, the conductor of the plant should be cut so that it is 0.3–0.4 m higher than the upper branch. In this case, the conductor will remain straight during growth. Cut off by ¼ or 1/3 of the length of those growths, the extensions of the branches that are longer than 0.6 m. The lateral shoots should be shortened to 15 centimeters by the bud oriented downward. At a distance of half a meter from the trunk, you need to start forming skeletal branches of the second order. It should be borne in mind that the distance between the skeletal branches of the second order, located on the skeletal branch of the first order, must be at least 0.3 m.
In the fourth year of growth, after the next shortening of the conductor, all skeletal branches should be 6 buds shorter than it. The conductor should be trimmed regularly until its height is 250 cm, then only new growth will need to be trimmed every year. Particular attention should be paid to the formation of the top; for this, regularly remove those shoots that grow incorrectly. The shape of the crown should be pyramidal; therefore, when the tree begins to bear fruit, its guide must be cut to the level of the upper lateral skeletal branch. Shortening last year's gains helps to stimulate the growth of new gains in the next season.
After 4 years, the main crown shaping will be completed, from that time pruning will be necessary to stimulate the growth of new fruit branches, which give the bulk of the fruit. Fruit growth is observed on young fruit wood, which is 2–3 years old. Branches that are 4 years old that bore fruit last season must be removed. Pruning old branches regularly will not need any anti-aging pruning at all.
You only need to cut the plant with a very sharp tool, and the places of the cuts should be coated with garden varnish.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pruning plums in spring
Experts recommend pruning the plum tree in the spring and it is best to do this in the last days of March or the first in April. At this time, all branches injured and frostbitten in winter are cut off, and the crown is formed. When forming tiers, you will need to bend the branches. To do this, the skeletal branch is tied with twine, after which it is pulled down from the trunk at an angle of 50-60 degrees, while it must be done so that during bending the branch does not take an arched shape. Then, at the base of the trunk, the lower end of the twine is fixed. It is necessary to put rubber to the trunk or branch of the tree under the twine fastening, this will help to avoid injury to the plant bark. An event such as bending branches is carried out in order for the plum to begin bearing fruit 2 or 3 years earlier. If the bending of the branches is not carried out in April, but later, then the result of this procedure will be noticeable only in the next season.
Pruning plums in summer
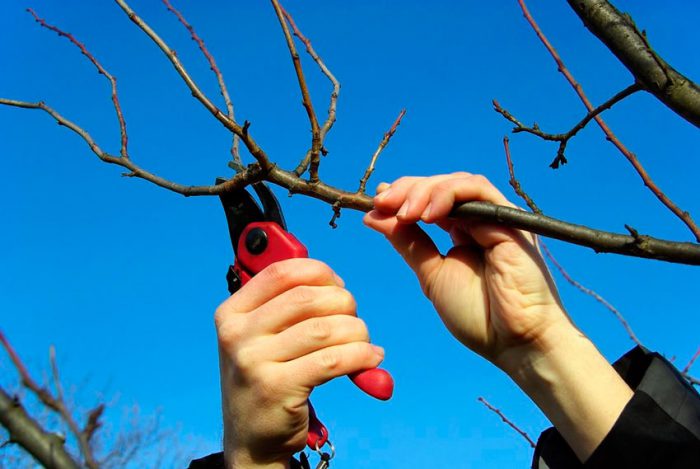
While the plant is young, it is characterized by extremely intensive growth, as well as a tendency to thicken the crown. Therefore, the formation of the crown can be done throughout the growing season, when necessary. In summer, experts recommend pruning the plum in the last days of June. In the youngest plants, lateral shoots are shortened by 20 centimeters, and premature shoots by 15 centimeters. In summer, the center conductor is not trimmed. Also in June, those branches that have suffered from frost in the winter are clearly visible, so they should be pruned to healthy tissue. You should also cut out all the shoots that contribute to the thickening of the crown.
Pruning plums in autumn
When leaf fall ends, you should make sanitary pruning of the tree, this time falls on the second half of September. To do this, cut out all dried, injured and diseased branches, and, if necessary, shorten the central conductor. After that, they are engaged in cutting out the stems, which are characterized by rapid growth, as well as competing shoots, which contribute to the thickening of the crown. All cut branches and stems must be destroyed. However, it should be borne in mind that such pruning in the fall can be done only in those regions where winters are quite mild and warm. Otherwise, this procedure should be carried out in the spring.
Plum propagation
Plums can be propagated by seeds, but it is easier and faster to do this by vegetative methods, such as: grafting, cuttings (root or green cuttings) and shoots. All of these breeding methods will be described in more detail below.
Plum propagation by root suckers
Plum has a fairly large number of root suckers during the season, so reproduction by them is very simple. You can try to get a new plum tree from such a growth, and you do not lose anything, because the root suckers still need to be regularly removed, while trying to keep the plant's near-stem circle always clean. You will need to find a well-developed root sucker, located at a fairly large distance from the tree itself. Its root should be excavated and cut off from the parent plant, while stepping back 20 centimeters from the stem. Then the offspring must be removed from the ground, and the places of the cuts must be smeared with garden pitch. After that, he is planted in a new permanent place. In the case when there is no well-developed shoot near the plum, it is possible to separate a relatively thin and small root offspring, but it will need to be grown in a school for a year.
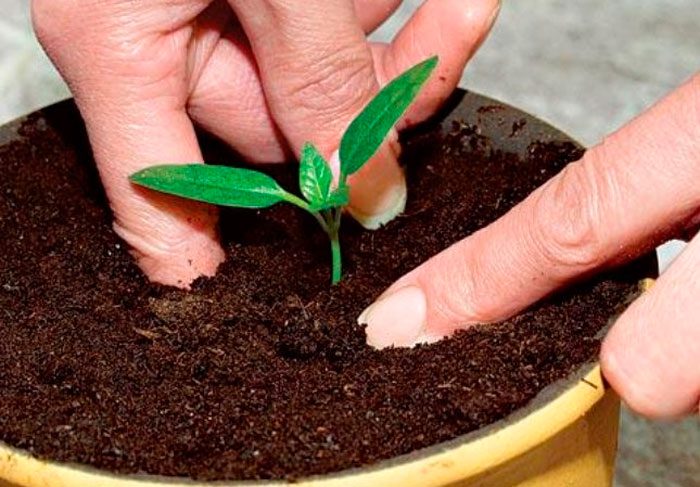
Propagation of plums by seeds
As a rule, seedlings grown from seeds are used as rootstocks for varietal grafting. The bones must be stratified before planting. To do this, they need to be wrapped with a cloth or gauze and placed on a refrigerator shelf, where they should stay from mid-autumn to early March. Then, in March, the seeds are planted in individual pots. The emerging seedlings are provided with systematic watering and feeding. In the autumn, the grown plants need to be planted for growing in a school or in a greenhouse. After 12 months, the seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place and used for grafting varietal plums.


Watch this video on YouTube
Plum propagation by green cuttings
Plum propagation by green cuttings is becoming more and more popular with gardeners every year. The fact is that this method is very simple, while the survival rate of such cuttings is extremely high. But it should be borne in mind that only those cuttings that have been cut from trees prone to the formation of a large number of root suckers will root well.Cuttings should be harvested in June, it is at this time that intensive growth of shoots is observed, and for this you should choose a cloudy day. Young trees are chosen for cutting cuttings. Their length should be equal to 0.3–0.4 m. For rooting, the cuttings must be placed in a container with water, first you need to trim their lower part using a very sharp tool, and also cut off all the lower leaf plates, leaving only ½ part petiole. Immediately above the third leaf plate, you need to make an upper cut at the cutting. Next, the cuttings must be tied with a bundle, and then their lower ends are immersed by 15 mm in a container with a solution of Heteroauxin, so they must stand all night. In order for the cuttings to take root, they need greenhouse conditions, so they need to make a mini greenhouse for them. The container should be filled with a substrate, which includes sand and peat (1: 1), and it is covered with a centimeter layer of sand on top. The soil mixture needs to be watered and tamped a little. It is necessary to deepen the cuttings at an angle of 45 degrees to the petiole of the removed leaf plate. A distance of 5-7 centimeters should be maintained between the cuttings, while the row spacing should be about 5 centimeters. The mini-greenhouse must be covered with a dome on top, which must be transparent. It is transferred to a well-lit area and protected from direct sunlight. Watering the cuttings is carried out using a divider. 4 weeks after planting, the plant should be fed with a weak solution of slurry or a solution of nitrogen-containing fertilizer (30 grams per bucket of water). After the rooting of the cuttings, the dome should be removed. In order for the cuttings to be preserved until the onset of spring, they should be dug up in the last days of September. Next, their roots need to be overlaid with moistened moss and wrapped in foil. They need to be stored in a shed, or you can do this in a trench in a garden plot, while the cuttings are covered with moss, sawdust, or flying leaves on top. In springtime, cuttings should be planted in open soil, where they will grow for 2 years. Then they can be transplanted to a permanent place.
How to propagate by root cuttings
Root cuttings are cut in autumn or spring. To do this, select root shoots, which are at a distance of at least 100 cm from the parent plant.First, you need to remove the offspring from the soil along with the root system, only then you can start cutting the cuttings, the length of which should be about 15 centimeters, and the diameter - approximately 15 millimeters. If the harvesting was carried out in the autumn, then the resulting cuttings must be placed in a box, while sprinkling them with sand, and stored until spring in a place where the air temperature will be from 0 to 2 degrees. The planting of such cuttings is carried out in the first days of May, while using the same scheme as when planting green cuttings. They are planted at an angle, keeping a distance of 10 centimeters, and covered with a cap on top, which should be transparent. Further, root cuttings must be grown in the same way as green ones, while all the necessary procedures must be carried out at the same time.
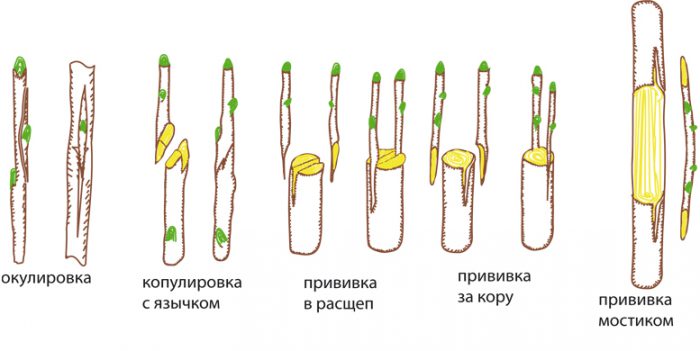
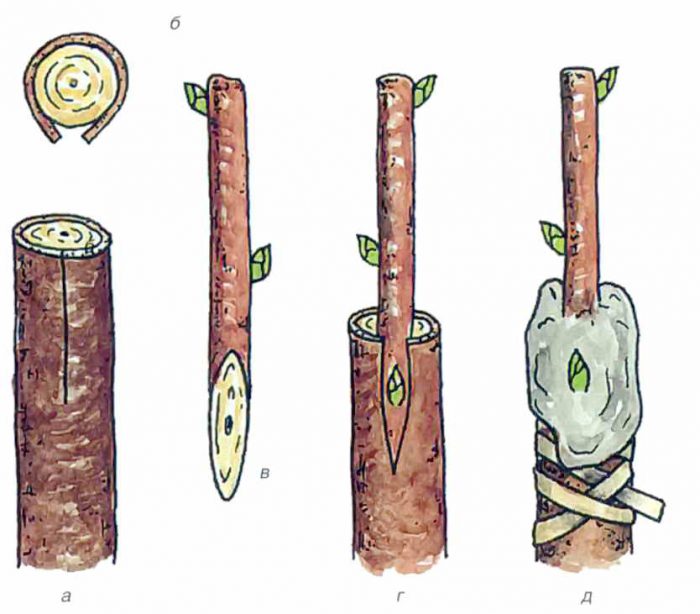
Plum propagation by grafting
To propagate a plum by grafting, you need a scion and rootstock. As a rootstock, you can take a seedling grown from a stone, and the root offspring of an adult plum tree, previously removed from the ground and transplanted to a new place, is also suitable for this role. Experienced gardeners recommend taking root shoots from the most frost-resistant plum varieties, for example: Moskovskaya, Ugorka, Skorospelka krasnaya, Renklod kolkhozniy and Eurasia 21. You can also use thorny plum, felt cherry, cherry plum or blackthorn as a stock.
There are several ways to vaccinate:
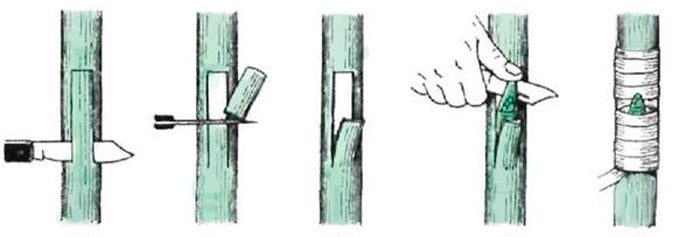
Kidney vaccination
The rootstock needs very good watering, as a result of which there will be an increase in sap flow, while it will be very easy to separate the bark from the wood. It is necessary to remove all dust and dirt from the stem with a moistened sponge or rag, then all leaf plates must be cut off from the scion, from which only petioles 5 mm long should remain. On the rootstock, 40 mm should be retreated from the root collar upwards, then using an eyepiece knife, a T-shaped incision should be made on the bark. The cut bark must be carefully peeled back. From a varietal scion, it is necessary to cut off a bud with a strip of bark three centimeters long and half a centimeter wide. This bark needs to be placed in a wood-to-wood T-cut. Then firmly press the bark and wrap the site of inoculation with tape, eyepiece film or a strip of polyethylene, while the kidney should remain open.
Budgeting in the butt
In dry weather, the flexibility of the bark is significantly reduced, so at this time it is better to use budding in the butt. On the rootstock, an incision should be made in the bark, reaching 7 centimeters in length so that a thin layer of wood is captured. At the scion, you need to make an oblique lower cut with a length of 7 centimeters, while the ledge must be made immediately under the kidney. Insert this cut under the bark of the rootstock wood to the wood, then wrap the grafting site with plastic or eyeliner film, leaving the bud of the scion not closed. After 20 days, the film must be removed, and at the beginning of spring, the top of the rootstock must be cut off or cut down so that a thorn remains above the bud, reaching 15 centimeters in length. For budding, you can use a pair of buds, with one of them placed at a height of 40 mm above the surface of the ground, and the other 7 centimeters above the first.
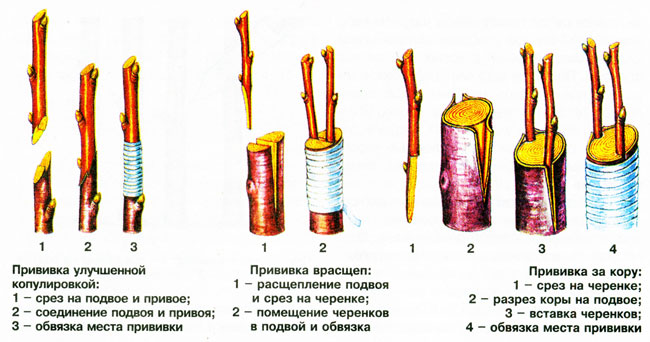
Grafting by cuttings
In spring and summer, this culture can be grafted with cuttings. It is necessary to make an oblique cut on the rootstock, reaching 25 mm in length and 15 mm in width, while it is necessary to grab the wood. On a recently harvested varietal cuttings, it is necessary to make an oblique cut 25 mm long. It must be installed in the cut on the stock with a cut to the outgoing part of the split. The vaccination site must be wrapped with an eyelid film. As soon as you notice that the cutting is well established, the film can be removed.
Cleft grafting
The stem of the stock must be cut down, and in the center of the cut, a split of three centimeters deep must be made. Make a couple of lower cuts on a varietal cuttings so that a wedge is formed. This wedge is installed in the split, and the grafting site is wrapped in polyethylene and film.
Bark grafting
During intensive sap flow, the bark lags behind the wood best. The stem of the stock must be cut down, and 2 or 3 cuts in the bark are made from the place of the cut with movements from top to bottom. Peel back the bark and place a varietal cutting in each cut, cut obliquely and having 3 buds, while the cut should be turned towards the rootstock wood. Then the vaccination site is fixed with tape, film or electrical tape.
If you want to plant several cuttings on one rootstock at once, then you will need to choose the method “for the bark” or “in the split”. In this case, the thickness of the rootstock will affect how many cuttings you can graft. The film should be removed after 4 weeks.


Watch this video on YouTube
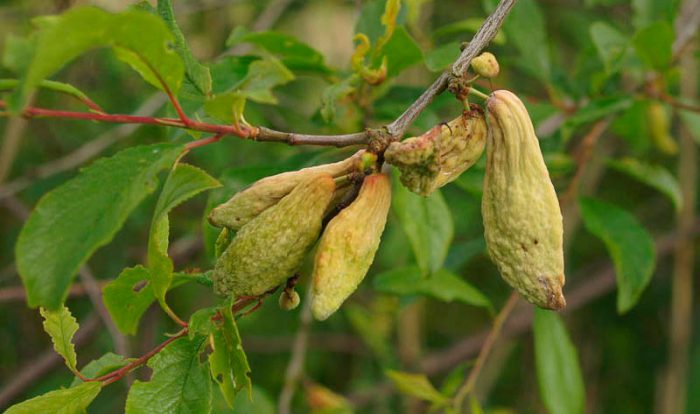
Plum diseases with photos and descriptions
There are many different diseases that plum can get sick with. There are diseases that affect the plum tree, and there are those that affect all stone fruit crops. The plum grown in the garden can get sick with clasterosporia or perforated spotting, moniliosis or gray rot, gommosis or gum disease, rust, fruit rot, coccomycosis, sooty fungus, root cancer, marsupial disease and milky shine.
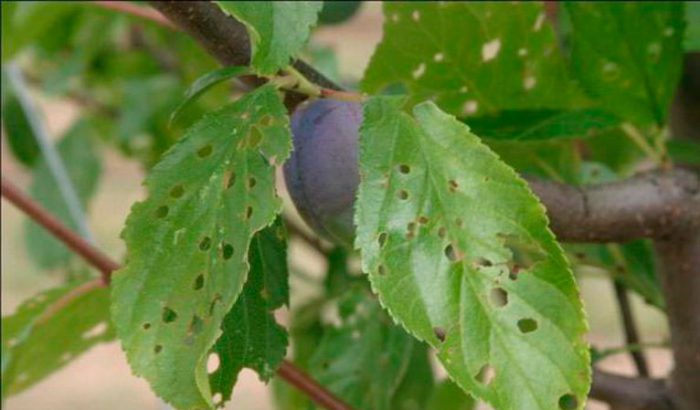
Clasterosporium disease
Clasterosporia is a fungal disease.It affects branches and leaf plates, and in flowering plants, also buds with flowers. The first symptoms of the disease are the formation of brown spots on the surface of the leaf plates, which have a border of a darker shade. Over time, they first become ulcers, and then holes. The defeat of the fruit occurs to the very bone, while they become ugly. This disease develops most intensively in wet weather. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to systematically thin out the crown so that it does not thicken. When in autumn all the leaves fall off, it is imperative to rake them up and destroy them, after which you should start digging the site. Infected parts of the tree should be cut and burned as soon as possible. When the plant blooms, after 15–20 days it must be sprayed with a solution of copper oxychloride (for 1 bucket of water from 30 to 40 grams) or a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%).
Moniliosis
A fungal disease such as moniliosis can affect the ovaries, fruits, flowers, foliage and branches of a plant. The color of the fruits changes to brown, they become soft, gray pillows appear on their surface, inside which there are spores of the fungus. The activation of moniliosis is observed in spring, and damp weather accelerates its development. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to cut out the dead branches, as well as collect and burn the fruits affected by the disease. Before the plum blooms, it must be sprayed with copper or iron vitriol, Nitrafen or Bordeaux mixture (1%). After the tree has faded, it must be immediately sprayed with a Bordeaux mixture or a solution of a fungicide, for example: Cuprozan, copper oxychloride, Phtalan, Kaptan, etc.
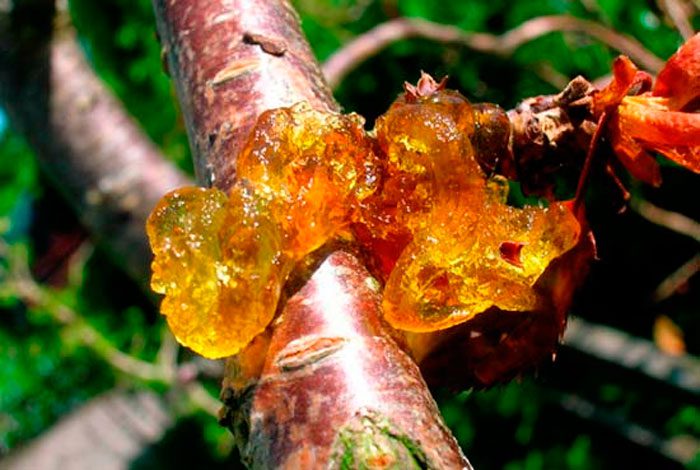
Hommosis (gum flow)
Gum removal (comosis) is observed in all stone fruit cultures. In the affected specimen, a light yellow or colorless drying resin flows from the wounds on the bark. The branches that flow like gum dry up and die. Damage to wood and bark, sunburn, a large amount of nitrogen and liquid in the soil contribute to the occurrence of this disease. In the cold season, comosis is the greatest danger for plums, and often it affects those specimens that have been weakened by harmful insects or very strong pruning. In the bark saturated with gum, pathogenic microorganisms can begin to actively develop, which contribute to the development of cancer of the branches and trunk. If the gum flow is very strong, then this leads to the drying out and death of the plum tree. For prevention purposes, try to completely eliminate the possibility of mechanical damage on the branches and trunk. If there is damage, the wound should be thoroughly cleaned, then it is disinfected using a solution of copper sulfate (1%). At the very end, the wound must be treated with petralatum. All severely affected branches must be removed. Remove the dead bark from the trunk, and then rub this place 3 times with horse sorrel foliage, while the intervals between these procedures should be 10 minutes. Then the wound is coated with garden varnish.
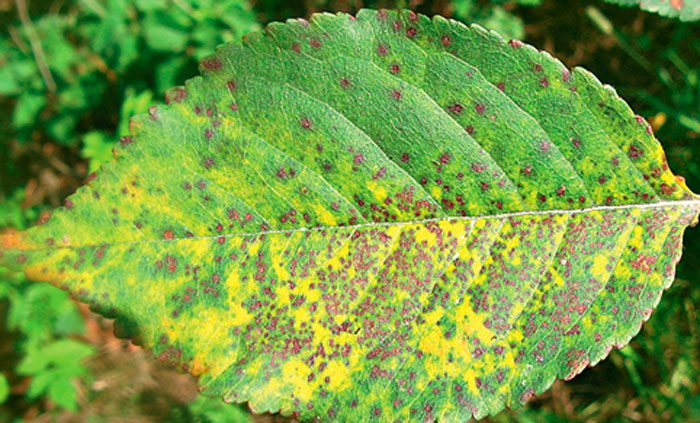
Rust
Another fungal disease is rust. In this case, the foliage of the plum tree is affected. This disease is especially active in July. Convex brown or red spots appear on the front surface of the leaves, which become larger over time. Affected plants weaken, become less frost-resistant, and foliage flies around ahead of time. For the purpose of prevention, you need to clean the area of fallen leaves in time. Before the tree blooms, it must be sprayed with a solution of copper oxychloride (for 1 bucket of water 80 grams), while processing one plant should take 3 liters of the mixture. When all the fruits have been collected from the tree, it should be sprayed with Bordeaux mixture (1%).
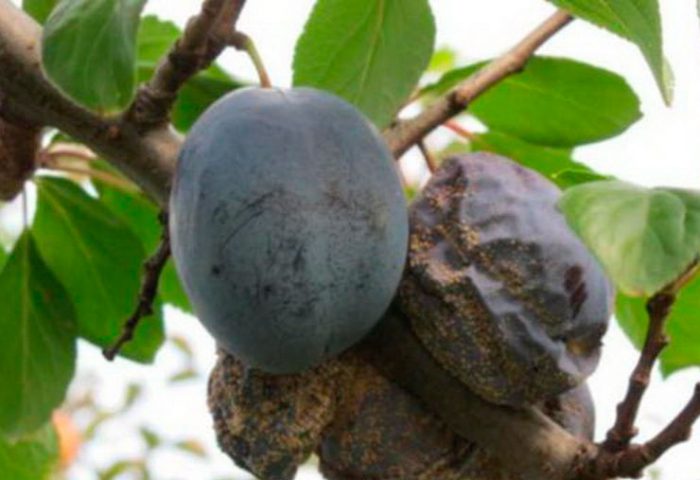
Fruit rot
Fruit rot can affect both stone fruit and pome plants, for example: cherry, sweet cherry, apricot, quince, peach, apple, pear, etc.The first symptoms of this disease appear in mid-July, when the fruit is being poured. At the beginning, specks of brown color are formed on the surface of the fruit, gradually increasing in size. After a while, light gray pads appear on the fruits, in which the spores of the fungus are located, they are arranged in concentric circles. For prevention purposes, all infected fruits must be cut off and burned. But this should be done very carefully, since when sick fruits come into contact with healthy ones, the latter are infected. The tree should be sprayed with Bordeaux mixture (1%).
Coccomycosis
Coccomycosis is one of the most dangerous fungal diseases. In the affected specimen, not only leaf plates, but also young shoots, as well as fruits, may suffer. The first symptoms of such a disease can be seen in the middle of the summer period, for example, specks of purple-purple or brown-red color appear on the surface of the leaf plates, they gradually increase in size until they merge with each other. A pinkish bloom appears on the seamy surface of the affected leaves, consisting of fungal spores. In the affected tree, a decrease in frost resistance is observed, the leaf plates turn yellow, then brown and fly around, the development of fruits stops, they become watery and dry after some time. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to rake and burn loose leaves in the autumn, as well as to dig the site. When all the fruits are harvested, the infected plant must be sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%) or copper oxychloride (for 1 bucket of water from 30 to 40 grams).
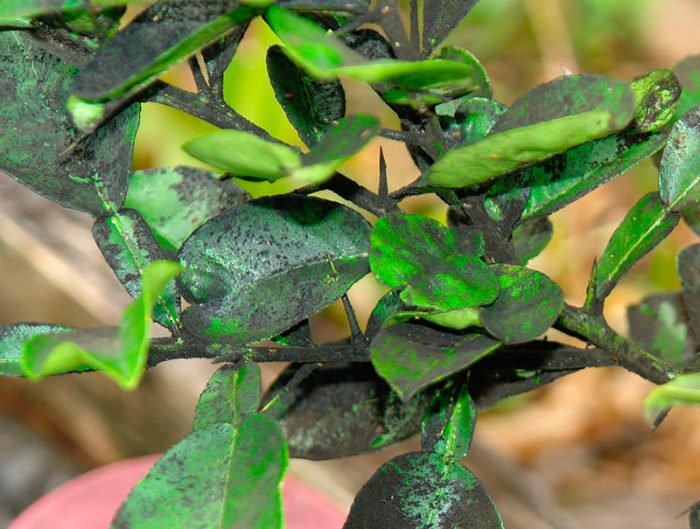
Sooty fungus
If a bloom of black color appears on the surface of the foliage, then this indicates that a sooty fungus has settled on the plant. It is very easy to wear off. This plaque contributes to the fact that the access of oxygen and light to the plant cells is significantly hampered, as a result of this, a process such as photosynthesis slows down. The first step when a raid appears is to find out why it happened. An excessively thickened crown or high soil moisture can become the cause of the appearance of a sooty fungus. First, you need to completely eliminate the cause of the appearance of this plaque and only then spray the tree with a copper-soap solution (for 1 bucket of water 150 grams of soap and 5 grams of copper sulfate). If desired, instead of copper sulfate, you can use copper oxychloride or Bordeaux mixture.
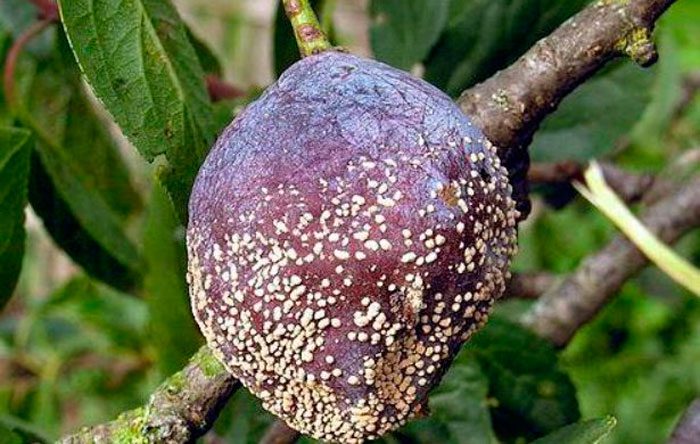
Marsupial disease
Marsupial disease is also a fungal disease. The appearance of its first symptoms is observed after the plum tree has faded, while its fruits are damaged, which become ugly. The growth of the affected fruits is observed, while the bone does not develop, a powdery-waxy coating appears on their surface, in which the spores of the fungus are located. To avoid further spread of the disease, the affected branches should be cut out immediately after detection. It is also necessary to collect and destroy the affected fruits. The infected plant should be sprayed with a Bordeaux mixture solution 2 times: during the period when the buds are stained in a light pink shade and immediately after the plum has faded.
Root cancer
When a plum tree is damaged by root cancer, growths form on the surface of the root collar and roots. The disease begins to develop due to pathogenic bacteria in the soil, they penetrate into the roots through wounds and cracks. In an adult plant affected by cancer, growth stops, while diseased seedlings do not take root, which leads to their death. This disease develops especially actively during the dry period, especially in slightly alkaline or neutral soil. Where plants infected with this disease used to grow, plum seedlings cannot be planted. All gardening tools should be treated with a solution of chloramine or formalin.The growths that have appeared on the root system must be cut out, and then it is disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate (1%).
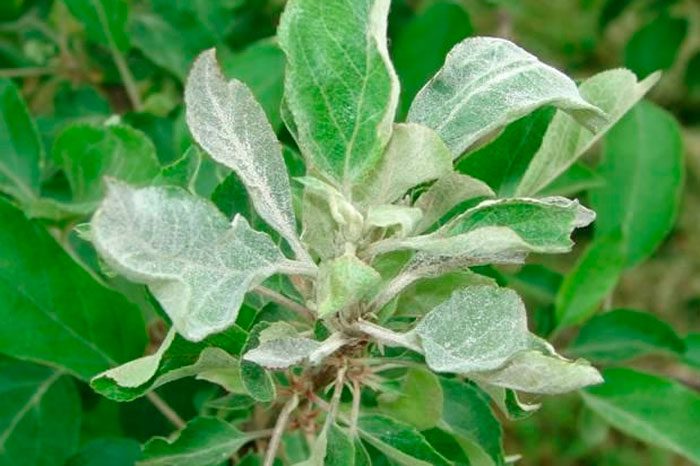
Milky shine
Milky shine is a very dangerous and fairly common disease that affects most fruit crops, and also kills trees from it. In the affected specimen, the leaf plates change their color to white-silver, holes appear on their surface, the tissue of the leaf plates dies off, and the bark of the plum becomes dark. Often this disease affects young trees that have been damaged by frost in the winter. For prevention purposes, before wintering, it is imperative to whitewash the base of skeletal branches and boles with lime. At the beginning of spring, a preventive spraying of the plum with a urea solution should be carried out, as a result, it will become more resistant to fungal diseases, and also receive the nitrogen that it needs at this time. Infected stems and branches must be cut and burned.
In addition to these diseases, the plum tree can suffer from brown spot, witch's broom, fungus burn, dwarfism, mosaic disease, smallpox and branch death.


Watch this video on YouTube
Plum pests with photos and descriptions
There are a large number of pests that can settle on the plum tree. Most often, it is home to hawthorn, cherry shoot moth, cherry slimy sawfly, goldtail, plum and apple moth, ringed silkworm, plum pollinated aphid and apple comma-shaped scale.
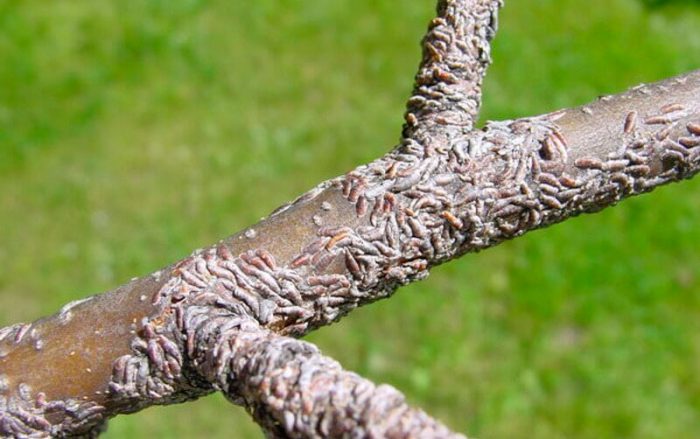
Apple comma scale
An apple comma-shaped scabbard spreads along the bark of the plant. She, being on the surface of young branches or shoots, freezes, after which it is completely covered by a shield. If there are a very large number of scale insects on the tree, this will lead to its exhaustion and death. In the fight against these pests on dormant kidneys, it is necessary to spray the plum and the surface of the trunk circle with a solution of Nitrafen (for 1 bucket of water from 200 to 300 grams). As soon as the plant fades, it must be sprayed with a solution of Karbofos (10%).
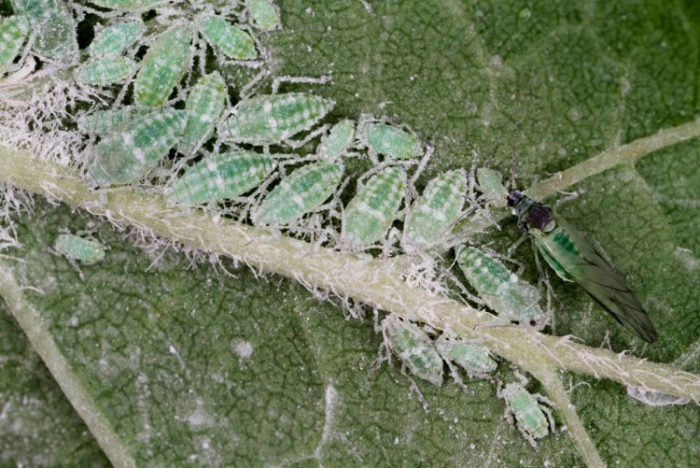
Plum pollinated aphid
Plum pollinated aphids are quite common in garden plots. Such a pest can settle on peaches, apricots, thorns, almonds and plums. They live in very large colonies. If you look at the seamy surface of the leaf plates of the affected plant, then it will be covered with a very thick layer of such aphids. This insect contributes to the foliage folding and drying, as well as rotting of the affected fruits. In addition, a sooty fungus settles on the waste products of such an insect. To get rid of this type of aphid, it is necessary to spray the plum with a solution of Nitrafen at the beginning of the spring period, and during the budding period and when the plant fades - with a solution of Benzophosphate or Karbofos (10%). For prophylaxis, root suckers must be removed in a timely manner.
Apple moth
The apple moth is a butterfly, the caterpillars of which damage the fruits of the plum, while they eat up the passages in the bones, which they disguise with food waste glued together with cobwebs. In the fight against such a pest, it is necessary to regularly collect early fallen fruits, which must be destroyed. You should also regularly clean and disinfect the bark. After the tree has faded, you need to wait half a month, and then treat it with a solution of Karbofos (3%) or a solution of Chlorophos (2%).
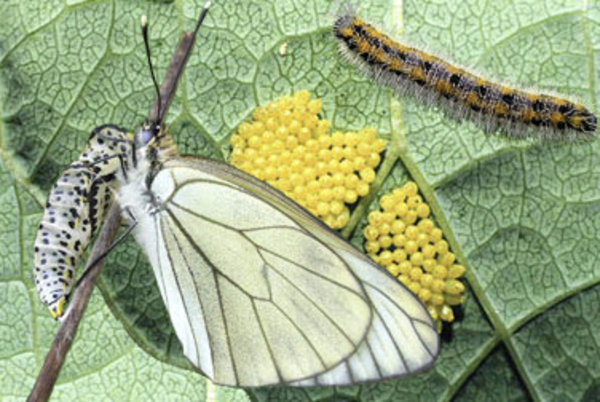
Hawthorn
The hawthorn is a very large butterfly with a wingspan of up to 70 mm. The length of its caterpillar is about 0.45 m, its surface is covered with dense hairs. The caterpillar itself is painted black, and 2 bright stripes of brown-yellow color run along its back. She eats the front surface of the leaf plates, as well as flowers and buds.In some cases, caterpillars expose not only individual branches, but the entire plant. In the fight against them, you need to inspect the plum, collecting nests of hawthorns and caterpillars, then they are burned. Caterpillars emerge from the nests in the last days of April, the first in May, at this time the tree needs to be processed, and it is necessary to repeat the spraying in the summer, when flowering ends. For processing, a solution of Corsair, Actellik or Ambush is used, while its concentration should be 1%.
Cherry shoot moth
The cherry shoot moth also prefers to settle on stone fruit trees. Caterpillars of this moth damage buds, leaf rosettes and buds, and in young green shoots they gnaw through the passages. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to systematically loosen, as well as dig the soil at the site. Before the sap flow begins, the drain and the surface of the trunk circle must be sprayed with a solution of Nitrafen (2-3%). During the swelling of the kidneys, it must be treated with a solution of Karbofos (10%).
Cherry slimy sawfly
In gardens, cherry slimy sawfly is also quite common. It settles on crops such as cherry, sweet cherry, quince, pear, plum and hawthorn. The larvae of such a pest gnaw the front surface of the leaf plates. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to systematically loosen the soil on the site, and also dig it up. If there are a lot of pests, then the tree should be sprayed with a solution of Trichlorometaphos-3 or Karbofos (10%).
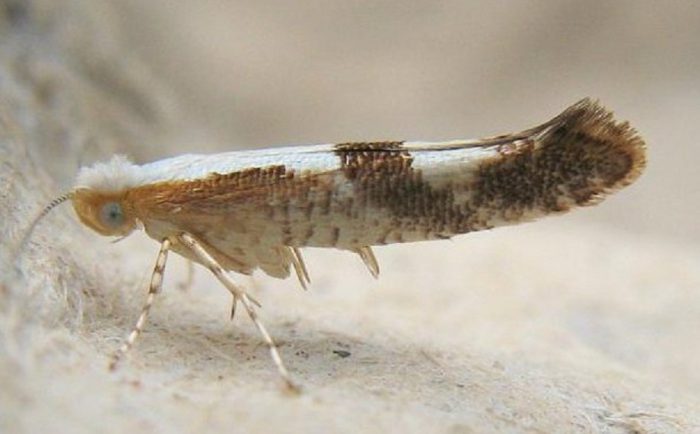
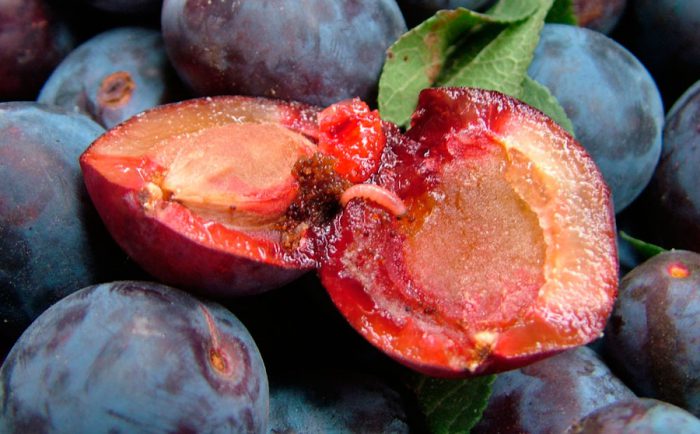
Plum moth
The plum moth prefers to settle on plums, apricots, cherry plums, peaches and thorns. In a green fruit, 1 butterfly is capable of laying about 40 eggs. The hatched caterpillars eat up the pulp of the fruit, then they crawl out of them and move to a place more suitable for wintering. Gum droplets form on damaged fruits, their color changes to purple, and they fall off. When plum is infected, the caterpillars should be manually collected and sprayed with a solution of Karbofos or Benzophosphate, the concentration of which should be about 10 percent, during the period when the caterpillars appear. After half a month, re-spraying is carried out.
Ringed silkworm
The ringed silkworm is a moth. The caterpillars of such an insect devour the buds and foliage of the plum, while in the forks of the branches they make spider nests. Examine the plant and collect any winter nests, as well as eggs to be burned. The plum itself during the opening of the buds, and then during the period of the appearance of caterpillars, must be treated with an infusion of tobacco, pharmacy chamomile or wormwood. Also, biological agents are often used to treat plants, for example, Dendrobacillin or Antobacterin, and spraying should be done according to the attached instructions.
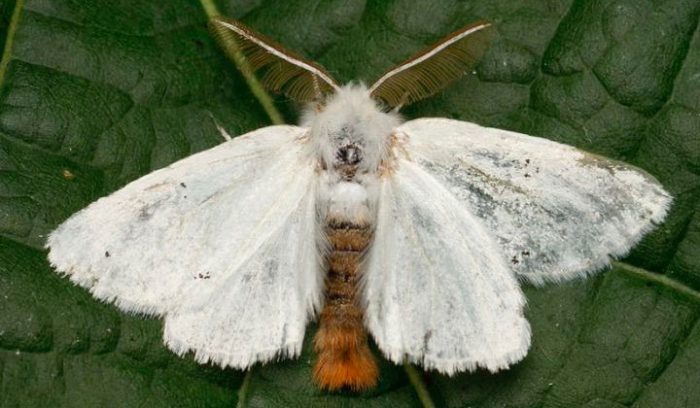
Goldtail
The goldtail is a fairly large butterfly, painted white, the wingspan of which can reach 50 mm. The danger to the plant is represented by its pale green caterpillars, which devour all the pulp from the seamy surface of the foliage. Using a cobweb, they make nests from the remains of leaf plates, where they settle down for the winter. Find all winter nests and burn them. Before the plum blooms, it must be sprayed with a solution of Karbofos (3%).
Also, a plum tree can suffer from apple-plantain aphids, apple glass, black plum sawfly, fruit striped moth, plum gall mite, peppered moth, down silkworm, subcrustal leafworm, fruit moth, gypsy moth, miner moth, red apple mite, casserole mite winter moth, western unpaired bark beetle, sapwood, pear pipe-worm, eastern moth and brown fruit mite. First you need to determine which particular pest disturbed the plum, and only then make the choice of a suitable agent for spraying the affected plant.


Watch this video on YouTube
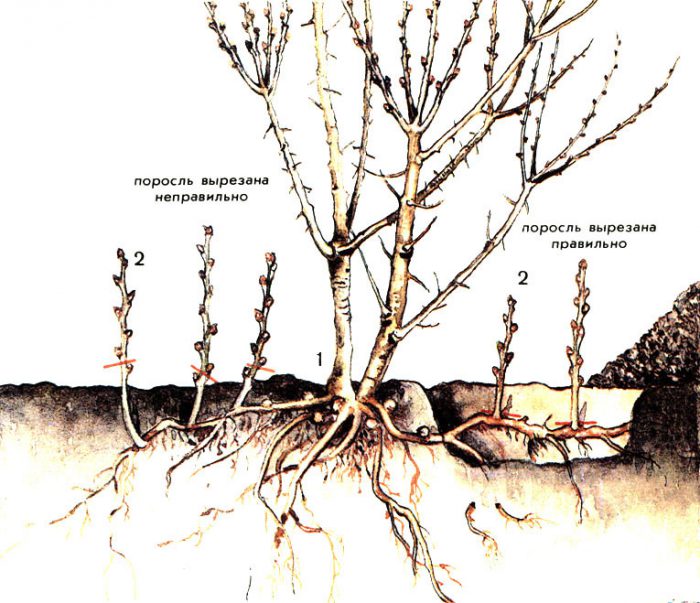
How to deal with plum growth
With the help of root shoots, the plum tree tries to preserve itself, which is absolutely natural for every living organism. Pruning of branches or injury to the bark can provoke intensive growth of root processes. Also, root suckers grow very actively in the event that the scion and stock do not match. It should be remembered that an overgrowth of growth suggests that the plum tree has some kind of problem. Cutting out root suckers is necessary not only because they can spoil the appearance of the garden plot, but the shoots also contribute to weakening the plum and reducing its yield. To stop the intensive growth of overgrowth, it is necessary to find out the cause of this problem and try to eliminate it.
The easiest way to remove overgrowth is with a pruner. To do this, you need to dig out its root, then you need to cut it off at the place where the parent tree leaves the horse. Then the hole is filled with soil, which is well tamped.
Some gardeners are sure that if they get rid of root suckers on certain days, they will no longer bother. These days are: April 3, June 22 and July 30. Believe it or not, every gardener decides for himself.
Plum varieties with photos and descriptions
In the garden plots of middle latitudes, hybrids and varieties of four types of plums are grown, namely: prickly plum (thorn), Chinese, domestic and American (this also includes Canadian). Among gardeners, varieties of home plums are the most popular; they are divided into 4 subspecies: rennlode, Hungarian, thorny and mirabela.
Also, varieties are divided into late-ripening, mid-ripening and early-ripening. They also distinguish drought-resistant and moisture-loving, frost-resistant and frost-resistant, as well as self-fertile and self-fertile varieties.
Plum varieties for the Moscow region
There is a very large number of very different varieties of plums, so for any region you can choose several that are most suitable. In regions with a mild climate and relatively warm winters, the plum tree, which bears fruit for a long time and abundantly, is a common thing. However, the varieties grown in the Moscow region will have slightly different qualities. Most of the problems are caused by the fact that this culture has a relatively low frost resistance. However, thanks to the many years of work of specialists, such varieties have appeared that can be safely grown not only in the Moscow region, but also in colder regions. Recommended varieties for the Moscow region:
- Hungarian Korneevskaya... This drought-resistant variety begins to bear high stably high fruit from the age of 6, on average, 40-50 kilograms of fruit are harvested from one tree. The plant has been producing rich harvests for 20 years. Medium-large fruits have a brown-violet color, there is a waxy bloom on the surface. The yellow pulp is juicy and sweet. It should be borne in mind that under the weight of the fruit, the branches can be injured.
- Yakhontova... This variety is distinguished by its yield, resistance to drought and fungal diseases, it is not afraid of recurrent frosts that can destroy flower buds in non-frost-resistant varieties. The height of the tree is about 5 meters, the shape of its compact crown is spherical. The sweet-sour fruits are deep yellow and weigh about 35 grams. There is a small waxy coating on their surface. About 50 kilograms of fruits are harvested from one plant every year.
- Kolkhoz renklode... This early self-fertile variety has a stable yield and resistance to frost. Medium-sized fruits are colored yellow-green. The juicy pulp has a delicate sweet-sour taste. This variety is obtained using ternosplum and green Renklode. The tree begins to bear fruit in its third year of growth. It is considered a very good pollinator for other plum varieties.
- Smolinka... Self-infertile early variety with high yield.Large fruits of dark purple color have a regular oval-ovoid shape and weigh about 35 grams. The yellow pulp has a dessert taste, the stone is easily separated from it. This plant is a hybrid that was created using the varieties Ochakovskaya Zheltaya and Renklod Ullesa. For such a plum as a pollinator, you can use the following varieties: Opal, Superearly or Blue Gift.
- In memory of Timiryazev... Self-fertile late-ripening variety, characterized by frost resistance, does not need pollinators. On ovoid fruits of yellow color there is an uneven reddish blush, in weight they reach about 22 grams. The loose yellow flesh is very fragrant. Fruiting in this tree can be periodic.
In addition to these varieties in the Moscow region, it is recommended to cultivate such as: Dashenka, Peresvet, Eurasia-43, Zagorsk, Kantemirovskaya, Yellow large, Memory Finaev, Large nova, ELSE-R, Skorospelka nova, Tulskaya black, Seyanets of Volgograd, Morning, Early yellow, Volga beauty, Sissy, Red ball, Egg blue, etc.
Early varieties of plum
Ripening of fruits of early maturing varieties is observed from the last days of July to the end of the first decade of August. Early varieties:
- July rose... The early, partially self-fertile variety is resistant to disease and frost. The egg-shaped fruits of yellow color weigh about 35 grams. The pulp of medium sugar content is slightly juicy. The pulp does not completely lag behind the stone.
- Oh yeah... Ukrainian early-growing variety has a high yield and resistance to frost and fungal diseases. The brown-purple fruits are large enough and oval in shape. The taste of yellow tender pulp is spicy, sweet and sour. The small bone is very easy to separate from the pulp. It is recommended to use the varieties Kirke, Vengerka and Ekaterina as pollinators.
- Opal... Self-fertile dried fruit variety has a high yield. The shape of the red fruits is round. Juicy dense sweet flesh has a dark orange color. The bone is not completely separated from the pulp.
- Record... The partially self-fertile variety is frost-resistant and high yielding. The violet-blue fruits of an elongated oval shape weigh about 30 grams. The fragrant dense juicy pulp is colored green-yellow. This variety is one of the most delicious varieties. It is recommended to use the variety Hungarian or Skorospelka red as a pollinator.
- Alyonushka... A self-infertile variety that is resistant to frost and disease. The tree is not afraid of frosts down to minus 25 degrees. The dark red oval-round fruits weigh about 35 grams. The crispy juicy pulp has an orange color. The pulp cannot be separated from the bone.
- Renklod Karbyshev... This Ukrainian self-infertile variety was created using Jefferson and Peach. It is recommended to use such varieties as Vengerka Donetskaya, Vengerka Donetskaya early, Renklod early as pollinators. Rounded purple fruits have a bluish bloom, they weigh about 50 grams. Juicy fragrant dark yellow pulp has a sweet taste with a slight sourness.
The following varieties are also quite often grown: Early Renklod, Kuban Early, Red Ball, Golden Ball, Hungarian July, Hungarian Wangenheim, Monfor, Early, Sapa, Skorospelka red, Ternosliv summer, Kliman, Nadezhda, Zarechnaya early, Skoroplodnaya, Kirgiz excellent, Sharovaya , Kuban comet, Early pink, Morning, etc.
Medium plum varieties
Medium varieties of plums ripen from the second decade of August to 10 September. Medium varieties:
- Gigantic... American self-fertile, drought tolerant. Large dark purple fruits are elongated. The sweet-sour juicy pulp has a yellow-green color.
- Souvenir of the East... The variety differs in yield, but it lacks frost resistance. Heart-shaped maroon fruits are large in size. The pulp is sweet, dense, honey, spicy taste.
- Hungarian Azhanskaya... Partially self-fertile moisture-loving French variety with high yields and resistance to fungal diseases. Medium-sized egg-shaped fruits have a purple color and a fairly strong bloom of wax. The delicate pulp has a sweet, slightly sour taste, the pulp easily falls behind the stone.
- Romain... The foliage is red. Burgundy heart-shaped fruits have a red flesh with a slight almond flavor.
- California... An American semi-self-fertile cultivar with chlorosis resistance and high yields. Medium density pulp is very tasty and juicy. The pulp is not completely separated from the seeds.
Also, gardeners grow the following varieties: Memory Vavilov, Duche, Krasa Orlovshchina, Kuban legend, Hungarian Donetsk, Hungarian Belarusian, Bogatyrskaya, Vetraz, Svetlana Primorskaya, Voloshka, etc.
Late plum varieties
Late varieties begin to ripen in the second decade of September. Popular varieties:
- Stanley. The variety is distinguished by its yield and frost resistance. On the surface of the dark purple fruit there is a strong bloom of wax, as well as a clearly visible seam. Medium juicy dense pulp has a yellow color, it separates from the stone easily.
- Zhiguli... A self-infertile variety that is resistant to frost, moth and aphids. Begins to bear fruit in the fifth year. Oval-shaped large blue fruits weigh about 31 grams and have a bloom. The sweet-sour juicy and tender pulp has a green-yellow color.
- Vicana... This Estonian variety was obtained using American plum and Victoria variety. Oval burgundy fruits weigh about 24 grams and have a strong wax coating. The sweet-sour flesh has a yellowish color, it lags well behind the stone.
- Tula black... A self-infertile variety that is resistant to fruit rot and frost. It is recommended to use the following varieties as pollinators: Renklod kolkhoz, Renklod Tenkovsky, Ternosliv Dubovsky or Ternosliv Tambovsky. Egg-shaped fruits have a slight bloom and dark blue, almost black color. The yellowish buttery flesh has a sweet-sour taste, easily lagging behind the stone.
- Hungarian italian... The variety is popular all over the world. It is susceptible to damage by sawflies, moths and aphids. Oval large fruits have a dark blue, almost black color and a bluish bloom. Juicy pale green pulp has an excellent sweet taste with a slight sourness, it lags well behind the stone.
- Hungarian large late... Self-fertile variety, distinguished by its yield and resistance to drought, frost and fungal diseases. On the surface of the purple-red oval fruits there is a coating of wax. They weigh about 40 grams. Delicious juicy pulp has a sweet and sour taste.
Also, gardeners often grow the following varieties: Vizhen, Primorskaya abundant, Svetlana, Krasnomyasaya, Canadian Vision, Hungarian Pulkovskaya, Valor, In Memory of Timiryazev, Golden Drop, Prunes 4-39 TSKHA, Renklod Michurinsky, Anna Shpet, Winter red, Winter white, Vengerka Moscow, Ternosliv autumn, Hungarian October, Ternosliv Tambovsky, Ternosliv Dubovsky, Pamyat Finaev, Tern large-fruited, etc.
Self-fertility and self-infertility of the plum - this characteristic is conditional and unstable. In different regions, depending on the climate, the same variety can be self-fertile, self-fertile, or partially self-fertile. In addition, the same plant could have been self-fertile last season, and this season it will need pollinators. Partially self-infertile varieties are capable of self-bearing, but if pollinators grow nearby, this will increase the yield of such plants.


Watch this video on YouTube
Useful properties of plums
Plum fruits are not only tasty, but also healthy. They contain minerals and vitamins that the human body needs.The fruits contain proteins, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, free organic acids, potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, fluoride, provitamin A, vitamins B1, B2, B6, PP, C and E.
Dried and fresh fruits have a slight laxative effect, in this regard, doctors advise them to eat with constipation and intestinal atony. With hypertension and kidney disease, such fruits help to reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood. Potassium compounds have a diuretic effect, while salt deposits and edema are eliminated. Such fruits are recommended for rheumatism, metabolic disorders, gout, kidney damage, heart disease. They also improve appetite and improve the secretion of gastric juice.