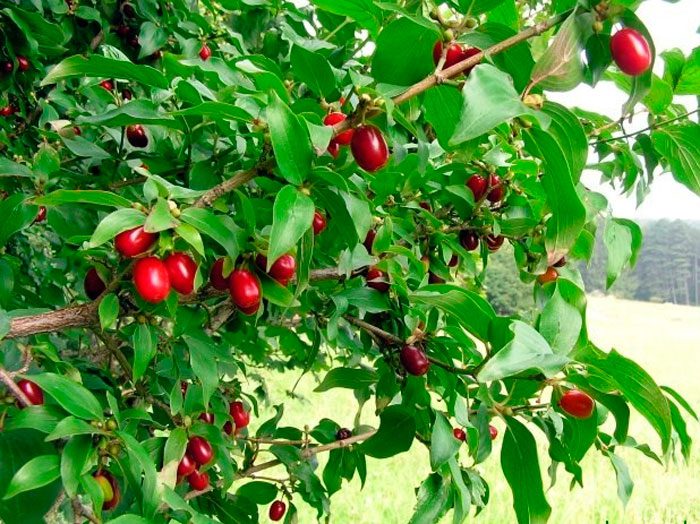
Dogwood (Cornus) is a member of the dogwood family. This genus includes about 50 species. Dogwood is often a deciduous tree or shrub, but in some cases it is a perennial herb or woody winter-green plant. This genus has 4 subgenus. The word cornelian is borrowed from the Turkic language, and it is translated as "red", probably this plant was named after the color of the fruits of the most common species. Under natural conditions, such a plant can be found in Southern and Eastern Europe, Asia Minor, Japan, China and the Caucasus. People began to engage in the cultivation of dogwood since ancient times. So, the ancient Greeks and Romans selected the best types of dogwood for cultivation in gardens, and if you believe Virgil, then in this case they achieved some success. In middle latitudes, such a plant began to be cultivated in the 17th century, under Tsar Alexei Mikhailovich, who showed considerable interest in outlandish plants. At the same time, the dogwood, thanks to the very useful fruits from which decoctions were prepared in those days, aroused special interest in the king. The first people who settled in America used such a plant to cleanse their teeth, while the aborigines of this continent made arrows from it. Since dogwood has a high hardness, over time, handles for doors and hammers, tennis rackets and shuttles for weaving equipment began to be produced from it. There is information that the Holy Cross was also made from this plant. The Pacific dogwood flower is the official flower of British Columbia, a province in Canada. At the same time, the flowering dogwood tree is the official tree of such states of America as Virginia and Missouri.
Content
Features of the dogwood shrub
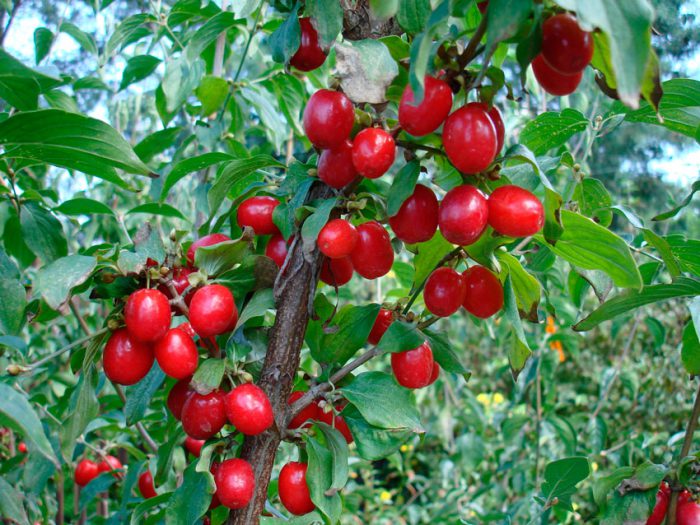
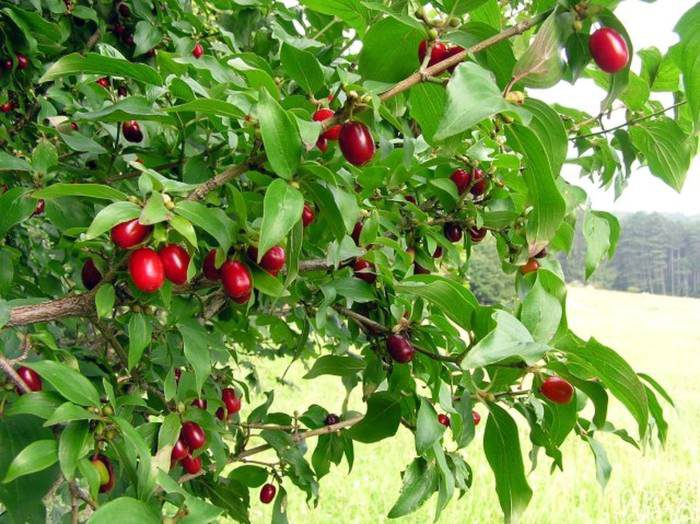
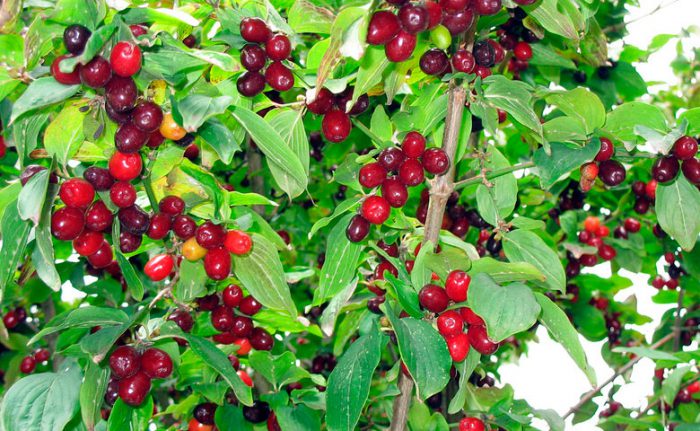
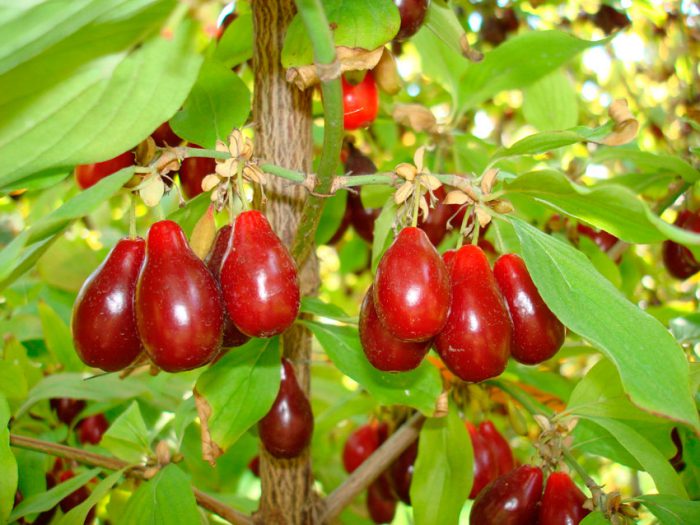
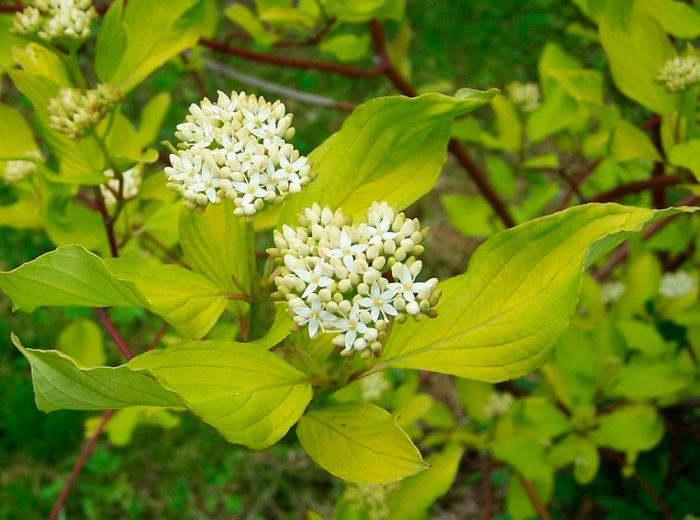
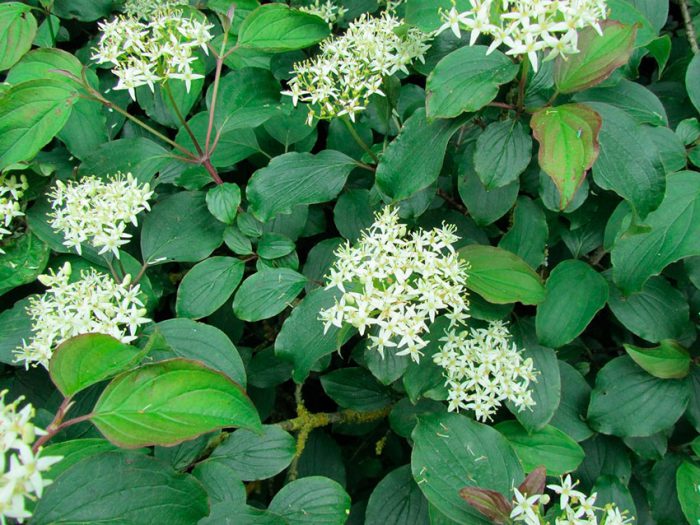
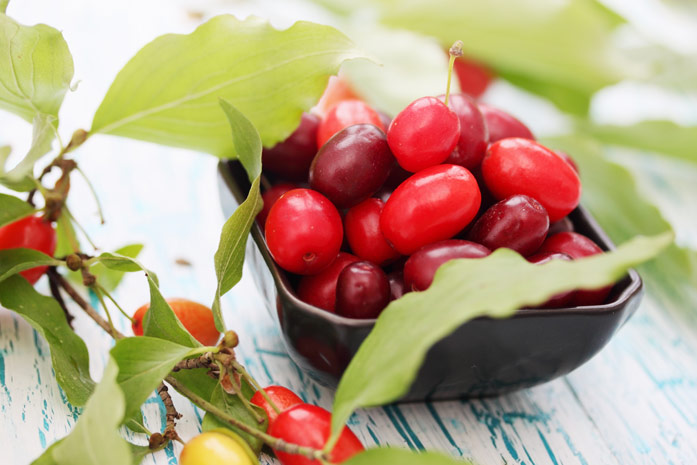
The most famous species of this genus is the common dogwood (male), which is a shrub. It reaches a height of 2.5 meters and has glossy orange-red hanging stems. If the shoot comes into contact with the soil surface, then it takes root quickly enough.Alternately or oppositely located leaf plates are painted in a deep green color. Milky white flowers are part of the inflorescences with a five-centimeter diameter. Flowering begins in May and lasts half a month. Fruits can have 1 or 2 seeds, they ripen in August-October, they can differ in shape and color. In cultural forms, the length of the fruits is equal to three centimeters, as a rule, their shape is elongated-cylindrical, but sometimes it is almost round, and also pear-shaped or barrel-shaped. As a rule, the color of the fruit is deep red, but there are also yellow, black, pink, and also purple. Fruits also differ in their taste, so they can be tart, sweet, sweet-tart, dryish or juicy. The dogwood itself can be formed as a bush or as a tree. This is a frost-resistant plant, but if the temperature drops below minus 30 degrees, then the tips of its stems freeze. A bush of such a plant can live longer than a hundred years.
Planting dogwood
What time to plant
It is recommended to plant dogwood in open ground immediately after the leaf fall of the poplar begins. In autumn, planting such a shrub is much better than in spring. The fact is that in spring time it is necessary to have time to plant a seedling in a rather short time period, namely, when the soil warms up, but the buds have not yet begun to open. For such a shrub, a site in partial shade and located on the southern or southwestern side of the garden is well suited. The soil should be saturated with lime, while the groundwater should not lie closer than 1.5 m to the soil surface. Cornel can be grown in acidic soil, but it will develop worse, and the quality of the fruit will noticeably decrease. There should be a distance of at least 3-5 m between the shrub and any building, fence or other plant. In order for the shrub to bear fruit, it needs a pair, and it is better if you have 3 dogwoods growing at once, while the distance between them should not be more 3-5 m.


Watch this video on YouTube
Landing
The seedlings that are used for planting must be 2 years old. In height, they must reach 150 centimeters, and their trunk must have a two centimeter diameter, while the seedling must have from 3 to 5 skeletal branches. The depth and diameter of the planting hole should be about 0.8 m. When the hole is ready, a stake should be driven into it, which will serve as a support for the seedling. In this case, it is recommended to place the stake on the side from which the wind blows most often. When digging a hole, the topsoil, saturated with nutrients, must be combined with mineral fertilizers and humus, then the resulting mixture must be poured into the center of the planting hole with a mound. On this mound, it will be necessary to install a seedling, from which the roots are then carefully straightened. Then the hole must be covered with the same soil mixture, while the root collar of the plant should rise 3-4 centimeters above the soil surface. Water the planted plant using 30 liters of water. After the liquid is completely absorbed, the root collar should be flush with the soil surface. Then you will need to shorten the stems of the plant by 1/3 and tie it to the stake. The trunk circle must be covered with a layer of mulch (humus or dry soil from the lower layer of the earth, which is not so fertile).
Dogwood care
It is necessary to grow dogwood in almost the same way as other fruit bushes (for example, barberry or gooseberry). Such a shrub must be watered, weeded, cut, fed in a timely manner, and you also need to regularly loosen the soil on the site. This plant has one feature, namely, there is no periodicity in its fruiting, which means that it gives a crop every year. The next year's harvest is laid from May to June of this year.In this case, flower buds must have time to fully form before the end of the period of active growth, their formation occurs at the same time with the growth of the stems. In this regard, timely watering and feeding is very important for dogwood.
To prevent the liquid from spreading over the soil surface during irrigation, it is necessary to make a furrow around the shrub. This will allow the superficial root system to be well saturated with water. Watering the plant should be moderate, while avoiding stagnation of liquid in the roots. When watering is finished, it is necessary to weed and loosen the soil surface to a depth of 8 to 10 centimeters, and in no case more. Until the middle of the season, fertilizers containing nitrogen and phosphorus are used for feeding. At the same time, from the second half, they feed the dogwood mostly with fertilizers containing potassium (for example, wood ash). Also, the plant responds well to feeding with humus or compost. But for it to give a good harvest, the presence of calcium in the soil is simply necessary.
Pruning
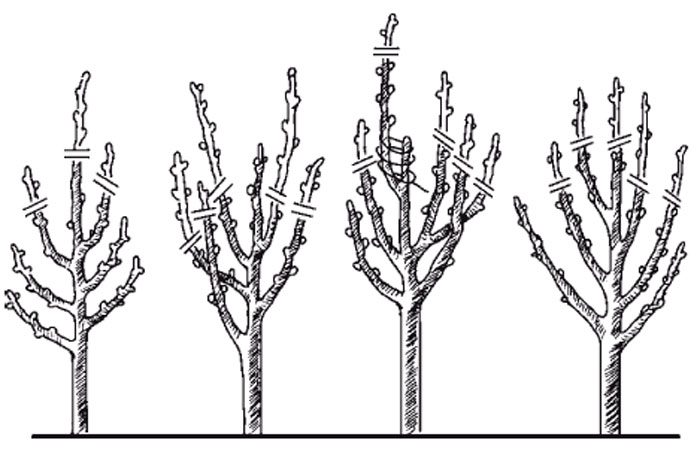
Dogwood needs systematic pruning. In winter or early spring, when the dogwood is still dormant, it is necessary to cut off those branches from the bush that are injured, affected by frost or dried out, since it is on them that pests or pathogenic microbes most often settle. Each time you cut a branch, you need to dip the scissors in a solution of bleach (1: 3). If this is not done, then pathogens can easily be transferred to healthy plant tissues. Excessively old shoots should be shortened or cut to the base, this will lead to stimulation of the growth of young stems. It is also imperative to remove the stems and branches that grow inside the shrub. If the bush is grafted, then it is necessary to cut off all the stems located below the grafting site. It is necessary to form a crown in very rare cases, since it naturally has a very spectacular appearance.
Diseases and pests
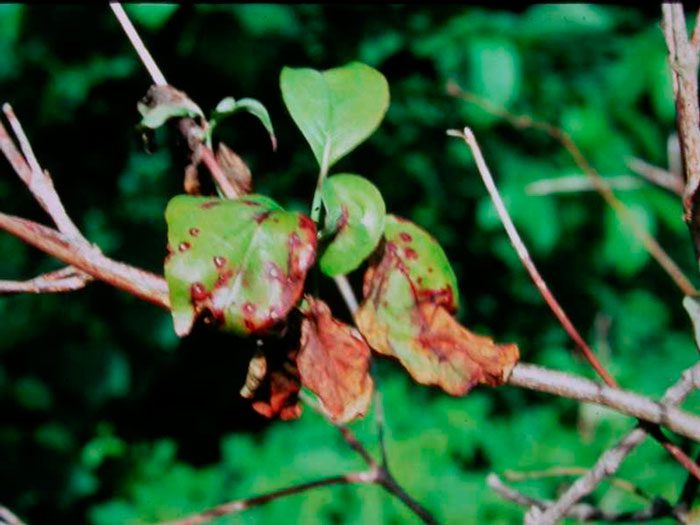
Cornel is highly resistant to various diseases and harmful insects. However, dogwood can contract a fungal disease such as rust, but this is extremely rare. In an infected specimen, specks of yellow color appear on the surface of the leaf plates. To get rid of this disease, it will be necessary to treat the plant with Bordeaux liquid. Another plant occasionally falls ill with powdery mildew, which is disposed of with the help of colloidal sulfur. And it also happens that the dogwood gets sick with spots, which Bordeaux liquid helps to cope with. Also, the snail worm can settle on the bush, which is destroyed by spraying the bush with lime, and it can also be disturbed by a polychrome caterpillar, it is killed with Parisian greenery.
Dogwood in the suburbs
Most gardeners believe that such a plant will not survive in the Moscow region and Moscow, and therefore it cannot be cultivated there. But this is not the case. Thanks to the labors of breeders, frost-resistant varieties of dogwood appeared, capable of not dying even in a frost of minus 30 degrees, in this regard, the plant can be quite successfully grown even in the middle lane, while it will give a rich harvest. It will be necessary to plant and care for the shrub in the same way as in places with mild winters. However, it happens that in winter the ends of the plant's stems freeze slightly, and with the onset of spring they will need to be cut off. To protect a young plant from frost, in the first years of life it will need to be covered with burlap, while the trunk circle should be covered with a thick layer of mulch (humus or peat) from both old and young shrubs.
Dogwood propagation
Amateur gardeners propagate dogwood most often by vegetative methods, but sometimes seeds are also used for this.
Seed reproduction
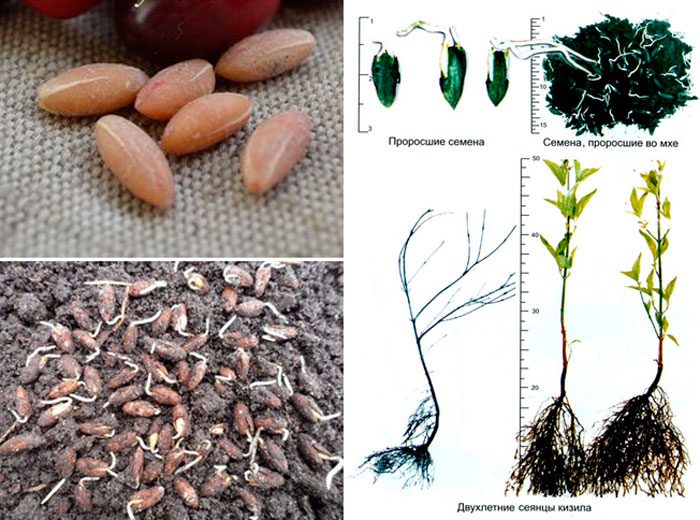
Before sowing, the bones, previously cleaned from the pulp, must be stratified.To do this, they are placed in moistened sawdust or moss, where they must stay for about 12 months, while the environment must be constantly moist. On the cotyledon, the seed does not separate; therefore, it must be buried in the soil by about 3 centimeters. If the seeds are not stratified, the seedlings will appear only after a couple of years, while only a small part of the seeds will germinate. If stratified bones are sown, then the seedlings can be seen in the same year. It is necessary to take care of crops and seedlings as usual, or rather, water, feed, weed in a timely manner, while at first they will need protection from direct rays of the sun. By the end of the first year, the seedlings will reach a height of only 30–40 mm, and by the end of the second year, their length will be 10–15 centimeters. In the fall, two-year-old seedlings can be transplanted into open soil in the nursery. The first fruits on such a plant will appear only after 7-10 years.
The seeds for sowing are taken from wild plant species. After the young seedlings grown from them get stronger, they are used as rootstocks for cultivated species of this plant.
Cuttings
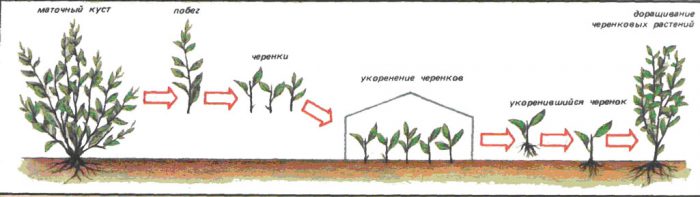
Dogwood can only be propagated by green cuttings, which are taken from shrubs at least 5 or 6 years old. Lignified cuttings root very poorly. Cuttings vary in length from 10 to 15 centimeters and are cut early in the morning from actively growing stems. It should be remembered that on each cutting there should be 2 pairs of leaf plates and a well-developed growth point. Cut cuttings should be placed in water immediately. When harvesting cuttings, it should be taken into account that the cut at the bottom must be oblique and pass 5-10 mm below the bud. Before planting the cutting, all the leaves must be cut off from the lower part of it, and it must be placed in a solution of heteroauxin (3%) for 6–12 hours. After that, the cuttings must be rinsed in running water and planted in a shaded place at an angle of 45 degrees. From above, the soil should be sprinkled with washed sand, with a layer thickness of 7 to 10 centimeters. Then the planting should be covered with plastic wrap so that there is a gap of 15–20 centimeters between its surface and the handle. Planting must be well watered and then make sure that the soil is slightly moistened all the time, while the cuttings must be protected from direct sunlight. Watering should be done through a fine sieve, as water must be sprayed. Under the film, the temperature should not be more than 25 degrees, so if it becomes excessively hot under the shelter, then it is necessary to raise it so that the plantings are aired. The cuttings will give roots after 15–20 days, then you will need to start hardening them, which lasts about half a month. When the plant is hardened, the shelter will need to be removed for good, and the cuttings should be fed using liquid ammonium nitrate (for 10 liters of water, 30 grams of the substance). When the next autumn period comes, the plant will need to be planted in a permanent place.
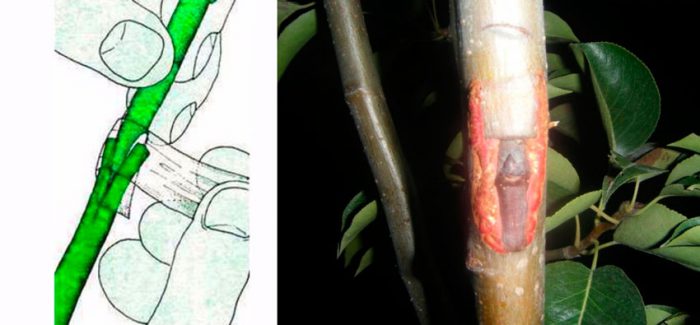
How to propagate by vaccination
Budding is carried out in August and September, for this, rooted or planted wild dogwood seedlings, which should be 2 years old, are used. As a graft, take cultivars of dogwood. Armed with a sharp knife, a cruciform incision should be made on the surface of the rootstock, while the depth of the vertical incision should be about 30 mm. From the scion it is necessary to cut a bud with a piece of bark, a leaf stalk and a small part of wood. It should be placed in a vertically located incision, while the bark on it must be gently pushed apart in different directions. To fix the scion, you should use an eyeliner tape, or you can take a simple stationery tape. If everything was done according to the rules, then after 15–20 days the petiole should fall off. The tape is removed in October. Next, you need to timely remove the emerging rootstock shoots.
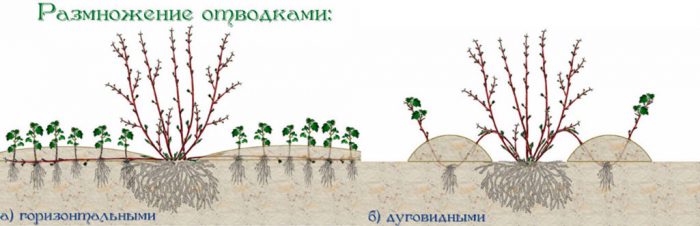
How to propagate by layering
To obtain a layering, an annual, horizontally located arcuate stem should be selected. In spring, after the soil warms up, you will need to dig up the soil around the shrub, while adding fertilizer to it. Having leveled the surface of the soil, it is necessary to make grooves in it. Then, in these grooves you will need to bend and put the stems that you have chosen to obtain layering, they are fixed and covered with soil at the point of contact with the ground. Next, you need to pinch the tops of future layers. After green stems up to 10-12 centimeters in height grow in the place of fixation with the ground near the layer, they must be covered with earth by ½ part. After 15–20 days, when the shoots will increase in growth by the same amount, they must be sprinkled with earth by ½ part again. In autumn or with the onset of the next spring period, the layers should be cut off from the parent plant and planted in a permanent place.
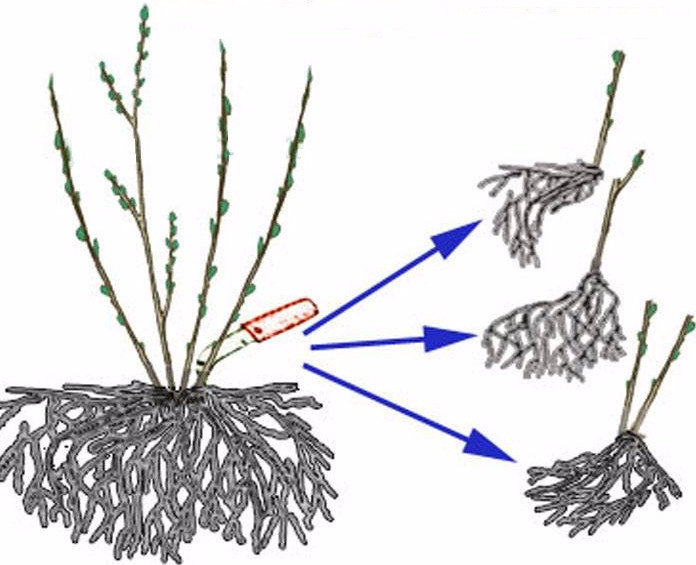
How to propagate by dividing a bush
This breeding method is used only when it is necessary to transplant a shrub. This can be done in the spring, before the buds swell, or in the fall, 4 weeks before the first frost. To do this, you need to dig up the dogwood and cut off all the old branches from it. Then you should carefully remove the earth from the root system, and only then divide the bush into several parts of approximately equal size. At the same time, each section should have good roots, as well as a non-diseased and not injured aerial part. Before planting a delenka, you need to remove the old roots from it, and shorten the remaining ones a little.
In the event that you have planted a rooted plant, then it can be propagated by root suckers. To do this, you need to dig out the growth and plant it in a new place. If the dogwood is grafted, then its root shoots will grow from the stock. And since wild species of dogwood are often used as a stock, it is recommended to simply remove such growths.
Types and varieties of dogwood with photos and names
Common dogwood (Cornus mas)
This type is the most popular among gardeners, and you can familiarize yourself with its detailed description above. The most popular varieties:
- Pyramidalis... Its crown shape is pyramidal.
- Nana... Dwarf variety with a ball-shaped crown.
- Variegata... The leaves have a white border.
- Aurea... The leaf plates are golden in color.
- Aurea variegata... The variegated leaf plates are yellow.
White dogwood (Cornus alba)
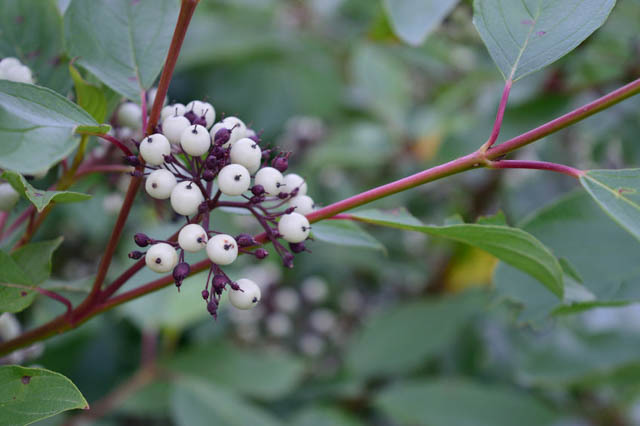
It is also a fairly popular species that can be found in the wild in Japan, China, Korea, and also practically throughout Russia. This shrub reaches a height of 3 meters. Its thin, flexible branches are orange-red in color, but there are varieties with brown-red and red-black branches. There is a bluish bloom on the surface of young stems. The shape of the slightly wrinkled leaf plates is broadly ovate, their length varies from 10 to 12 centimeters. Their front surface is dark green, and the back is whitish. In autumn, their color changes to a dark purple-red. Small white flowers reach 5 centimeters in diameter, they are part of the corymbose inflorescences. Lush bloom is observed twice a year, namely, until mid-summer and as early as September. The white, globular berries have a blue tint and are fully ripe by the time they re-bloom. Common decorative forms:
- Silver-bordered... Green leaf plates have a cream-white edging. In autumn, they change their color to carmine red. The bark is red in color. The bush reaches a height of 2 to 3 meters.
- Elegantissima... It has a very high frost resistance and grows quickly. The bush can reach a height of three meters, the stems are red, which looks especially impressive in winter. The leaf blades have an uneven edging of a cream color, and there are also stripes and specks on the surface.
- Siberica Aurea... The height of the bush can vary from 1.5 to 2 meters. On erect, red stems, there are pale yellow leaf plates. The flowers are white-cream. When the pale blue fruits begin to ripen, re-flowering may begin.
- Siberica Variegata... The bush can reach a height of 2 m. On the leaf plates there is a wide border, stripes and spots, which are painted in white-cream color. The main background of the leaves is green, while in autumn it turns purple, and the edging and stripes with spots do not change their color. In winter, the bark on the stems remains coral red. This variety gives a poor harvest, and the bush itself is slow-growing. It is perfect for small gardens.
Dogwood red, or blood red (Cornus sanguinea)
Under natural conditions, this species can be found from the Balkans to the southern part of Scandinavia and from the lower reaches of the Don to the Baltic, while it prefers to grow in the undergrowth of mixed and deciduous forests, as well as on the shores of lakes and rivers. In height, such a deciduous shrub reaches 4 meters, while its crown is branched. The stems are drooping and can be colored red, green or purple. Ovate, rounded leaf plates have a rich green front surface with small pubescence and a whitish seamy surface with dense pubescence. In autumn, the leaves change their color to deep red. Small dull white flowers are part of the multiflorous corymbose inflorescences, reaching a diameter of 7 centimeters. Flowering in this species lasts from 2 to 3 weeks. A lot of black berries ripen on the bush, which look very impressive against the background of deep red foliage. Decorative forms:
- Greenest... Stems, leafy fruits and berries are green in color.
- Variegata... The bush reaches a height of 4 meters. The variegated leaf plates are yellow. The pale green young stems eventually turn into a burgundy color. The berries are blue-black.
- Dogwood Mitch... There are small specks on the surface of the light yellow leaf plates.
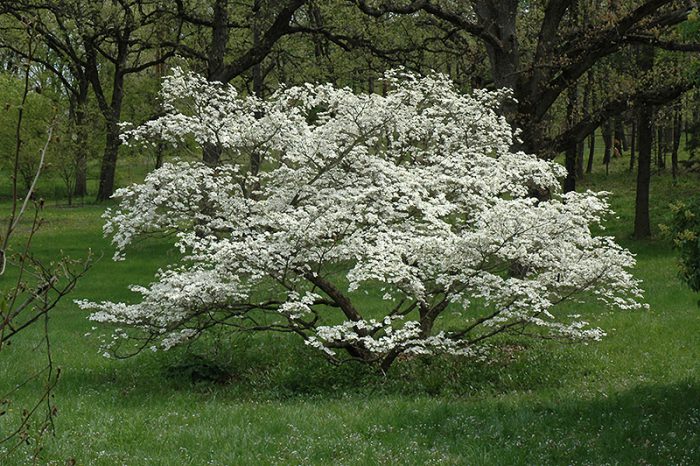
Flowering dogwood (Cornus florida)
Homeland is the eastern part of North America. Such a deciduous tree has a dense and spreading crown. Flowering is observed before the disclosure of leaf blades. In autumn, the leaves turn deep red. Varieties:
- Cherokee Chief... It reaches a height of 4 to 6 meters. The color of the bractea is pink-red.
- Rubra... Height varies from 4 to 6 meters. The color of the bractea can range from deep red to pale pink.
Dogwood (Cornus stolonifera)
It occurs naturally in North America, where it prefers to grow on the shores of watercourses in humid forests, while climbing to an altitude of 450-2,700 m above sea level. This species is very similar to the white dogwood, but in contrast to it, a large number of offspring grows near the bush. Such a shrub reaches a height of 250 centimeters, has glossy coral-red stems, rich green leafy plates, white-milky flowers that are part of inflorescences that reach 5 centimeters in diameter. The berries are whitish blue. Decorative forms:
- White bordered... The variety White Gold is related to it - it is a medium-sized shrub with green leaf plates with whitish edging.
- Flaviramea... This shrub grows very quickly and has a round shape. In width and height, the bush can reach from 2 to 3 meters. The crown is yellow in winter and spring, and greenish-yellow in summer and autumn. Some of the green leaves become pale red in autumn, and the rest does not change color.
- Kelsey... In such a dwarf shrub, the height can reach 100 centimeters, and the width is about 150 centimeters. The bark can be deep green or light red. The leaf plates are green, they do not fly around until late autumn, but at the same time they turn orange or dark red.
Cornus kousa
The homeland of this kind is China and Japan.It is a deciduous, winter-hardy shrub that can grow up to 9 meters high. The bracts are graceful and very beautiful. In autumn, the leaves turn deep red. Varieties:
- Gold Star... The bush reaches a height of 5 to 7 meters. There is a yellow pattern on the surface of the green leaf plates.
- Milky Way... The bush is high enough. The marriages are white-cream.
There are also creeping dogwoods, their experts have identified in a separate genus (Canadian and Swedish dogwoods). The genus Svyda also stands out, which include Meyer's dogwoods and Georgian.


Watch this video on YouTube
The benefits and harms of dogwood
Beneficial features
As a rule, the literature describes the benefits of common dogwood. The benefit of this plant is that its berries contain a lot of vitamin C, even more than lemon. And they also have an antiscorbutic effect, in this regard, from such berries they make a paste for seafarers and astronauts. The fruits also contain tannins that effectively hold the stool together. Such berries are recommended for diabetics to eat, as they lower blood sugar levels, and also make the pancreas work more actively, which produces the desired enzyme. Also, this plant has a choleretic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, diuretic and astringent effect. The fruits of such a plant improve appetite, normalize digestion, normalize blood pressure, eliminate pain in the head, and improve metabolic processes in the body. This herb is used to treat gout, swelling of the legs, intestinal diseases (for example, dysentery and diarrhea), cystitis, skin diseases and inflammation of the venous vessels. Medicinal properties are found both in the berries of the plant and in the foliage, roots, flowers and bark.
Popular recipes
- Tincture of foliage. 200 ml of edible alcohol must be combined with 50 grams of finely chopped leaves. The tincture will be ready after half a month, it will only be necessary to strain it. Drink 3 times a day, 10-15 drops, diluted with water. The remedy is suitable for the treatment of eczema, skin infections, hemorrhoids, gout, and is also used to get rid of intestinal parasites.
- Decoction of berries. Combine 200 ml of water with 1 large spoon of dried fruits. The mixture must be boiled for a third of an hour over low heat. Then she must brew for a couple of hours. The strained broth should be drunk at ¼ st. with vitamin deficiency three times a day before a meal.
- Decoction of roots and bark. 200 ml of water should be combined with 1 small spoon of finely chopped bark and roots. The mixture must be boiled for a quarter of an hour, and then let it brew for a couple of hours. The filtered broth is taken for rheumatism three times a day, 2 large spoons.
Drinks and jams from the fruits of such a plant are also very tasty and useful. Dried berries are used to prepare a delicious and healing broth in the winter.
Contraindications
Cornel is contraindicated for people with high acidity, with weak intestinal peristalsis, with frequent constipation, with individual intolerance to such a plant and with an unstable nervous system.