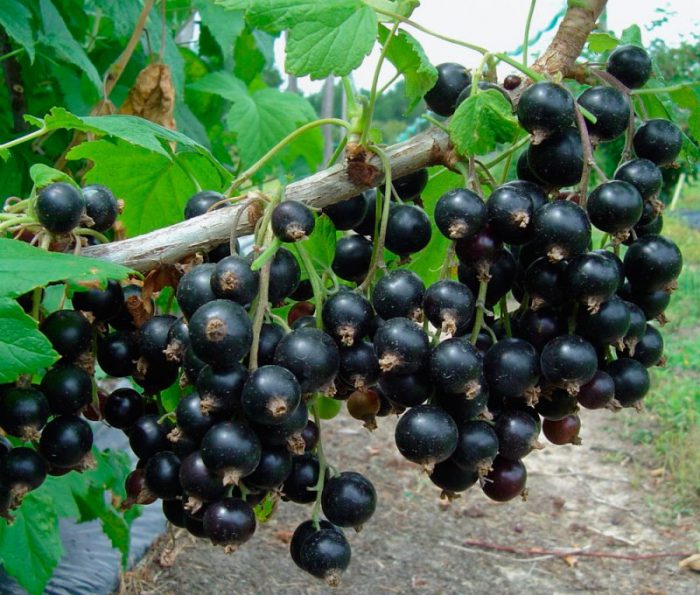
Currant (Ribes) - this genus is a representative of the gooseberry family. It unites about 200 species of plants, with 50 of them naturally occurring in the Northern Hemisphere. In the monastery gardens of Russia, this culture began to be grown in the 11th century, and then it ended up in European countries. In Russia, currants are very popular among gardeners. Along with red and black currants, both golden and white currants are also grown. However, of all types, black currant is considered the most useful and tasty. Its fruits are eaten fresh, and they are also used to prepare jellies, jams, compotes, syrups, liqueurs, wines and liqueurs. Also, this plant is used as a raw material for the pharmaceutical industry.
Content
Features of currants
Currant is a perennial shrub that can be spreading or compact. Its height varies from 100 to 200 centimeters. Greenish fluffy stems turn brown with age. Young shoots grow out of dormant buds every year. The plant's root system is powerful, and it penetrates into the soil to a depth of about 0.6 m. Three-lobed or five-lobed leaf plates with a serrated edge have a diameter of 3–12 centimeters. The front surface of the leaves is dark green in color, and the back is pubescence along the veins. The racemose drooping inflorescences consist of light pink or lavender bell-shaped flowers. The fruit is a fragrant berry. The color and size of the fruit is influenced by the type and variety of the plant. Flowering occurs in May and June, and fruiting in July and August. The plant begins to bear fruit in the second year after planting in open soil. Currants are considered a popular crop as, for example, strawberries, blackberries, strawberries, raspberries and blueberries.It is cultivated by gardeners on their plots, and currants are grown on an industrial scale. Currant is a relative of another popular culture - gooseberry.
Planting currants in open ground
What time to plant
The currant is considered a long-liver in comparison with other horticultural crops. Already the next season after planting in open ground, it gives the first fruits. If the shrub is well cared for, it will bear fruit for more than 15 years. It is best to plant currants in open soil in the first autumn weeks, but in extreme cases this can be done in spring. It is recommended to purchase a two-year-old seedling with 3 skeletal roots. Take a good look at him before buying, as he may be very weak or sick.
The suitable area should be well lit and protected from strong gusts of wind. A non-acidic, well-drained soil is suitable for such a culture. If the soil is acidic, then this can be corrected by introducing lime into it for digging (per 1 square meter from 0.3 to 0.8 kg), do this before planting the plant. In addition, from 100 to 150 grams of granular superphosphate, from 2 to 4 kilograms of organic matter and from 20 to 30 grams of potassium sulfate per 1 square meter of the site should be added to the soil. You need to dig up the soil to a depth of 20 to 22 centimeters.
Planting currants in autumn
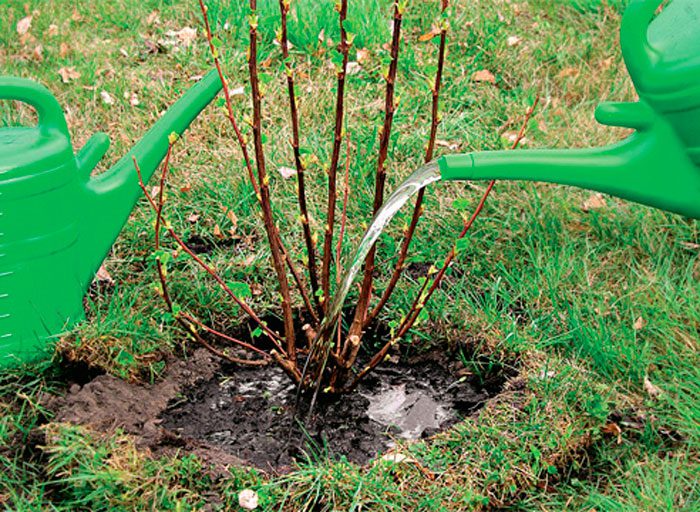
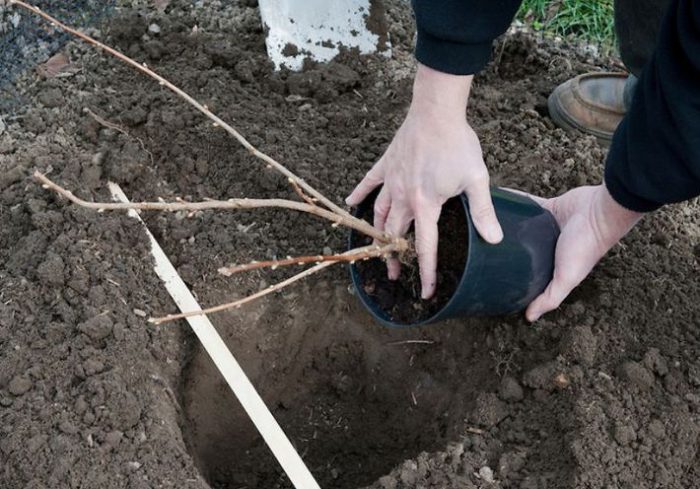
The length and width of the planting pit should be about 0.55 m, and its depth should be about 0.45 m. A distance of 1.5–2 m should be maintained between the bushes. 100 grams of superphosphate, 1 bucket of humus and 45 gram of potassium chloride. In order to prevent the roots of the plant from getting burned, the fertilizer must be covered with a layer of soil, the thickness of which should be from 7 to 9 centimeters. The preparation of the pit must be done 15 days before planting the currants, in this case the earth will be able to settle well. The plant is placed in a hole at an angle of 45 degrees, while making sure that its root collar is 50 mm buried in the soil. Spread the roots very carefully. This procedure is very important because it promotes the active growth of new roots and shoots from the buds trapped in the ground, resulting in the formation of a strong shrub with many powerful branches. The hole is covered with a small amount of soil, which is well tamped. Then 5 liters of water are poured into it, after which the pit is filled to the top with earth. A furrow must be made around the seedling, which must be filled with water. To avoid the appearance of a crust on the surface of the soil, it must be covered with a layer of mulch (humus). Shorten the shoots to 10-15 centimeters, with 4 or 5 buds remaining on the segments. If desired, stick the cuttings into moist soil where they can take root.
Planting currants in spring
Planting currants in the spring is carried out only as a last resort, and you need to be in time before the start of sap flow and before the buds open. The difficulty of planting this crop in spring is that at the beginning of the growing season it is very difficult to choose the moment that is suitable for planting currants. The fact is that the currant bush starts growing very early, while the soil often does not have time to warm up to the temperature that is necessary for the rooting of the plant. In the event that the planting pit was prepared in the autumn and the soil in it had time to settle, then planting currants in the spring will be easier.
Currant care
Currant care in spring
It is very easy to take care of currant bushes in spring, you just need to adhere to the following scheme:
- It is necessary to cut out all the kidneys affected by the mite. If you need to remove most of the buds, then in this case, the affected shoots on the bush are cut off almost to the ground.
- Dig in the bush to a shallow depth, while the surface of the soil around it must be covered with a layer of mulch (humus or manure).
- During active growth and flowering, the bush needs regular watering.
- Weeding and loosening the soil around the bushes to a depth of 6 to 8 centimeters is necessary at least 2 or 3 times every 7 days. To reduce the number of weeding and loosening, you need to cover the area with mulch.
- After wintering, the plant will need sanitary pruning.
- In early spring, the bushes need to be sprayed in order to prevent diseases and pests.
- When the plant blooms (usually in May), you need to make a careful inspection of the flowers. Any double flowers found will need to be removed. If there are a lot of such flowers on the plant, then it is dug up and burned in order to avoid the further spread of terry.
- Feed the bush with nitrogen fertilizer.
Summer currant care
In the summer, you need to provide the currants with timely watering. How to properly water this crop is described in great detail below. You also need to weed the currants on time, you need to make sure that the surface of the site is always clean. Also in the summer, the shrubs are fed with organic matter, which must be carried out in conjunction with watering. Inspect the bushes regularly and treat them with an appropriate product if pests or symptoms of illness are found. However, remember that 20 days before the fruits ripen, you need to stop any treatment of the plant with chemicals, but they can be replaced with harmless folk remedies. The fruits should be picked selectively as they ripen, while the white and red currants are torn off with brushes, and the black currants - on the berry.
Currant care in autumn
When all the fruits are collected from the bush, it should be watered, after which the soil is loosened. In the last days of September, the shrubs are fed with organic matter and mineral fertilizers. And also at this time formative and sanitary pruning of shrubs is carried out. Also at this time, planting and reproduction of currant bushes is carried out. If there is very little rain in the autumn, then the shrubs will need water-charging podzimny watering. It should also be treated in order to prevent pests and pathogens of various diseases, which often hibernate in the bark of a plant or in the upper layer of the soil.
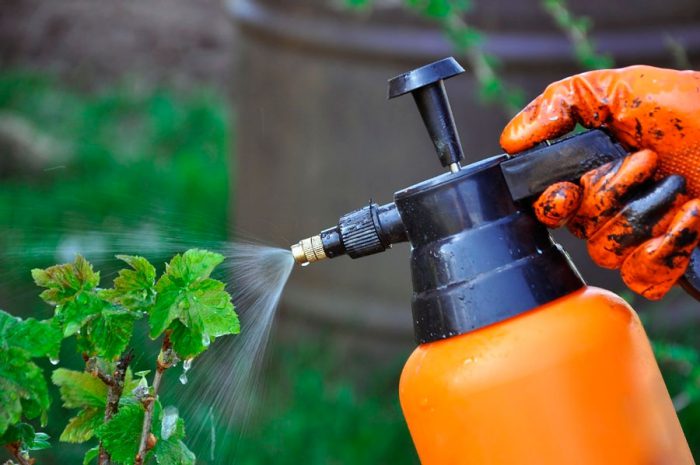
Currant processing
If the currant bushes are powerful and healthy, then they are unlikely to get sick, and pests will also bypass them. However, experts, despite this, advise not to neglect systematic preventive treatments. What should be used to spray this crop to keep it healthy throughout the season? Remember that along with the awakening of the buds, pests wake up, as well as pathogenic microorganisms that have hidden for the winter in the bark of a plant or in the upper layer of the soil. The first time you need to process the shrub before the buds swell, for this, use a one percent solution of Bordeaux mixture, Karbofos or copper sulfate. You can replace these drugs with Nitrafen, while remembering that during treatment you need to spray not only the bush, but also the surface of the soil. At the end of the growing season, the site should be cleaned of plant debris and loose leaves, since pests and pathogens are very fond of hibernating in them. Then, the currants are preventively treated with the same means as described above.
How to water
If there was a lot of snow in the winter, then the currants in the spring often do not need to be watered, because the soil already contains a large amount of moisture after the snow melts. After a winter with little snow in the spring, the plant will need systematic watering. During the formation of ovaries and the filling of fruits, especially in dry, sultry weather, the bushes should be watered with lukewarm water approximately once every 5 days. It is necessary for the soil to get wet to a depth of 0.3 to 0.4 m, in this regard, 2-3 buckets of water are taken per 1 square meter of the plot.Pour water strictly under the plant, while making sure that the water does not get on the foliage and berries. Experienced gardeners recommend making irrigation areas around the bush, which should be limited to a relatively high (about 15 centimeters) roller made of earth. If desired, they can be replaced with circular grooves, the depth of which should be 10-15 centimeters, while they should be made at a distance of 0.3 to 0.4 m from the crown projection. If there is a drought in the autumn, then currant bushes will need water-charging podzimny watering.
White and red currants are less demanding for watering than black currants.
Feeding currants
If, during planting, all the necessary fertilizers were added to the hole, then for 2 years the currants can not be fed. Starting from the third year, fertilizers will need to be applied to the soil systematically. At the beginning of the spring period, this crop is fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizer. To feed one young shrub, take from 40 to 50 grams of urea. Starting from the age of four, for feeding 1 bush, 15 to 20 grams of urea are used, while two feeding are carried out. In autumn, 4–6 kg of organic matter (manure, chicken droppings or compost), 15 grams of potassium sulfate and 50 grams of superphosphate are introduced into the soil under the bush. These feeding should be carried out annually.
What do experts recommend to use for feeding currants so that they are more resistant to diseases and pests, and also give a rich harvest? From June to July, it is necessary to make 3 foliar dressings, for this, the following nutrient mixture is used: you need to take 5 grams of potassium manganese, 3 grams of boric acid and 35 grams of copper sulfate, they should be diluted separately, and then mixed with 1 bucket of water. It is necessary to spray the plant with this composition on a cloudy day or in the evening, when the sun goes down, while there should be no wind.
Currant pruning
Currant pruning in spring
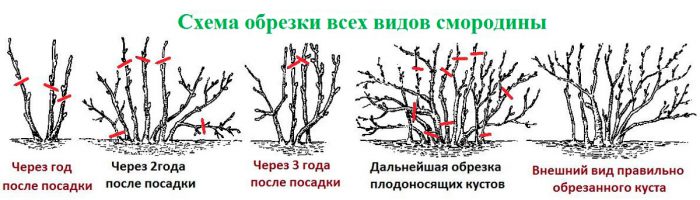
Pruning currants is necessary, because during this procedure, all unnecessary, injured, diseased and weak branches are removed, which means that the plant will no longer have to spend its strength and nutrients on them. Most of the ovaries are on the last year's increments of four-year and five-year branches. In this regard, branches that are more than 6 years old must be cut out, because they are no longer needed. You also need to cut out diseased and dried branches. With timely and systematic pruning, the fruiting of black currant bushes can be extended up to 20 years, and red - up to 15 years.
In autumn, when leaf fall ends, the main currant pruning should be done. In early spring, before the buds open, it is necessary to shorten the stems damaged by frost in the winter to healthy tissue, and also remove all dead and injured branches. In the summer, it is recommended to pinch the ends of young shoots, this is necessary to stimulate their tillering, as well as to give the shrub a neat and regular shape.
Pruning currants in autumn
After the seedling is planted in open soil, all its stems are shortened to 10-15 centimeters from the surface of the site. In the second year, the bush will need to choose 3-5 of the most powerful zero shoots, they will become skeletal branches, and the rest must be cut out. On shrubs of the third and fourth years of growth, you should choose from 3 to 6 of the most developed zero shoots, and the rest are removed. Avoid thickening of the bush, for this you need to remove weak and underdeveloped shoots in the middle of the bush. Trim the tops of last year's stems. Two- and three-year branches are shortened, while there should be 2-4 buds on each branch. If you cut the bush correctly and regularly, then by this age it will already be fully formed.In subsequent years, it will be necessary to cut all branches older than 6 years at the root. Pruning the remaining branches is carried out according to the scheme described above.
Rules for pruning white and red currants
Pruning of white and red currants is carried out in the spring. The rules and pruning schemes use the same ones that are intended for black currants, however, pinching the tops of the growths is not necessary, as well as shortening the shoots of the second and third years. You will need to cut out all the old branches that are more than 7 years old, you also need to remove all excess young shoots, injured and diseased branches. In the event that a branch over 7 years old continues to bear fruit, then it should be shortened to the nearest powerful fork. In this case, she will live and bear fruit longer than usual.
Reproduction of currants
Often, gardeners use arcuate cuttings, green or lignified cuttings to propagate currants, and also root two-year-old branches cut from a bush. Red currants are relatively difficult to propagate by cuttings; for this it is better to use layering. Only specialists are involved in the cultivation of currants from seeds, because this method of reproduction is very long and ineffective.
How to propagate lignified cuttings
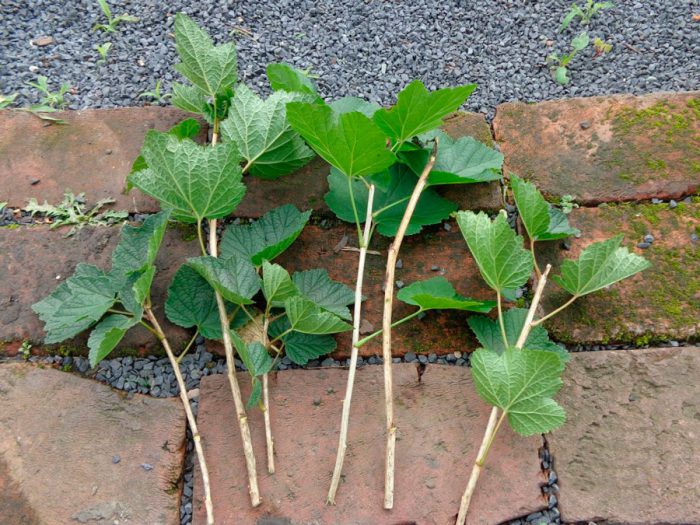
This culture can be propagated by both green and lignified cuttings. The most affordable method is growing currants from lignified cuttings, because you can prepare them when you need it. Planting of cuttings for rooting is carried out in spring and autumn. Experienced gardeners recommend that you start harvesting cuttings in the first winter weeks, but you need to catch it before severe frosts, as they can destroy the buds. The length of the cuttings can vary from 18 to 20 centimeters, while their thickness should be 0.8–1 centimeters. It is recommended to cut them from the middle of the annual shoots that grow from three-year branches or from the root. In order to prevent moisture from evaporating from the cuttings during storage, the places of the cuts must be covered with molten paraffin or garden varnish. Then the cuttings should be wrapped with slightly damp paper and put in a plastic bag, which should be buried in a snowdrift or put on the refrigerator shelf. At the very beginning of spring, cuttings should be planted on training beds. They need to be planted at an angle of 45 degrees, a distance of 15 centimeters must be maintained between the cuttings, while the width between the rows should be about 20 centimeters. The lower end of the cutting, covered with paraffin, should be cut obliquely. The planted cutting should be buried in the soil so that only 2 buds rise above its surface. The planted cuttings need abundant watering, then the surface of the garden bed must be covered with a layer of mulch (humus, sawdust or small peat). Then, arched supports are installed above the bed, which reach a height of about 0.5 m, and a plastic wrap is pulled over the top. The shelter should be removed only after new leaves grow on the cuttings. Watering the garden bed should be done sparingly, and the soil should not be allowed to dry out even for a short time. In the summertime, cuttings need timely weeding, watering and feeding with a mullein. In early autumn, cuttings will become seedlings that can reach a height of 0.3–0.5 m, while they will have 1 or 2 shoots. Well-developed and strong cuttings in autumn can be planted in a permanent place, while weak ones - you need to grow until next fall.
Reproduction of currants by green cuttings
You will need a greenhouse to root green cuttings. But there is another way. For cutting cuttings, only well-developed shoots are used, while it should be remembered that the top is not rooted.In length, the stalk should reach from 5 to 10 centimeters, while it should have 2 green leaf plates. Cuttings for rooting must be placed in a container with water. After half a month, they will have roots, the length of which will reach 1–1.2 cm. After that, the cuttings are planted in packages that are filled with soil. Holes must be made in the bags in advance so that excess liquid flows down. The cuttings must be watered with a frequency of 1 time in 2-3 days, while the soil in the package must have a creamy consistency. After 1–1.5 weeks, watering should be reduced, while the soil should be of normal consistency. The cuttings will be kept indoors until May, by the time they are planted, their height should reach 0.5–0.6 m. During transplantation, you just need to cut the package and pull out the cutting. It is dipped obliquely into the ground, while it should be planted 15 centimeters deeper than it grew before.
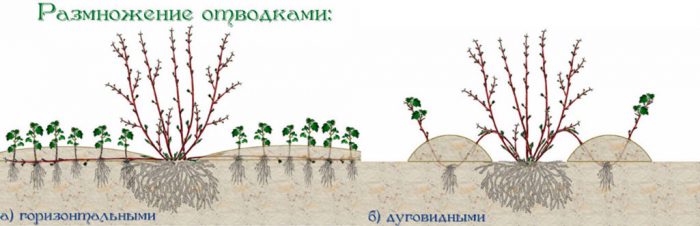
Reproduction of currants by layering
It is very simple and easy to propagate such a shrub by layering. Within a year, you will have powerful seedlings with a well-developed root system. For layering, a two-year-old branch is chosen, which must be absolutely healthy and at the same time grow on the periphery of the shrub at an angle. Under this branch you need to make a groove deep enough (10 to 12 centimeters). Then the branch is carefully bent down and placed in this groove, while taking into account that the top of this branch should rise by 0.2–0.3 m above the soil surface. In the middle, the branch is fixed with a wire hook or a metal bracket. The furrow must be filled with soil. Layers during the summer period will need systematic watering. By the onset of autumn, the cuttings should become a strong seedling with several branches and a developed root system. If desired, the layers can be removed from the ground, cut off from the parent bush and transplanted to a new permanent place.
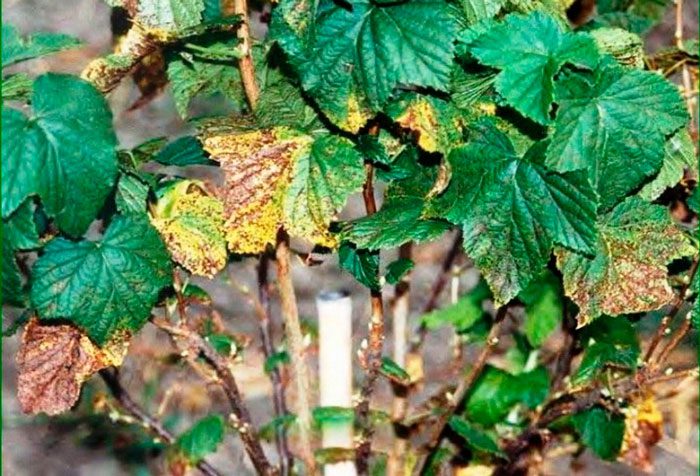
Diseases of currants with photos and descriptions
Currants suffer from the same diseases as many other garden crops, such as gooseberries. As a rule, a shrub becomes ill if it is improperly looked after or due to poor heredity. The diseases that are most common will be described below:
Anthracnose
On the surface of the leaf plates, small specks of brown color with small tubercles appear, which eventually merge with each other. The foliage dries up and dies off. First, the lower branches are affected, and then the disease rises higher.
Septoria (white spot)
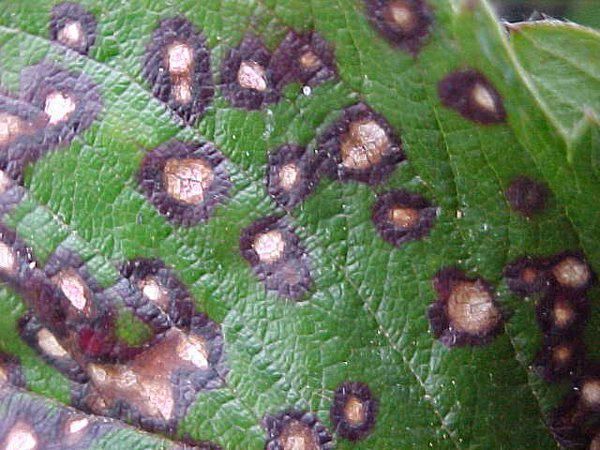
On the foliage, specks of an angular or round shape appear. At first they are colored brown, but over time they brighten and acquire a dark border. In some cases, fetal damage occurs.
Goblet rust
On the leaf plates there are large light yellow pads, inside which there are spores of the fungus.
Terry
On the bush, you can find ugly "double" flowers, which are painted in lilac color. On young shoots, darkening and stretching of the foliage is observed, blades appear on it, the veins become coarser. The foliage loses its smell, and the bush stops bearing fruit.
Gray rot
Brown specks appear on the surface of the foliage. In white currants, this disease can also damage wood.
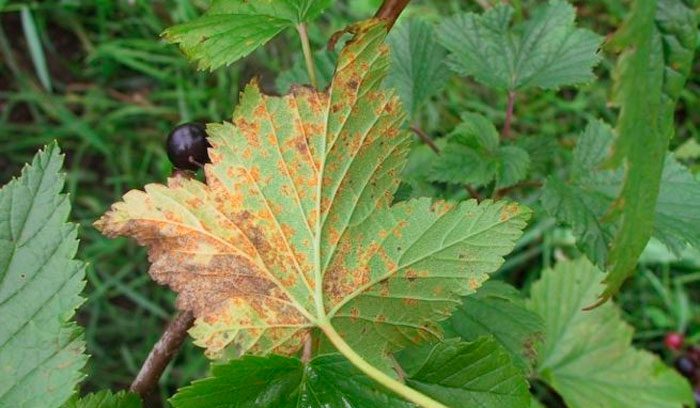
Columnar rust
Small yellow spots form on the front surface of the leaves. At the same time, growths appear on the seamy surface, in which there are orange-yellow spores, which are small hairs.
Necrosis of stems and branches
The bark loses its elasticity and firmness, as a result of which it cracks. This leads to drying out and death of the branches.
Striped mosaic
In the first summer weeks, a yellow pattern appears on the leaf plates around the main veins.
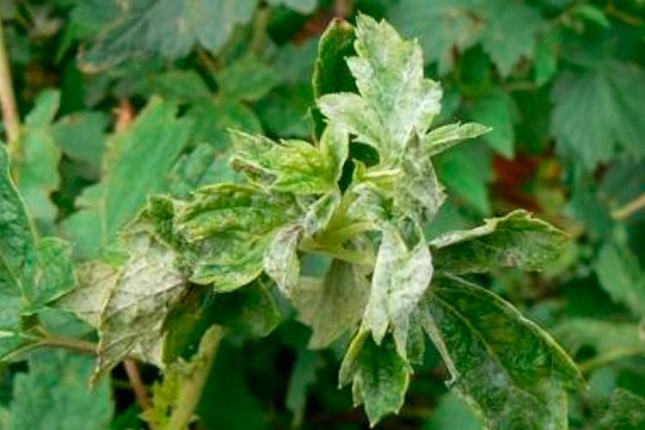
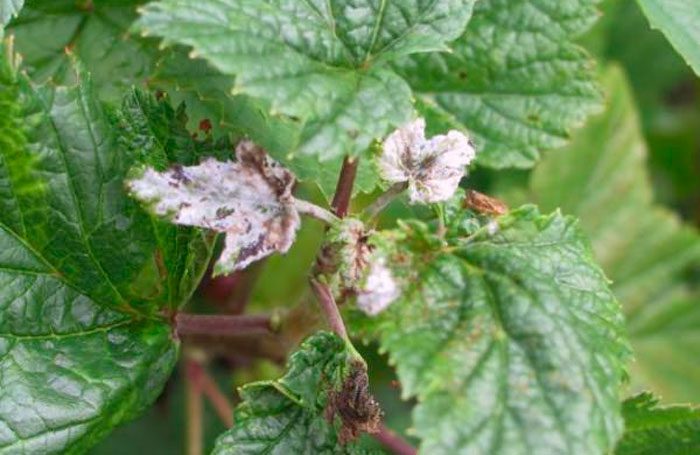
Powdery mildew
A loose bloom of white color is formed on the surface of fruits and foliage. After some time, it becomes a brownish film.
Nectric necrosis
In white and red currants, branches and stems are drying out.
It is not always possible to cure currants. No effective drug has been found for viral diseases. If you do not start the treatment of fungal disease in time, then during the season it can destroy half of the bushes. It should be remembered that subject to the rules of agricultural cultivation and with proper care, the plant will rarely get sick. Examine currant bushes regularly and start treatment when the first signs of illness are found. Also, do not forget about preventive treatments of currants and the soil around it, for this they use a solution of Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate, Nitrafen or Karbofos. Such treatments are carried out in early spring, before the buds swell, and in autumn.
Currant pests with photos and descriptions
The currant can also be greatly damaged by various harmful insects, which also prefer to settle on its close relative, the gooseberry. More often than others, the following pests settle on currant bushes:
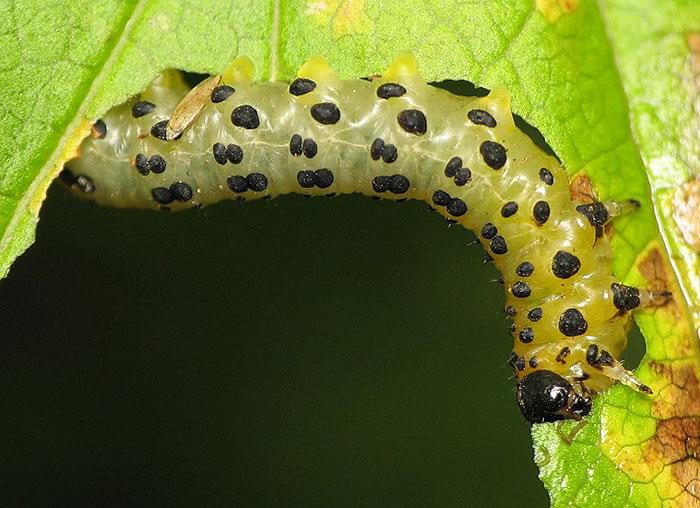
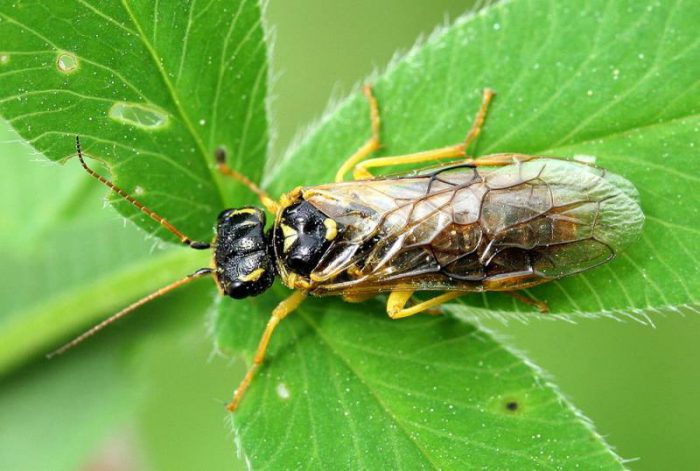
Pale-footed sawfly
Caterpillars of such an insect devour leaf plates, of which only veins remain.
Biennial leaf roll
The caterpillars of this insect harm the fruits and buds of the plant. They settle not only on currants, but also on grapes, gooseberries, viburnum and other berry crops.
Yellow sawfly
The caterpillars of such a sawfly live on red and white currants, they devour its foliage.
Fire
The fruits damaged by this pest begin to sing very quickly and dry out.
Sprout aphid
She feeds on the sap of the plant, sucking it out of the leaves. As a result, the shoots are curved, their growth stops, twisting, drying and flying around the foliage.
Moth
The caterpillars of this butterfly devour the foliage of not only white and red currants, but also gooseberries.
Red-gall and gall aphids
Often, such a pest, which gives 7 generations in 1 season, settles on white or red currants. The affected bush begins to turn yellow, deformation of the leaf plates occurs, red and yellow swellings appear on their surface. Then the foliage flies.
Spider mite
It is able to harm red and black currants, gooseberries, raspberries, strawberries, grapes, elderberries and other plants. In the affected bush, the color of the foliage becomes marble, it begins to dry out and fly around.
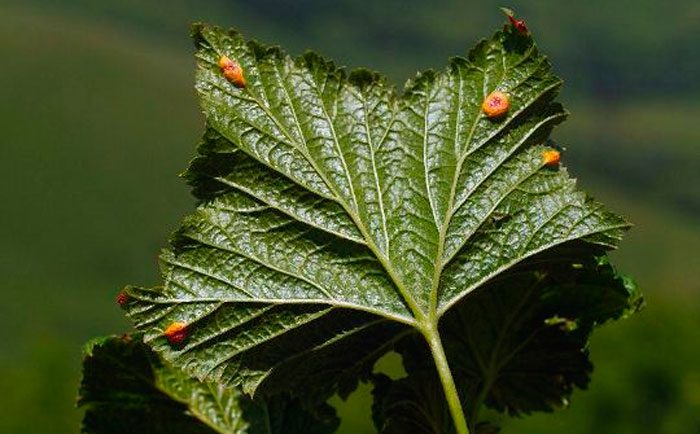
Kidney mite
He gnaws the kidneys and settles in them for the winter, eating them from the inside.
Glass-maker
Such caterpillars devour the core of the branches, which leads to their death.
Gall midges
There are several types of such pests:
- escapes - they eat up the stems from the inside, as a result of which they wither and die;
- flower - such pests feed on the buds of the plant, as a result, they turn red or yellow and die off;
- leafy - they gnaw holes in unopened young leaves.
Fruit sawfly
Affected black currant berries change their shape to faceted.
It is necessary to fight such pests exactly at the time when they settle on the bush. At the same time, there is a very large number of various rather effective drugs. Some of the gardeners use folk remedies, while others prefer modern chemicals. You can save the plant from the invasion of pests by treating it in spring and autumn with copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture.
Currant varieties with photos and descriptions
Numerous varieties of currants are divided not only by the color of the fruit, but also by the time of their ripening into: early ripening, mid-early, mid-ripening, mid-late and late-ripening.
Early maturing varieties
- Pearl... The fruits are sweet black and very large, weighing about 6 grams.
- Venus... Tall shrub. Fruits are black with a sweet-sour taste and weigh about 5.5 grams.
- Black BMW... The shrub is compact, vigorous. Black sweet fruits weigh about 7 grams.
- Jonker Van Tets... The fruits are very large red and have a sweet and sour taste.
- Ural white... Large white fruits are found on a spreading bush. They taste sweet.
Medium early varieties
- Bashkir giant... This variety is resistant to pests and diseases. The very large black fruits have a sweet and sour taste.
- Belarusian sweet... The very large black fruits have a sweet taste.
- Umka... The shrub is erect, vigorous. Fruits are sweet, large, white.
Mid-season varieties
- Sanuta... A vigorous shrub, compact enough. The sweet-sour black fruits weigh about 5.5 grams.
- Osipovskaya sweet... This vigorous shrub is slightly spreading. Sweet large fruits are red in color.
- Imperial yellow... Shrub medium spreading, medium height. The fruit is yellow, but it is a high-yielding variety of white currant. Fruits are small, sweet and sour.
- Versailles white... White berries can be large or medium in size. The taste is sweet and sour.
Medium late varieties
- Jubilee Digging... On a compact, vigorous shrub, there are black fruits with a sweet and sour taste.
- Roland... The variety is resistant to frost and fungal diseases. Fruits are red, sweet and sour.
Late-ripening varieties
- Lazy person... On a vigorous compact shrub grow very large black fruits of sweet taste.
- Valentinovka... Red sour fruits are very large. They are great for making jelly.
Today, golden currant is becoming more and more popular among gardeners. This shrub is decorative: fragrant flowers are painted in various shades of yellow, while in autumn the foliage changes its color to variegated and very rich. Depending on the variety, the fruits can be colored orange, red, yellow, brown, pink or blue-black. But such currants have a slightly lower taste for fruits than black, white and red ones.
Currant hybrids
Today, only 2 currant hybrids are popular.
Yoshta
This is a hybrid of common gooseberries, black currants and bulging gooseberries. It was born in 1970. It took specialists about 40 years to create it. It is a very strong, spreading shrub, reaching a height of about 150 cm, its diameter can also be 150 cm. The plant does not have thorns. The fruits are covered with a dense skin and weigh about 5 grams. They are painted black with a purple tint. The berries are collected in a cluster of 3-5 pieces. They have a nutmeg flavor that is quite pleasant. The bush is frost-resistant, resistant to certain pests and diseases. Life expectancy is 20 to 30 years. It is very popular in Western Europe.
Chroma
This gooseberry-currant hybrid was created in Sweden. Large smooth fruits are colored black and reach 20 millimeters in diameter. They are 3-5 pieces collected in a brush. The plant has no smell characteristic of currants. The fruits taste like currants and gooseberries. In Sweden, fruit ripening occurs in mid-July.