The herbaceous perennial plant eggplant, also called dark-fruited nightshade (Solanum melongena), or blue, or badrijan, is a representative of the genus nightshade. In natural conditions, it can be found in India, South Asia, as well as in the Middle East. Thanks to ancient Sanskrit texts, scientists have learned that eggplant began to be cultivated about 1.5 thousand years ago. It was the Arabs who were the first to spread this culture around the world. They brought eggplants to Africa in the 9th century AD. In Europe, this vegetable appeared in the middle of the 15th century, but it only became popular in the 19th century.
Content
Features of eggplant
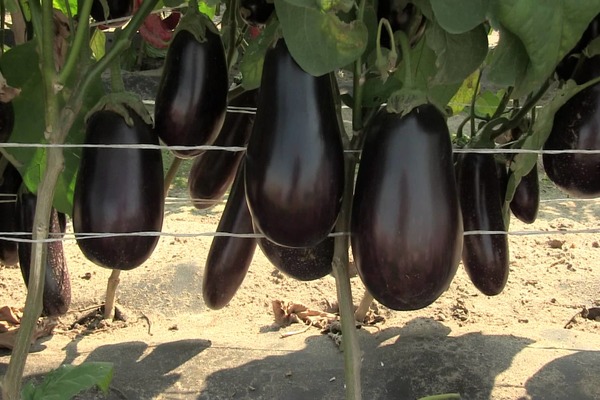
The height of an eggplant bush varies from 0.4 to 1.5 m. Large alternate leaf plates have a rough surface, they are painted green, sometimes with a purple tint. Semi-umbellate inflorescences consist of 2-7 flowers, which can also be single. In diameter, bisexual purple flowers reach 20-25 mm. Bloom is observed in July – September. The fruit is a large cylindrical, round or pear-shaped berry, it can reach about 0.7 m in length and about 0.2 m in diameter. Fruits weigh about 1 kilogram, they have a shiny or matte dark purple color. Inside they are flat, small brownish seeds that ripen in the last summer or first autumn weeks.
Growing eggplant from seeds
Sowing eggplant seeds
Eggplant belongs to the Solanaceae family, and it is considered its most thermophilic representative. Frost can destroy it, so in the middle latitudes it is grown exclusively in seedlings. Duration of ripening of early ripening varieties is 100 days from the moment the seedlings appear. In late-ripening varieties, the ripening period is about 150 days. It is recommended to sow seeds for seedlings in the first half of March, while it should be borne in mind that during planting the eggplant in open soil, the ground must warm up to at least 18 degrees, while only those seedlings that are at least 75 days can be planted.
The seeds of this plant need pre-sowing preparation. Experienced gardeners recommend choosing the seed of the second, not the first year of storage, since it is more viable.To activate the seeds, they must be immersed in a solution of potassium humate (3%) for three days. Then they are planted one by one in individual pots or cassettes. They need to be filled with a moist substrate, which includes humus (20%), high moor peat (60%), sawdust or sand (5%), vermicompost (5%) and sod land (10%). In the soil mixture, the seeds need to be buried only 10 mm. When the sowing is done, the substrate should be tamped, after which the container is covered from above with glass or film.
Growing eggplant seedlings
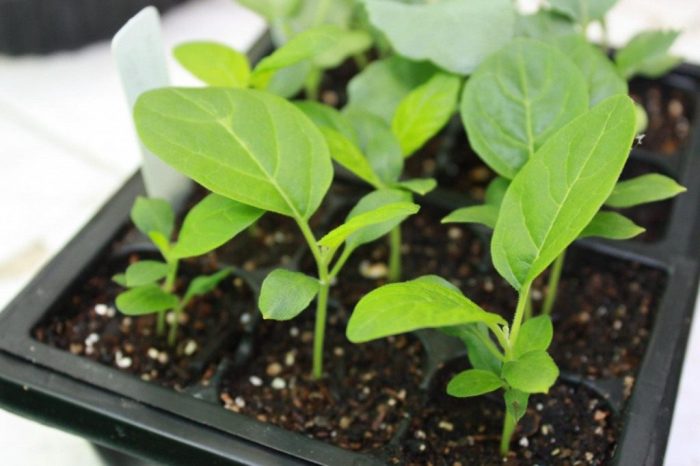
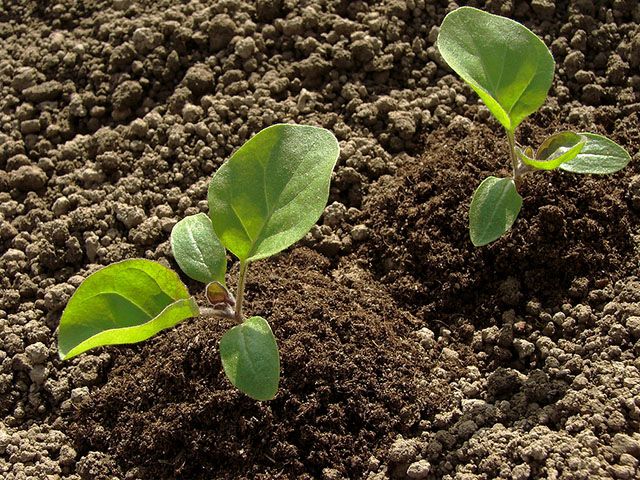
Containers with crops must be removed to a warm place (about 25-26 degrees). If everything is done correctly, then the first seedlings will appear after 1.5-2 weeks. After most of the seedlings appear, the shelter must be removed, while the containers are rearranged to a warmer and well-lit place. It is quite easy to care for such seedlings. From the moment of sowing and before buds appear on the bushes, you do not need to water the seedlings. Eggplant seedlings do not need high humidity. During the formation of buds, an increase in air humidity and substrate will be required.
If fertile soil was used for sowing seedlings, then there is no need to feed it. If the substrate contains a small amount of nutrients, then the seedlings will need to be fed 2 or 3 times with a weak solution of Crystallin (for 1 bucket of water from 12 to 15 grams).
Make sure that the seedlings have enough light. If it is not enough, the plants will be very elongated. If a prolonged cloudy weather is established, then in the room where the seedlings are located, the air temperature must be reduced by a couple of degrees (for this, you can resort to airing), and you also need to reduce the humidity of the air and substrate.


Watch this video on YouTube
Picking
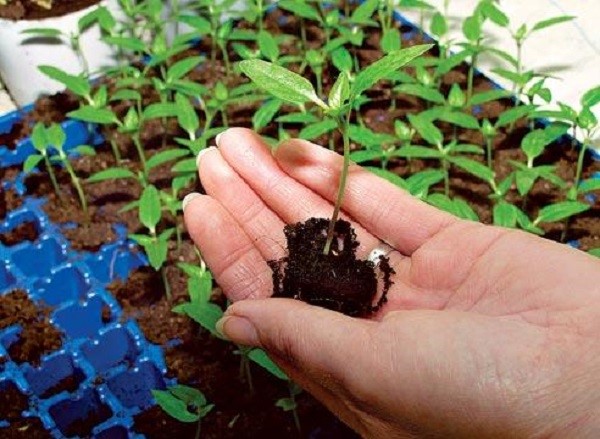
It was already mentioned above that eggplants react extremely negatively to picking, therefore individual containers should be used for planting them. But if the seedlings have 1 or 2 true leaf plates, they need to be transplanted by transshipment, while individual pots of larger volume are used (diameter about 10-12 centimeters). This procedure can be called picking. Before transplanting, the seedlings are well watered, after which the plants are carefully pulled out together with a lump of earth from the old pots and placed in new ones. The hardening of seedlings should be started half a month before planting in open soil, while the temperature of the content should be reduced gradually, as a result, its result should be equal to 14-15 degrees. Immediately 2 days before disembarkation, the seedlings should be left outside for the whole daylight hours, but if the weather is warm, then it can not be brought in even at night. Tempering allows the seedlings to be more resistant to wind, as well as to improve their adaptation to direct sunlight and colder temperatures. Seedlings that are intended for planting in a greenhouse do not need to be hardened.
Planting eggplants in open ground
What time to plant
Planting eggplant seedlings in open soil should be done only when the ground warms up to at least 18 degrees, while the age of the plants should be 8-10 weeks (from the moment of emergence). The height of the seedlings by this time should be from 16 to 25 centimeters, and the plants should also have from 8 to 10 true leaf plates, while sometimes there are several formed buds. It will be very good if, after planting the eggplant in open soil, the threat of return frosts is left behind. As a rule, the first days of June are the best time to plant eggplant in open soil.
For planting eggplant, you should choose a well-lit area, which should be protected from gusts of wind. It is recommended to plant eggplants in the area where cabbage, cucumber, carrots, onions, garlic, zucchini, beans or peas previously grew. For planting, you should not choose an area where pepper, physalis, potatoes, tomatoes, and also eggplants were previously grown.
Suitable soil
Best of all, this vegetable crop grows in sandy loam or loamy soil. It also grows quite normally on heavier soil, but it must be prepared before planting. To do this, humus and peat must be added to it (one bucket per 1 square meter of the plot), and sawdust or coarse river sand are also added to it. It is recommended to prepare the soil in advance in autumn, about 6 months before planting seedlings on the site, while fertilizers should be applied when digging the soil to the depth of a shovel bayonet. Also, if you wish, you can add manure to the soil: in the fall it is used fresh, and in the spring you can only take rotted manure. Experienced gardeners recommend preparing a site for eggplants in autumn, while in spring, after the snow cover has melted, the soil should dry out well. After that, using a rake, it should be thoroughly loosened. If the soil is poor, then at the same time the following fertilizers should be applied to it: 1 tsp is taken per 1 square meter of the plot. urea, 2 tbsp. wood ash and 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate and superphosphate.


Watch this video on YouTube
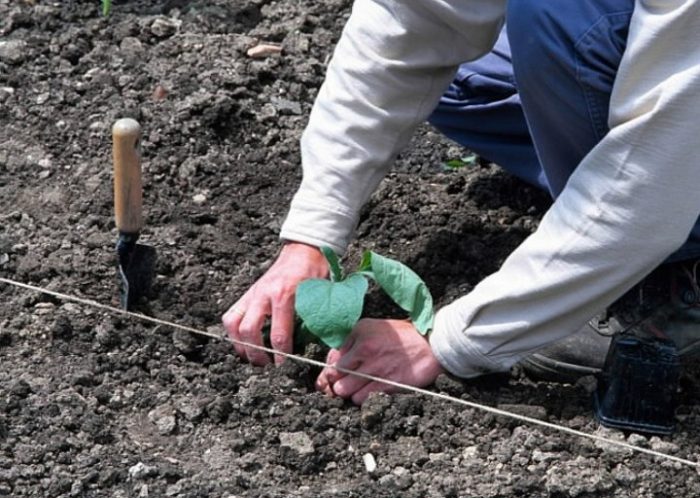
Open ground landing rules
Planting holes must be made on the site. Between them, a distance of 0.3 to 0.4 m must be observed, while their depth should be 20-30 mm higher than the height of the container in which the seedlings are located, while the row spacing should be approximately 0.6 m. After that, the prepared planting the pits should be filled with water. Seedlings are planted in the mud obtained in the pits. Before planting, the eggplants must be well watered, they are pulled out of the pot along with a lump of earth, after which they are planted in open soil. After the plants are planted, the ground around them must be tamped. Then the surface of the site must be mulched with peat or dry soil.
During the first 15 days, the land under the planted bushes should be moist all the time. In order to prevent the soil from drying out too quickly, its surface must be covered with peat.
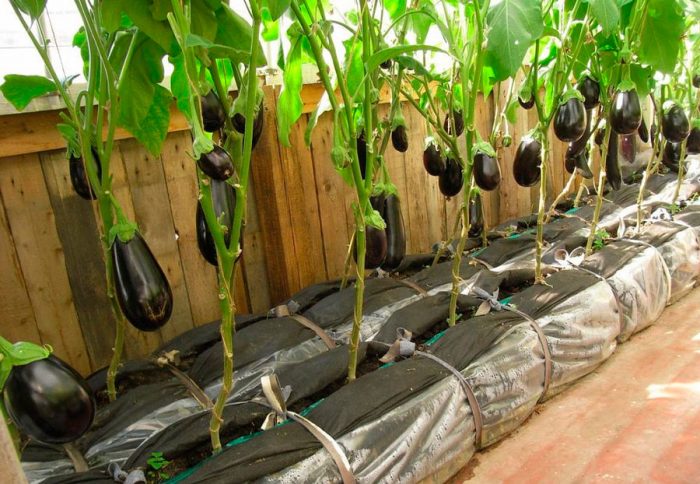
Growing eggplants in a greenhouse
For cultivation in a greenhouse, experts advise choosing hybrid varieties, and the best of them are: Purple Miracle, Nutcracker and Bagheera. Rules for planting eggplant seedlings in a greenhouse:
- Plants should have 8 or 9 true leaf plates.
- The root system of the seedlings must be very well developed.
- The height of the plants must be at least 20 centimeters.
- Planting in a greenhouse should be done after the seedlings reach the age of 65–75 days (from the moment of emergence).
It is very important to properly prepare the beds in the greenhouse. In autumn, the soil is cleaned from plant residues, after which it is disinfected, for this, a solution of copper sulfate is used (for 1 bucket, 2 tbsp. L.). 20 days before planting seedlings in the greenhouse, fertilizers should be applied to the soil, per 1 square meter, 60 grams of superphosphate, 15 grams of magnesium sulfate, 4 kilograms of humus, 30 grams of ammonium nitrate and the same amount of potassium sulfate are taken. Then you need to dig up the soil, after which the surface of the beds is leveled. The depth of the planting holes should slightly exceed the height of the pots in which the seedlings grow, while the distance between the bushes should be 0.45 m, and the row spacing should be about 0.6 m.
The seedlings must be well watered immediately before planting in the greenhouse. The plant must be carefully pulled out of the container along with a lump of earth, after which they are transferred into the planting holes. The void in the holes must be filled with soil, after which it should be tamped. The planted eggplants need to be watered. This culture is quite moisture-loving, in this regard, watering should be given special attention. Please note that the planted plants can be watered a second time no earlier than 5 days after transplanting. The further watering regime is once a week, when the fruiting period begins, the eggplants will need to be watered more often (2 times every 7 days).Watering is done in the early morning and lukewarm water is used for this. When the eggplants are watered, it is imperative to ventilate the greenhouse, since the air humidity in it should not be high. The recommended air temperature for growing eggplant is 28 degrees. It should be noted that the greenhouse should not be hotter than the recommended temperature, therefore, special attention should be paid to ventilation, especially if it is very hot outside. In addition, in hot weather, it is necessary to regularly water the paths in greenhouses. You need to feed the plants a couple of times throughout the season:
- The first time before fruiting begins, half a month after transplanting the seedlings into the greenhouse. For this, mineral and complex fertilizers are used (Kemiru or Solution).
- The second feeding is arranged after the beginning of fruiting. To do this, use phosphorus-nitrogen fertilizers (1 tbsp. Of water is taken in 1 tbsp. L. Superphosphate and ammonium nitrate).
Organic matter should be added to the soil only once, immediately before planting the eggplant. If it is introduced later, then this can provoke an active growth of greenery, as well as lush flowering, but there will be no ovaries on the bushes. It should be noted that in the greenhouse the bushes grow relatively fragile and rather tall, so it is recommended to tie them to supports. Also, experts advise to remove lateral processes from plants, while leaving only 5 of them the most powerful.
Due to improper care when grown in a greenhouse, eggplants can be struck by tobacco mosaic or late blight, diseased bushes need to be sprayed with a solution of Fitosporin or Zircon. For prevention purposes, it is recommended to systematically ventilate the greenhouse, because these diseases develop due to excessively high humidity. In the greenhouse, these plants can be harmed by insects such as whiteflies, aphids and spider mites. To prevent the appearance of pests, it is also necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse.


Watch this video on YouTube
Eggplant care
When growing eggplant in open ground, they should ensure timely watering, removal of weeds, loosening of the soil surface between rows, top dressing, and also bushes of late and mid-season varieties will need shaping.
How to water
These plants are especially in need of watering during mass fruiting. During the first decade after planting seedlings in the soil, abundant watering can cause bushes that have not yet had time to take root, can weaken very much. For irrigation, use lukewarm (25 to 30 degrees) water. It must be poured carefully under the root, while trying to prevent liquid from getting on the surface of the leaf plates of the bushes. When the plants are watered, gently loosen the surface of the soil between the rows, while pulling out all the weeds. Throughout the season, it will be necessary to loosen the surface of the site at least 5 times so that a strong crust does not appear on it. However, if after planting the site is covered with a layer of mulch (peat), then it will be possible to significantly reduce both the number of loosening and weeding.
How to tie eggplants
Greenhouse eggplants are much taller than those grown outdoors, so be sure to tie them up. Bushes are tied up in three places, while using stakes or trellis. As soon as the bushes are planted in the soil, you should start shaping them into one stem, while after a while he will need a garter to the support. The most powerful shoot should remain on the bush, while all other lateral processes must be cut off. If there are only flowers and leaves on the bushes, their resistance is quite good.But after the formation of the ovaries and during the growth of the fruit, there is a manifold increase in the load on the stem, in this regard, their resistance is sharply reduced (especially in tall varieties). The method of growing single-stem bushes is great for greenhouses because it is very compact and can save a lot of space. If this vegetable crop is grown in open ground, then in this case, the formation of bushes into several stems is recommended.
To make the bushes more lush after their height is 0.3 m, it is necessary to pinch the top of the main stem. In an overgrown bush, remove all the upper lateral shoots, except for 2–5 of the strongest, using a pruner. When pruning, keep in mind that the remaining shoots should be evenly lit.
Fertilizer
These plants need to be fed quite often, about 1 time in 15-20 days. The first feeding is carried out 2-3 weeks after transplanting the seedlings into open soil. For top dressing, mineral fertilizers should be used, while 10 grams of superphosphate and ammonium nitrate, as well as from 3 to 5 grams of potassium sulfate, are taken per 1 square meter of the plot. You can replace the listed fertilizers with crystalline, ammophos or nitrophos (per 1 square meter from 20 to 25 grams). During the next top dressing, the fertilizer rate should be increased by 1.5–2 times, but this is done gradually. After feeding is done, do not forget to water the area. Also, this culture can be fed with slurry. This plant also needs foliar feeding; for this, the foliage on the bushes must be sprayed with a solution of boric acid of weak concentration. If the summer turned out to be cool, then it is recommended to spray the eggplant foliage with a solution of trace elements. Remember that the solution prepared for spraying plants on the leaf should be several times weaker than that poured under the root.


Watch this video on YouTube
Diseases and pests of eggplant
Diseases
Most often, eggplants are sick with mosaic, late blight, black leg, stolbur and gray rot.
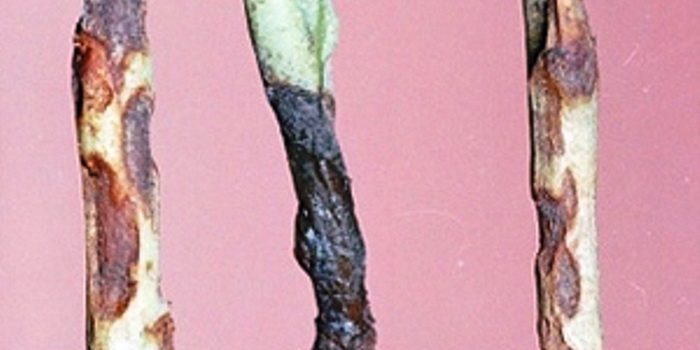
Blackleg
Blackleg is considered a fungal disease. In the affected plant, the root collar turns black and collapses. After the root system is damaged by the disease, the bushes dry up and die. Most often, this disease affects eggplant seedlings, and excessively high humidity of the air and substrate provokes its development.
Mosaic
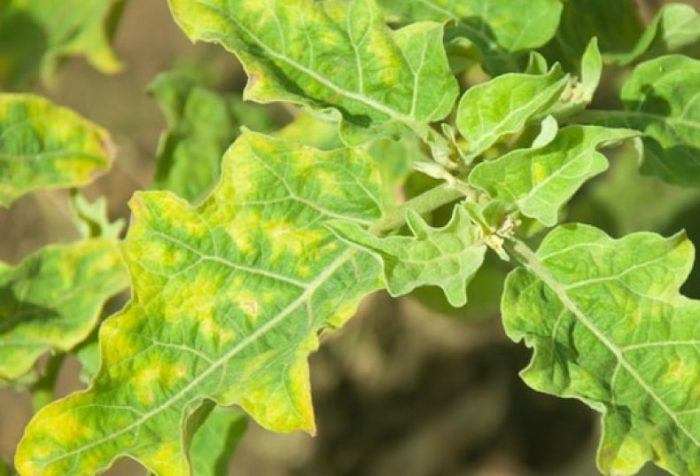
Due to the mosaic, the gardener can lose about 15 percent of the eggplant crop. In an infected bush, an unusual motley color appears on the surface of the leaf plates. As a rule, plants are affected by this virus during a dive.
Pillar
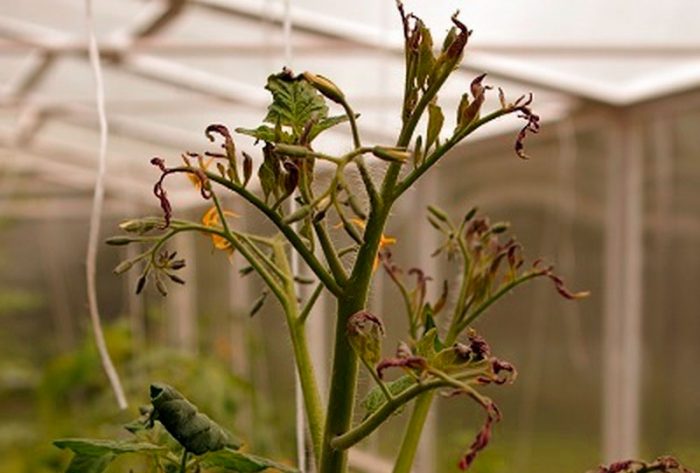
Stolbur phytoplasma disease most often damages those plants that are grown outdoors, while greenhouse plants are less frequently affected by it. In the affected bushes, the leaf plates acquire a purple-red color, while the upper ones become corrugated. The shoots become thicker and more fragile, deformation, drying and foliage are observed. They carry such a disease of leafhoppers.
Gray rot
Gray mold is also a fungal disease, and its spread occurs through infected plant debris. This fungus is especially active at high air humidity, while the temperature should be at least 20 degrees. In affected plants, dark water spots form on the foliage, fruits and shoots, on the surface of which a gray bloom appears after some time. As the disease progresses, inflorescences and also fruits are affected.The flower stalks turn black and dry, and the fruits first form vague, like subcutaneous, spots, which gradually become larger.


Watch this video on YouTube
Pests
The greatest danger to this culture is posed by such harmful insects as: spider mites, aphids and naked slugs. Spider mites and aphids are sucking insects that feed on plant sap. They pierce the surface of shoots and leaf plates, as a result of which they dry, wilt and curl. Slugs damage foliage, leaving only streaks of it, and they also harm the fruit.
Eggplant processing
To cure eggplants or get rid of harmful insects, the bushes need to be processed in a timely manner and correctly. But it is better to prevent infection with the disease than to fight it. For prevention purposes, the rules of crop rotation should be observed; for this, these plants cannot be planted in the area where unwanted predecessors, for example, nightshade, previously grew. Also, eggplants need to be provided with proper care, and you will also need preventive soil treatment on the site and seed material before planting. To disinfect seeds, they are immersed for 30 minutes in a strong solution of potassium manganese or in a weak solution of hydrochloric acid. Soil processing is carried out before planting the eggplant, then when they take root, as well as after all the fruits have been collected and plant residues have been removed from the site. In this case, copper-containing agents are used for soil cultivation, for example, Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. Thanks to these preventive measures, plants will be protected from infection by mosaics or late blight. If the eggplants do get sick, then they will need to be sprayed with a solution of Fitosporin or Zircon. If the bushes are affected by a columnar or a black leg, then they will not be cured, but for prevention purposes, it is recommended to disinfect the substrate and seeds before sowing.
If there are not a very large number of slugs on the bushes, then you can try to collect them by hand. But in the event that there are a lot of pests, then the surface between the rows must be loosened, and then covered with a layer of a mixture consisting of tobacco dust, wood ash and lime. For other pests, it is recommended to spray the bushes before flowering and after it with insecticidal preparations that quickly decompose, for example, Karbofos or Keltan, or, if desired, use the Arrow tool, which is safe for humans.


Watch this video on YouTube
Collection and storage of eggplants
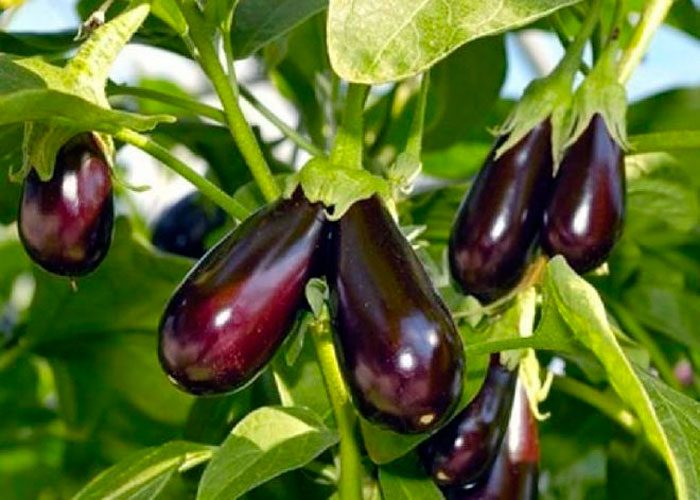
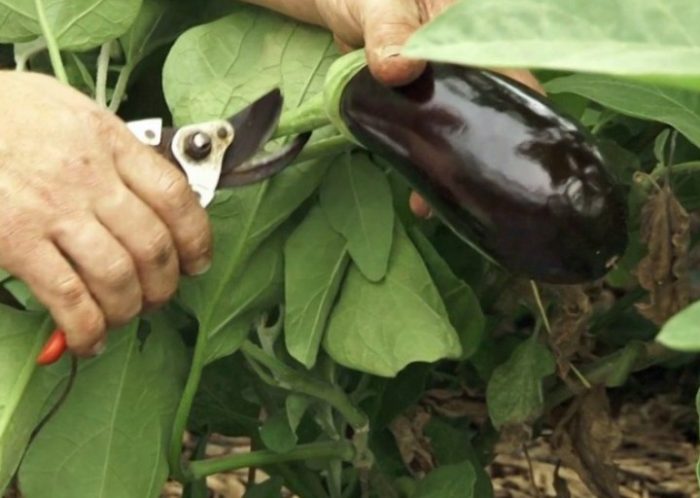
You can start harvesting eggplant fruits 30–40 days after the end of flowering, while they should become shiny. Only semi-ripe fruits are suitable for collection. It should be borne in mind that unripe or overripe fruits are tasteless. There are 2 types of maturity, namely: biological (the fruits are fully ripe, but tasteless) and technical (the fruits are suitable for harvesting and eating). A pruner is used to cut the fruit, while leaving a two-centimeter long stalk.
Eggplants are not suitable for long-term storage, in this regard, they must be used for food, or they can be used to prepare winter salads, as well as caviar, and it is also recommended to pickle or pickle them. Also, if desired, the fruits can be dried by cutting them into circles. Eggplants can be stored in a dark and cool (no more than 2 degrees) place for about 4 weeks. Also, eggplants can be folded in a box in one layer, with each fruit wrapped in a paper sheet. Then the container is transferred to a cool place where the eggplants can keep their freshness for some time.They can also be folded into a polyethylene bag that fits into the ventilation hole or stowed away in a dark and cold place. And the best place to store such fruits is the refrigerator shelf. Remember that they can only be stored in a dark and cold place.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of eggplant
Today there is a classification of eggplant, which divides this culture into 3 subspecies: European, Eastern and Indian.
- Eastern subspecies... Most of the varieties included in this subspecies are early and mid-early. The bushes of such plants are not very tall, spreading or semi-spreading. Thin stems and shoots are purple-green. Small green ovoid leaf plates have purple petioles and veins. Not very large fruits have a serpentine, pear-shaped, spherical, crescent or cylindrical shape, as well as a dark purple color. The flesh of the fruit is white or light green with a little bitterness.
- Western subspecies... It includes late and mid-season varieties. Semi-spreading or closed bushes, they can be of medium height or high. The shoots are thick and green, with purple pigmentation at their tops, which is rather weak. On the surface of large leaf plates, elongated-ovoid, there is pubescence, they have a green color, in some cases there is a brownish tint in the region of the petioles and veins. The shape of relatively large fruits can be different, after they reach technical maturity, their color will change to purple-brown, purple-black, purple or dark purple. The pulp is colored white-green or white-yellow, it differs in varying degrees of bitterness.
- Indian subspecies... It is represented in culture quite widely, however, in the middle latitudes the varieties included in this subspecies are not grown.
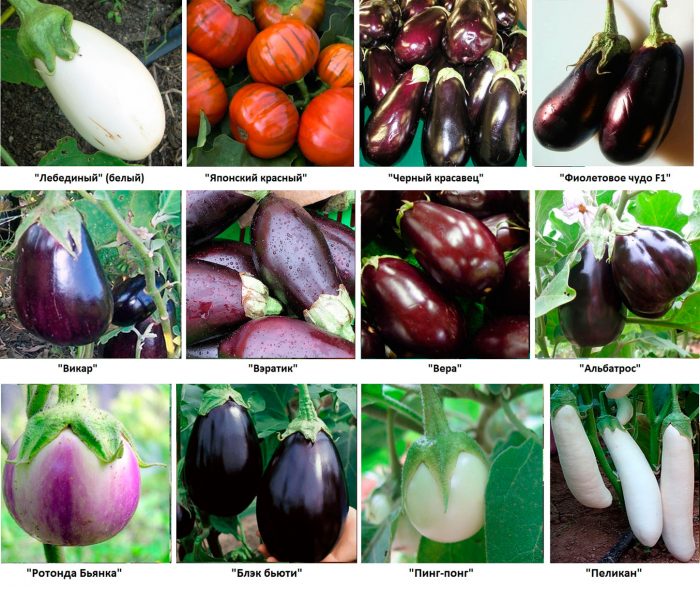
The most popular varieties of the western subspecies that are great for growing in mid-latitudes:
- Valentine... This early maturing variety is distinguished by its yield and resistance to tobacco mosaic. Black and purple fruits have a standard size of 5x26 centimeters. They have an elongated shape and taste great.
- Purple miracle... This hybrid is early, it is distinguished by its yield and resistance to wilting. Purple fruits weigh about 350 grams on average. The pulp has no bitterness and is light green in color.
- Czech early... It is a high-yielding early variety. Low bushes are compact and strong. The shape of the dark purple glossy smooth fruits is ovoid. The white-green flesh has no bitterness.
- Black handsome... This early maturing variety was created by Danish breeders. The height of the bush is about half a meter. The cylindrical fruits are very dark in color and weigh about 240 grams.
- Delicacy... Early grade. The bush reaches a height of 0.4 m. The dark purple fruits have white flesh without bitterness.
- Golden egg... This early hybrid is usually grown as an ornamental plant. The shape of the average size of the fruit is similar to a goose egg.
- Donskoy... This variety is medium-yielding. The bush is of medium height and is medium spreading. The fruit is pear-shaped, weighing about 180 grams.
- Epic... This early variety is high-yielding and unpretentious. The fruits have an unusual teardrop shape of a dark purple color measuring 10x22 centimeters.
- Donetsk fruitful... This early ripe variety has a dark color with fruits reaching 15 centimeters in length and 40 mm in width. They weigh about 160 grams.
- Black Beauty... This early maturing variety has a high yield. The fruits are very large, they weigh about 0.9 kg.
- Maria... The dark purple, not very large fruits have an elongated shape, they weigh about 220 grams.The fruits ripen very quickly, due to which their not very large size is compensated.
- Barbentane... The early variety is distinguished by its yield and a long fruiting period. Fruits are shiny dark purple.
- Nautilus... The fruits of this medium early variety are dark purple and saber-shaped, weighing about 0.5 kg. The variety grows well in a greenhouse.
- Arap... The height of a vigorous bush is about 100 cm. The length of the fruits is about 25 centimeters, they are painted in a very dark shade of brownish-purple.
- Albatross... The variety is mid-season and high-yielding. The height of the bush is about 0.5 m. The pear-shaped fruits of a violet-blue color weigh about 0.45 kg.
- Solara... This early variety is distinguished by its unpretentiousness and productivity. Large fruits of a dark purple color weigh about 1000 grams.


Watch this video on YouTube