A very popular ground crop cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea), also called groundnut, underground limbo peanuts, is a representative of the genus Peanuts of the legume family. Scientifically speaking, peanuts are legumes, not nuts. Peanuts are native to South America, where they were popular even when the mainland was not yet discovered by Columbus. The Spanish conquistadors brought this culture to Europe, and it came to Africa later thanks to the Portuguese, where peanuts became very popular, as they not only have nutritious properties, but also grows well on poor soils. Later, this culture was brought by slave traders to North America. In the thirties of the 16th century, peanuts came to the Philippines along with Spanish sailors, and they were brought to India and Macau by the Portuguese. After that, this plant got to China and became a real salvation from hunger for local residents. The industrial cultivation of this crop in South Carolina began in the early years of the 19th century, when peanuts fed both armies during the war between the South and the North. For many centuries, peanuts have been considered the food of the poor, so farmers did not pay much attention to this plant. However, everything changed in 1903, when George Washington Carver, an American agrochemist, was able to invent more than three hundred products from such a plant, namely: cosmetics, dyes, laundry soap, drinks, medicines, printing ink, a pest control agent, etc. And since in those years the cotton harvests suffered greatly from the weevil, Carver managed to persuade the farmers to alternate the cultivation of peanuts with the cultivation of cotton, which greatly depleted the soil. As a result, this plant became the main cash crop of the southern states, and a monument was even erected to Carver in Dothan, Alabama. Today, in various regions of the former USSR (Transcaucasia, Ukraine, etc.) peanuts are cultivated on an industrial scale.
Content
Peanut features
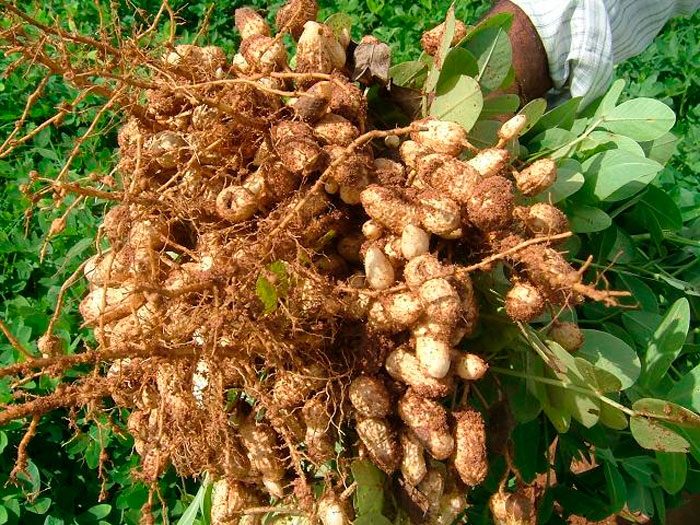
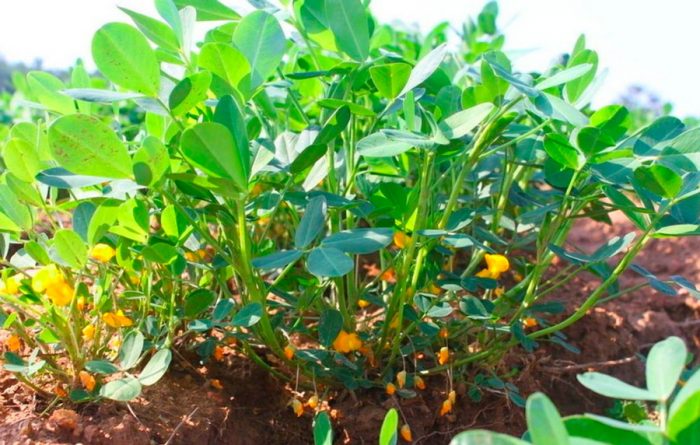
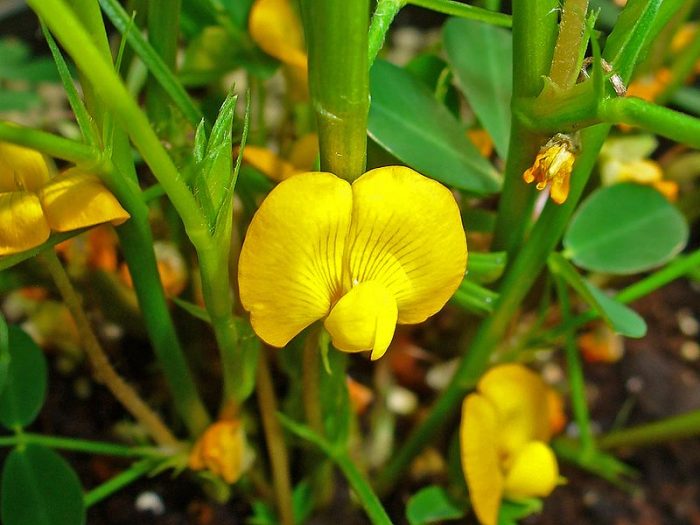
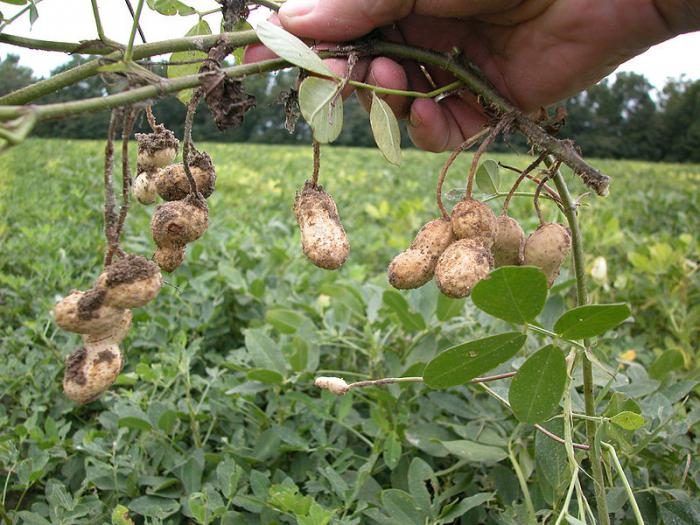
The cultivated peanut is an annual that reaches a height of 0.7 m. Its shoots are strongly branched. The taproot is also branched.The bare or pubescent erect shoots are slightly faceted, the lateral branches are directed upward or recumbent. There is pubescence on the surface of alternate paired-pinnate leaf plates, they reach 3–11 centimeters in length, their petiole is grooved and there are two pairs of pointed elliptical leaflets. Short axillary inflorescences consist of 4-7 flowers, red-yellow or whitish color. The life of each individual flower is only about 24 hours, but the peanut bloom is long, its beginning falls on the last days of June or the first days of July, and it ends in late autumn. The fruits are swollen oval-shaped two to four-seeded beans, they reach 15-60 mm in length, and have a spider-web pattern on their surface. During ripening, the fruits tilt to the surface of the soil, after which they are immersed in it. It is in the ground that they ripen. The seeds of this plant are the size of a bean, they have an oblong shape, and are covered with pinkish, dark red, yellow-gray or cream-colored skin on top. Fruit ripening is observed in September or October.
Planting peanuts outdoors
Peanut growth features
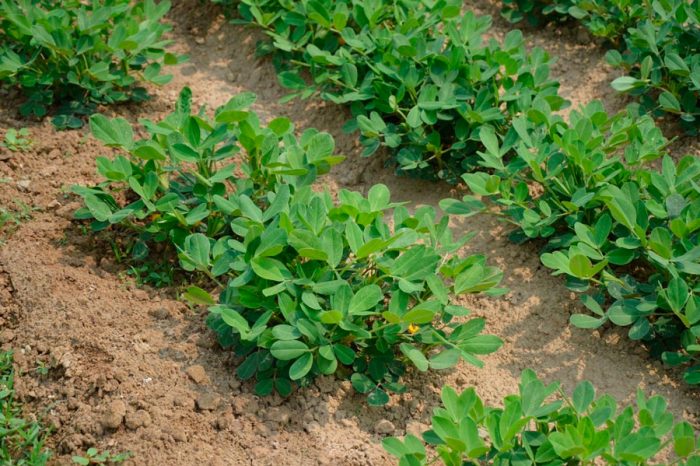
Only open and sunny areas are suitable for growing peanuts, where there is not even a slight shadow from other plants or buildings. The growth of this culture is observed only at temperatures above 20 degrees. If the temperature is less than the recommended one by at least a couple of degrees, then the growth of bushes stops. As a rule, peanuts in the open field are grown in areas with a warm climate, while the seeds are sown in the soil during the period when acacia is blooming. In Russia, especially in regions with a relatively cool climate, it is recommended to use the seedling method for growing peanuts.
What time to plant in open ground
Planting of peanuts should be done in spring in well-heated soil (about 12-14 degrees), while it is done after sowing melons. This time, as a rule, falls in mid-May or later. It should be remembered that return frosts can destroy this culture. Peanuts for planting can be purchased at the market or at the grocery store, however, remember that they should not be candied, roasted or salted.
Crop rotation rules
When cultivating peanuts, how you rotate is important. This crop grows very well after cucumbers, potatoes, cabbage and tomatoes, especially if organic matter was introduced into the soil during their cultivation. And the area where legumes (peas, lentils, beans and beans) were grown is not suitable for sowing, since there is a high probability of root rot development.
Suitable soil
A suitable soil should be light, moist and neutral and should contain relatively high levels of magnesium, humus and calcium. Sandy loam or black soil is best suited. Saline soil is not suitable for peanuts, while acidic soil must be limed before sowing. For sowing this culture, the site must be prepared in advance. To do this, the soil must be dug in the fall to a depth of 0.25 to 0.3 m, adding humus to it (1–3 kilograms per 1 square meter of the plot). In spring, the site is re-digged, but to a shallower depth, while Nitrofoska must be added to the soil (50 grams per 1 square meter of the site).
Landing rules
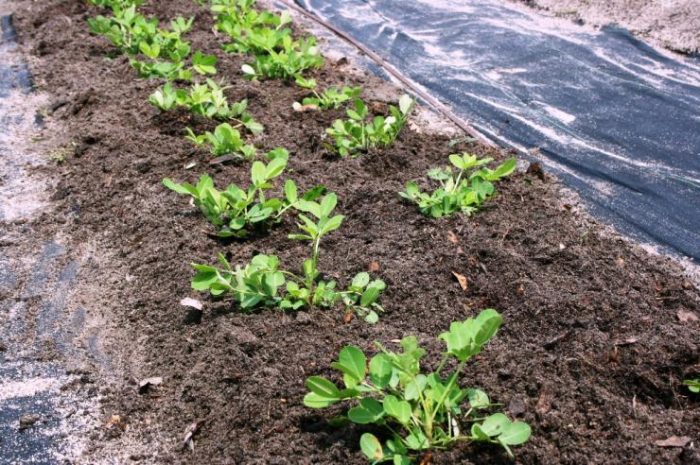
For planting this culture, ten-centimeter deep holes should be prepared, which must be placed in a checkerboard pattern, the distance between them should be half a meter. The row spacing should be 0.25–0.3 m. When sowing peanuts in the garden, the square-nest method is used according to the 0.7x0.7 m or 0.6x0.6 m scheme.It is also possible to sow such a plant with a wide-row method, while leaving a distance of about 0.6-0.7 m between the rows, and between the specimens in a row - from 15 to 20 centimeters.
It is necessary to place 3 large seeds in one hole, since small seeds very often do not germinate. When the seeds are planted, the crops must be watered very well, using a hose with a shower head for this, so as not to wash the seeds, the pressure should be made rather weak.
Growing peanuts in the garden
Caring for peanuts is easy enough. In a dry period, it must be watered in a timely manner, and the site must be weeded and loosened in time, and do not forget about top dressing. Particular attention should be paid to weeding at a time when the seedlings are still very young and short. During the removal of grass, you can also loosen the soil, and vice versa. Flowering should end 6–8 weeks after sowing. At this time, the ovaries will begin to grow and bend to the surface of the site, after which they will germinate into the ground, where the fruit ripens. After the ovaries begin to bend to the ground, the bushes should be earthed with loose and moist soil (like potatoes), in this case the receptacle will reach the nutrient medium much faster. Hilling can be replaced by mulching the surface of the site with sawdust, peat, humus or sand, while the layer thickness should not be less than 50 mm. On average, 30-50 fruits are formed under each plant, and each of them contains 1-7 seeds.
How to water
This culture needs a moist soil, but at the same time it should not be too wet. Watering should be done after the topsoil dries out. When the bushes begin to bloom, they will need abundant watering, which is arranged 1-2 times in 7 days in the morning. When the bushes have bloomed, it will be of paramount importance not to water, but to moisten the plants from a spray bottle, which is done in the evening 1 time in 1-2 days. If rainy weather is observed during the ripening of the fruits, then the surface of the site must be covered with plastic wrap. And during a prolonged dry period, sprinkling is recommended for this culture, if it is not possible to arrange it, then watering the bushes should be carried out along the furrows located between the rows. During the season, the plant will need 4 or 5 waterings.
Fertilizer
After the height of the seedlings reaches 10 centimeters, they will need top dressing, for this the following nutrient mixture is used: 45 grams of potassium salt, 20 grams of ammonium nitrate and 70 grams of superphosphate are taken for 1 bucket of water. At the beginning of fruiting, the bushes are recommended to be re-fed, but this top dressing is not required.
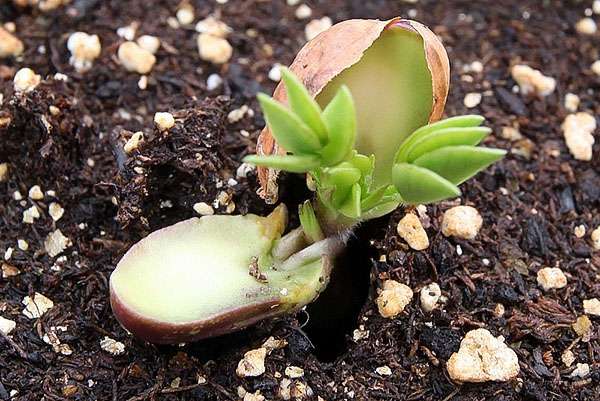
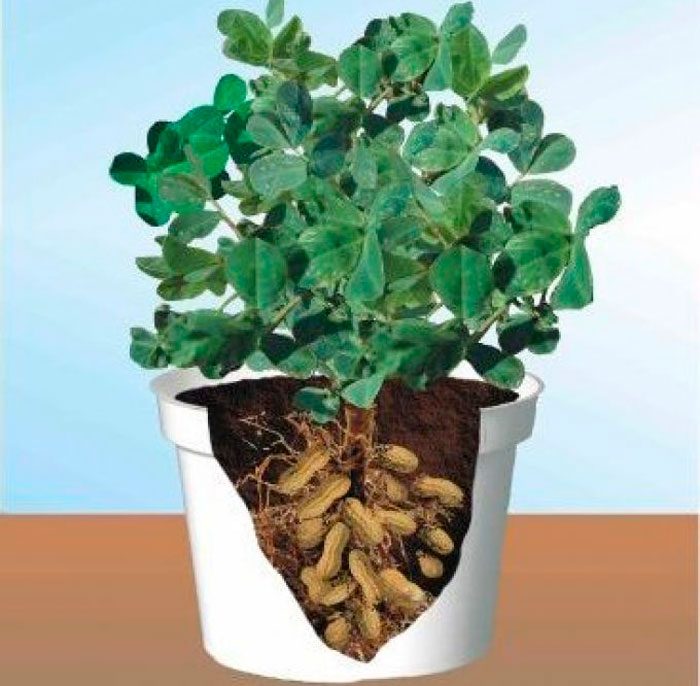
Growing peanuts at home
Select healthy and strong seeds, which should be filled with water overnight, after adding 1 drop of Epin to it. Already in the morning, small white sprouts can be seen on the seeds. Take a wide container and fill it with loose soil, into which the seeds are sown. The seedlings will appear quite quickly, and when the bushes fade, then hypophores will form in place of the flowers, they bend and go into the substrate, in which the fruit develops.
Seedlings should be protected from any drafts; they should be placed on a south-facing window. At noon, the bushes must be shaded. Watering should be systematic, but do not allow the liquid to stagnate in the substrate. On hot days, the bushes must be moistened with a spray bottle, in this case spider mites cannot settle on them. 10–12 weeks after the seedlings appear, the leaf plates begin to change color to red, indicating that the beans in the substrate are fully ripe.
Pests and diseases of peanuts with photo
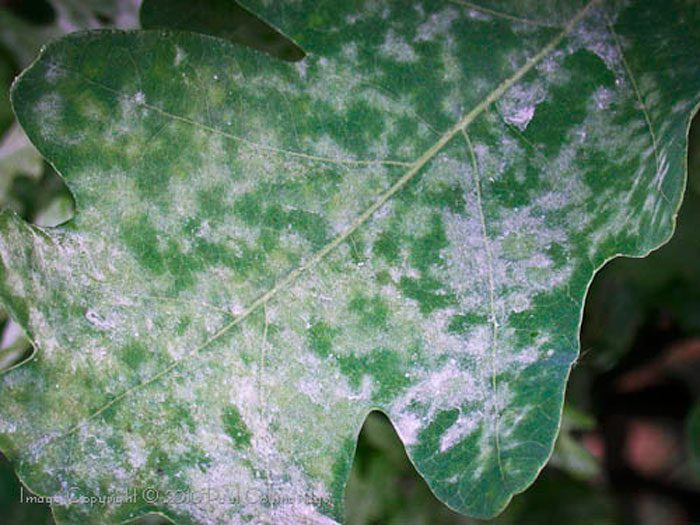
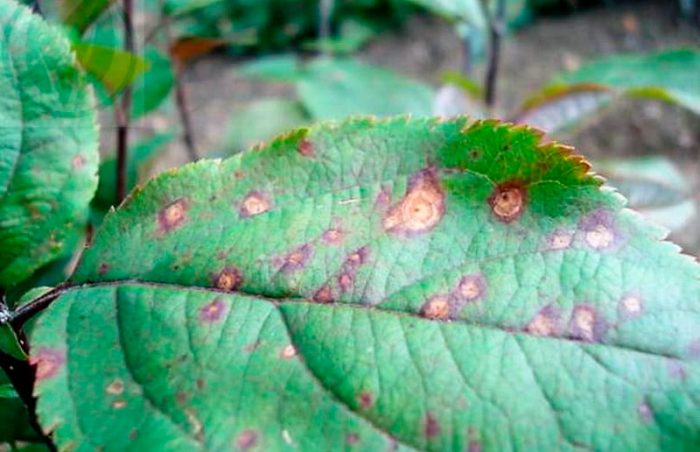
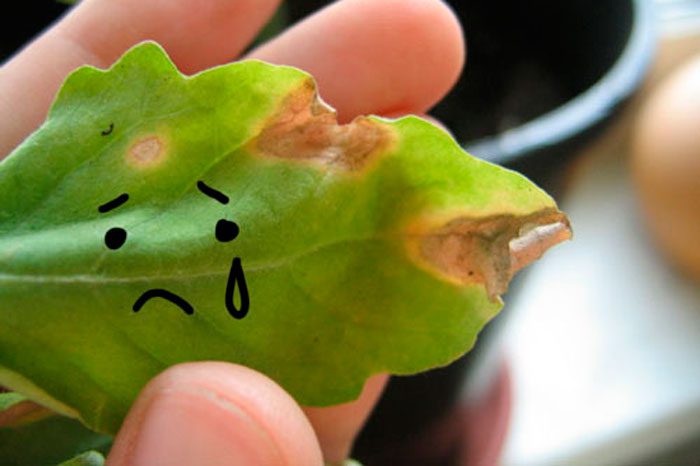
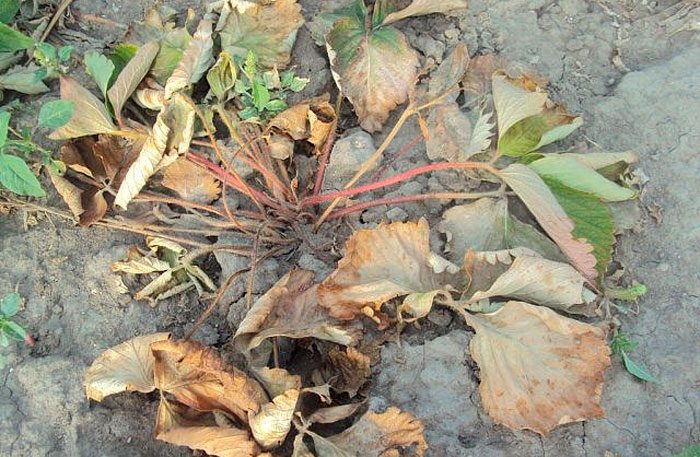
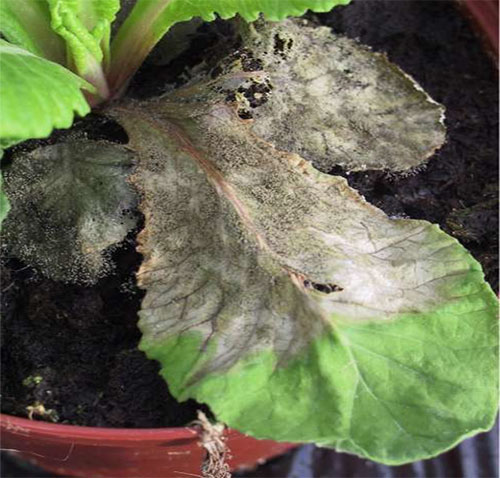
Peanuts can get sick with powdery mildew, phyllostictosis, Alternaria blight, fusarium wilt, and gray mold.
Powdery mildew
At the initial stage of development of powdery mildew, single specks of powdery plaque are formed on both surfaces of the leaf plates. Over time, they become more and more until they completely cover the entire plate, as a result, the leaf turns yellow and dies off. Not only leaves are affected, but also shoots, as well as embryos. If the bushes are very badly affected, then they need to be sprayed with a solution of a fungicidal preparation, for example: Quadris, Switch, Topaz, Bravo, Ridomila, Skor or Horus.
Phylostictosis
Leaf spot (phyllostictosis) is less dangerous than powdery mildew, but peanuts still need to be treated. The affected bush has small specks of brown color, which grow in diameter up to 0.6 cm.Over time, the middle in the spots fades, and the tissue in them dies off, while the border turns purple-brown. This disease develops most actively at high air humidity. It is recommended to fight such a disease by spraying with broad-spectrum fungicidal agents.
Alternaria
Black spot of foliage (Alternaria) develops in those years when at the end of the growing season there is prolonged warm and humid weather. In the affected bushes, specks of black color appear at the edges of the leaf plates, reaching about 15 centimeters in diameter. Over time, small spots become larger and merge with each other, due to which the edges of the leaf plates die off. On the surface of the specks there is a dense bloom of a black fungus. For prevention purposes, you need to follow the rules of agricultural technology of this crop, thanks to this, the bushes become more resistant to pathogenic bacteria.
Fusarium wilting
If a bush is affected by fusarium wilting, then root rot appears. The plant itself stops growing and developing, its aerial parts turn yellow and die off quickly enough. This disease is dangerous because it subsides for a while, however, during flowering and laying of beans, its more rapid development is observed, as a result, the bush dies even before the harvest is harvested. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to observe the rules of agricultural technology of this crop, and also to harvest on time.
Gray rot
The development of gray rot, as a rule, is observed at the end of flowering bushes. Infected plants have specks of rusty-brown color, from the leaf plates along the petioles they pass to the shoots. Because of this, the upper part of the stems wilt and die off. Bean formation is not observed on the affected bushes. And if the fruits have already formed, then their deformation occurs. The disease develops very quickly in the last weeks of the summer period, if the weather is warm and humid. To prevent the development of gray rot, it is necessary to grow such a crop on a high agricultural background.
Less often, peanuts get sick with dry rot, cercospora, dwarfism or ramularia.
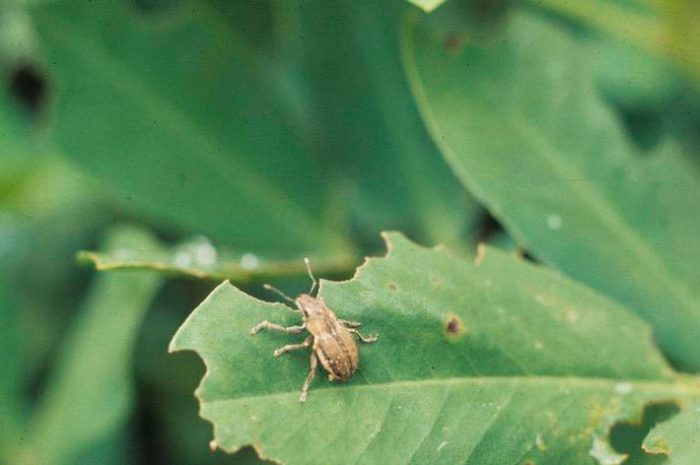
Pests
Aphids, thrips or caterpillars can settle on this culture. To get rid of such pests, the surface of the site must be covered with a layer of tobacco dust or wood ash. To get rid of thrips, the bushes must be sprayed with insectoacaricide.
It is much more difficult to get rid of the wireworm (the larva of the click beetle) that lives in the soil. Despite the fact that the fruits are covered with a shell, such pests easily gnaw the passages in it and eat away the seeds. You can get rid of such a pest using traps. To do this, in several places on the site it is necessary to dig holes, in which pieces of carrots, beets or potatoes should be put. The holes on top must be covered with a piece of slate, board or metal.After some time, the trap should be opened and the pieces of vegetables, along with the pests in them, should be destroyed. For the purpose of prevention, it is imperative to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of this crop, observe crop rotation, and also weed in a timely manner.
Collection and storage conditions
After the leaf plates of the peanuts turn yellow, 2 fruits must be removed from the ground. If the seeds can be very easily hulled out of them, then this means that it is time to start harvesting. As a rule, cleaning is carried out at a time when the air temperature outside is kept within 10 degrees. However, it is not worth delaying the collection of fruits, since if the soil is frozen, the seeds will become bitter and cannot be eaten. Harvest the fruits on a dry and cloudless day. Use a pitchfork to remove the beans from the soil.
The dug out fruits must be freed from shoots. They are laid out in a shaded area in the fresh air to dry. After their shells dry well, the fruits are poured into cloth bags, which are stored in a cool (about 10 degrees), dry room with good ventilation.
Types and varieties of peanuts
The legume family includes about 70 types of peanuts. In South America, several species of this plant are cultivated, and outside of this continent only 2 types of rachis are grown, namely: Pinto peanuts and cultivated peanuts. There are many cultivated varieties of peanuts, which are conventionally divided into 4 groups:
- Spanish group (Spanish varieties)... These small peanuts are grown in the Southwest and Southeast United States, as well as South Africa. Compared to other varieties, this one contains more oil. In such a plant, small kernels are covered with a brown-pink shell. Typically, these fruits are used for the manufacture of peanut butter, salted and candied nuts. Oklahoma and Texas are considered the largest suppliers of this variety of peanuts. The best varieties of this group are: Dixie Spanish, Spantex, Argentinian, Spanet, Natal ordinary, Star, Comet, Spanhoma, Florispan, Spankromm, Tamspan 90, O'Lin, Spanko, Wilco, Beloe Yadro, Shafers Spanish, etc.
- Valencia Group... Most varieties of this group have large kernels. The height of a vigorous bush is about 1.25 m, smooth fruits are three-seeded. The oval-shaped seeds are covered with a rich red shell, which is why they are often called redskin (redskins). This group is considered a Spanish subgroup.
- Runner Group... The varieties included in this group have higher yields, taste better than Spanish varieties, and are much better roasted. The oblong-shaped fruits are large in size. They are used to make peanut butter and salted peanuts for beer. The best varieties in this group are: Dixie Runner, Early Runner, Virginia Bunch 67, Bradford Runner, Egyptian Giant, North Carolina Runner 56-15, Georgia Green, Fragrant Runner 458, Southeast Runner 56-15, etc.
- Virginia group... In these varieties of peanuts, the fruits are large and selective, they are fried in the shell and used for the preparation of confectionery. Top varieties: Shulamit, Hull, Wilson, Gregory, Virginia 98R, Perry, Virginia 92R, North Carolina 7, North Carolina 9, etc.
Peanut properties: harm and benefit
Useful properties of peanuts
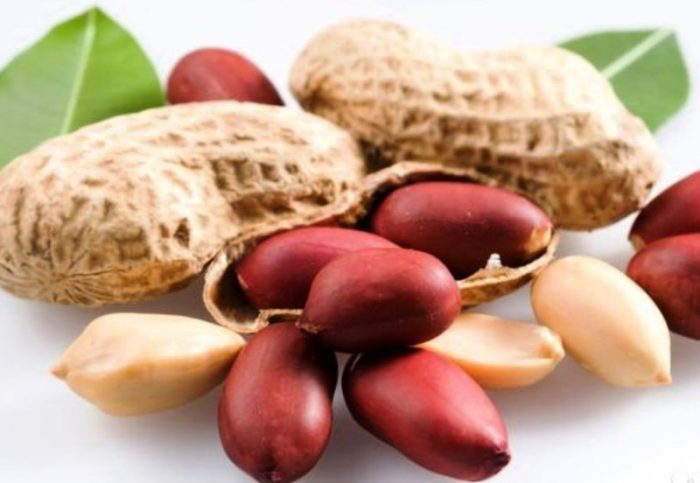
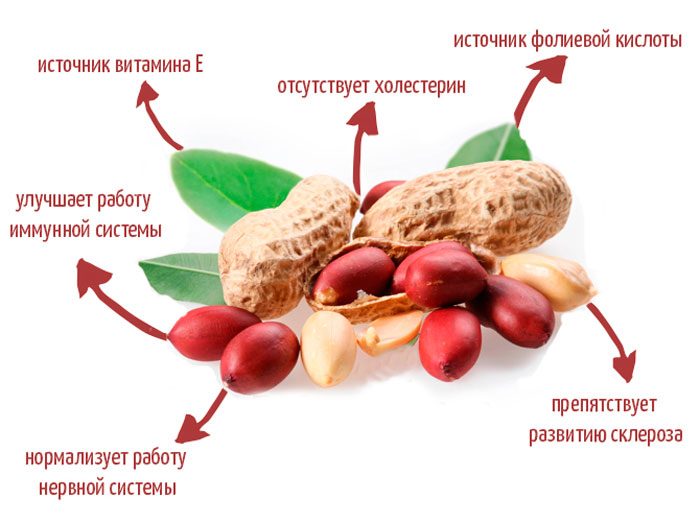
Peanut fruits contain linoleic, pantothenic and folic acids, vegetable fats, glutenins, easily digestible proteins, starch, sugars, vitamins A, E, D, PP, B1 and B2, iron, macronutrients magnesium, phosphorus and potassium. Beans contain antioxidants that are considered to be the most effective preventative agents for cardiovascular disease. These antioxidants are also found in pomegranate, red wine, strawberries and blackberries.An optimal ratio of amino acids is observed in the proteins of this plant, due to which they are perfectly absorbed by the human body.
The fats that make up the fruits have a slight choleretic effect, therefore they are recommended for stomach ulcers and gastritis. Folic acid is involved in cell renewal in the human body. And antioxidants, of which there are a lot of peanuts, help protect cells from free radicals, and are also an excellent prevention of heart disease, atherosclerosis, vascular ischemia, premature aging and the formation of cancer cells.
The fruits of such a plant have a sedative effect on a person with increased excitability, assist in the rapid recovery of strength, help improve memory, increase potency, increase sexual desire and eliminate insomnia. Since peanuts contain a large amount of protein, it contributes to an increase in the feeling of fullness, in this regard, nutritionists often use it as the basis of diets aimed at weight loss. It is also known that there is no cholesterol in such fruits.
Contraindications
If peanuts are eaten in excessive amounts, then they can harm even a relatively healthy person. In this regard, in its use, it is necessary to know the measure, especially for people suffering from excess weight. If a person is prone to allergies, then peanuts can greatly harm him, especially if the kernels are eaten together with the skin, which contains strong allergens. They should not be eaten with arthrosis and arthritis. You also need to remember that eating rancid or moldy fruits can cause poisoning.