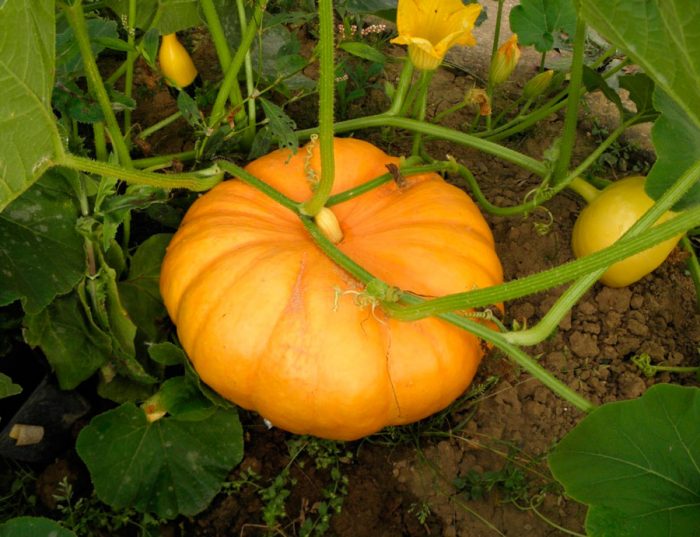
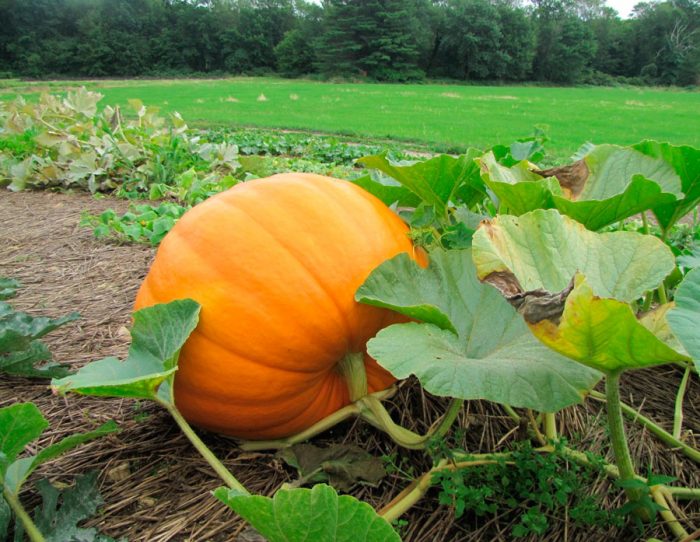
The herbaceous annual pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo) is a member of the genus Pumpkin of the Pumpkin family. This plant is considered a melon crop, it comes from Mexico. Pumpkin has been growing in the Oaxaca Valley for at least 8 thousand years. Already before the advent of our era, such a plant spread in North America in the valleys of the Mississippi and Missouri rivers. Such a culture was brought to Europe by sailors from Spain in the 16th century, since that time it has been widely cultivated both in Asia and in the Old World. India, China and Russia hold the record for growing this crop.
Such a delicious vegetable is very useful, its pulp contains a large amount of useful substances necessary for the human body, and it also contains the rarest vitamin T. The vegetable also contains pumpkin seeds, which include oil that has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, as well as it does not cause allergic reactions.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Landing... Sowing seeds in open soil is carried out after it warms up to 12-13 degrees, they should be buried in the ground by 70-80 mm. Sowing pumpkins for seedlings is carried out in April or the first days of May, and the plants are transplanted into open soil in the last days of May or the first days of June.
- Priming... Anyone is suitable, but pumpkin grows better on nutritious soil, which should be dug up in advance and all the necessary mineral fertilizers and organic matter should be added to it.
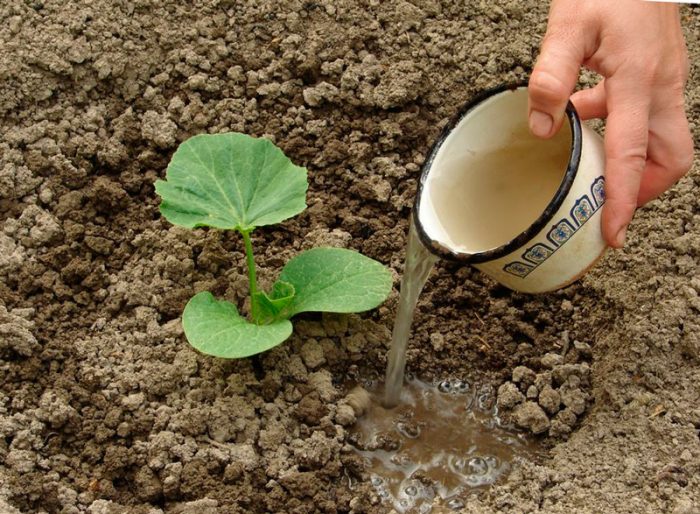
- Watering... When the seedlings are planted in the ground, they should be watered once a day before they take root. Then watering should be not very frequent until the size of the ovaries is equal to the fist. If in the summer it rains regularly, then the pumpkin can be left without watering at all. After the fruits begin to gain weight, it is necessary to gradually increase the abundance of watering to 10 liters per 1 adult bush.
- Fertilizer... 7 days after planting the seedlings in open soil, they are fed with a solution of mullein or chicken droppings.After that, once every 4 weeks, the bushes are fed with organic matter, while there should be 3 or 4 such dressings.
- Reproduction... Generative (seed) seedless method or through seedlings.
- Harmful insects... Melon aphids, podura (or white springtails), wireworms, slugs.
- Diseases... White rot, anthracnose, ascochitis, powdery mildew and black mold.
Pumpkin features
The stem-branching root of the pumpkin is creeping and pentahedral. On the surface of rough shoots there is a prickly pubescence, their length varies from 5 to 8 m. Alternate long-petiolate leaf plates have a heart-shaped five-lobed or five-part form, their length is about 25 centimeters, and on their surface there is pubescence, represented by short hard hairs. Each leaf sinus contains a spiral tendril. Large single-sex single flowers are orange or yellow in color. Female flowers have short pedicels, while male flowers have long ones. Flowering begins in June or July, cross-pollination of flowers. The large fleshy fruit is a false pumpkin berry that has a spherical or oval shape, inside there are many seeds that ripen in the last summer or first autumn weeks. The whitish-cream seeds are 10–30 mm long, with a protruding rim along the edge, the outer shell is woody.
Growing pumpkin from seeds
Sowing seeds
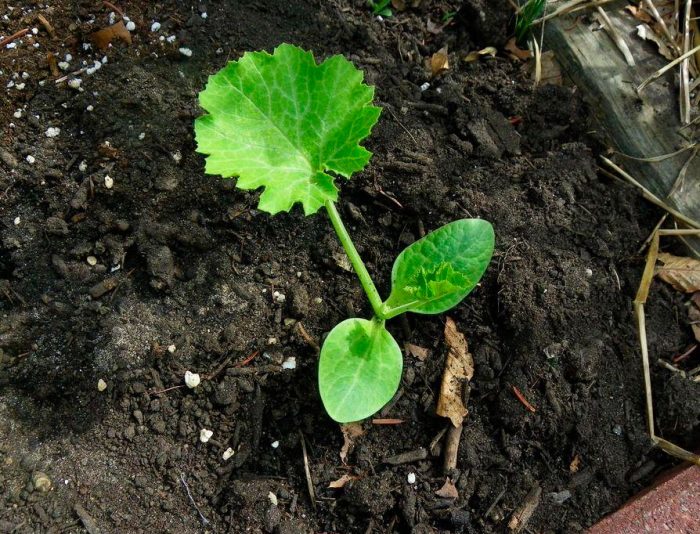
You can grow pumpkin from seeds through seedlings, and they can also be sown directly into open ground. But it should be borne in mind that such a variety as nutmeg pumpkin can only be grown through seedlings. Sowing in open soil is carried out only after it warms up at a depth of 70–80 mm to a temperature of 12 to 13 degrees. Before proceeding with sowing, the seeds and the site must be thoroughly pre-sowed preparation. To begin with, the seed is heated, for this it is placed in heat for 9-10 hours (about 40 degrees), after which it is placed in an ash solution for 12 hours (for 1 liter of freshly boiled water, 2 tablespoons of wood ash), thanks to this, the embryo will pass through a fairly thick and strong peel much faster. Then it should be warmed up in the oven, after which it is wrapped in several layers of gauze, which must be well moistened in a solution of wood ash. If pre-sowing treatment is not carried out, then the pumpkin will ripen later. If the summer in the region is short and cool, then if we neglect the pre-sowing treatment of seeds, then the pumpkin simply will not have time to finally ripen before the onset of frost.
Before you start planting the pumpkin, you need to outline the rows in a pre-prepared area, after which you need to make planting holes, which should reach 0.3 m in diameter.If there was very little snow in the winter, then the soil on the site may be too dry. In this case, 1.5–2 liters of lukewarm water (about 50 degrees) should be poured into each hole. After the liquid is completely absorbed into the ground, 2-3 seeds must be sown in each hole, while they are buried in medium loamy soil by 50-60 mm, and in the light soil by 80-100 mm. From above, the seeds need to be covered with nutritious soil, and then the bed is mulched, for this they use humus or peat crumb. The row spacing should be approximately 200 cm, while the distance between the holes in the row should be at least 100 cm. It is recommended to arrange the planting holes on the site in a checkerboard pattern. In order for the seedlings to appear as soon as possible, the site should be covered with a film, in order to fix it, soil is poured onto the edges.
If everything is done correctly, then the first seedlings should appear after 7 days, after which you need to remove the shelter.When the plants have two true leaf plates, they will need to be thinned out, while no more than two seedlings should remain in one hole. Excess plants should not be pulled out, instead they are cut off at the level of the ground surface, this will avoid injury to the root system of the remaining seedlings. If the return spring frosts have not yet been left behind, then a wire frame should be installed on the garden bed, onto which the film is pulled.
Growing pumpkin seedlings
Sowing seeds for seedlings should be carried out 2-3 weeks before transplanting the plants into open soil. After the pre-sowing preparation, the seeds that have emerged must be sown one at a time in peat or plastic pots, which should be 10 to 15 centimeters across. Half of them must be filled with a substrate, which consists of sod land, humus and peat (1: 2: 1). Seeds from above should be covered with the same substrate, but it should be mixed with 10-15 grams of wood ash and mullein solution (5%). The substrate must be moistened, then the container must be covered with a film on top.
Often, when growing seedlings in room conditions, it is strongly stretched. How to prevent this? Crops must be placed in a well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight, while the air temperature can vary from 20 to 25 degrees. After the seedlings appear, the pumpkin will need the following temperature regime: in the daytime - from 15 to 20 degrees, and at night - from 12 to 13 degrees. Elongated seedlings after 7-10 days are subjected to the following procedure: the plant's hypocotal section must be rolled up in a ring, after which it is covered with moistened soil along the cotyledonous leaf plates. Watering should be moderate, while water should not stagnate in the soil mixture. During the cultivation of seedlings, the pumpkin needs to be fed 2 times using a complex mineral fertilizer. The nutrient solution contains 1 bucket of water, 17 grams of ammonium sulfate, 20 grams of superphosphate, 1 liter of mullein and 15 grams of potassium sulfate. 500 ml of solution is taken to feed one plant. Before transplanting the bushes into open soil, they will need to be hardened. To do this, they are transferred to the balcony or veranda, at first you need to open the window for 1-2 hours, while the duration of the procedure should be gradually increased. When there are two days left before planting the seedlings, the window will not need to be closed at all.
Picking
It is impossible to dive pumpkin seedlings, since during transplantation, the root system can easily be injured. In this regard, individual cups must be used for sowing seeds.


Watch this video on YouTube
Planting pumpkins in open ground
What time to plant
It is necessary to plant pumpkin seedlings in open soil after warm weather sets in, as a rule, this time falls on the last days of May or the first days of June. Pumpkin is a melon crop, in this regard, it needs a lot of sunlight, so you need to choose a southern site for planting. The bushes grow best at an air temperature of about 25 degrees, but if it is colder than 14 degrees outside, the growth of the pumpkin stops. The best predecessors of this crop are green manures, onions, cabbage, carrots, beets, soybeans, peas, beans, beans, lentils or peanuts. And it is not recommended to grow it in those areas where potatoes, sunflower, cucumber, zucchini, squash, watermelon, melon and pumpkin grew before.
Suitable soil
This crop can be grown on any soil, but sweet and very large, it can only grow on nutritious soil. The preparation of the site for planting should be done in the autumn, for this it should be dug up, while manure or compost must be added to the poor soil (from 3 to 5 kilograms per 1 square meter of the site), and if the soil is acidic or heavy, then it is added lime or wood ash (per 1 square meter of the plot from 200 to 300 grams), and 15 to 20 grams of potash and 25 to 30 grams of phosphorus fertilizer must be applied to any soil.In spring, when the snow cover has melted, so that the soil does not dry out much, it should be harrowed, after which it is loosened a little and all weeds are removed from it. Before sowing seeds or planting seedlings, the soil should be dug to a depth of 12 to 18 centimeters. If, for some reason, the site was not prepared in autumn, the necessary fertilizer should be applied to each hole during planting.
Growing pumpkin in a greenhouse
Only in very rare cases is this crop grown in a greenhouse from start to finish. Most often, only seedlings of such a plant are grown in a greenhouse, and then they are transplanted into open soil. For sowing pumpkin in a greenhouse, peat pots 10x10 centimeters in size should be used, as a result, it will be possible to avoid diving of plants, since they react extremely negatively to this procedure.
Before the seedlings appear, the crops must be kept at a temperature of about 26 degrees, and after that it is reduced for 7 days to 19 degrees, and then it must be returned to the previous temperature regime. When half a month has passed since the emergence of seedlings, they should be fed with mullein solution. Watering is carried out as needed, but it should always be abundant. The soil should always be loose with an average moisture content. Planting of plants in open soil is carried out 1 month after the appearance of seedlings.


Watch this video on YouTube
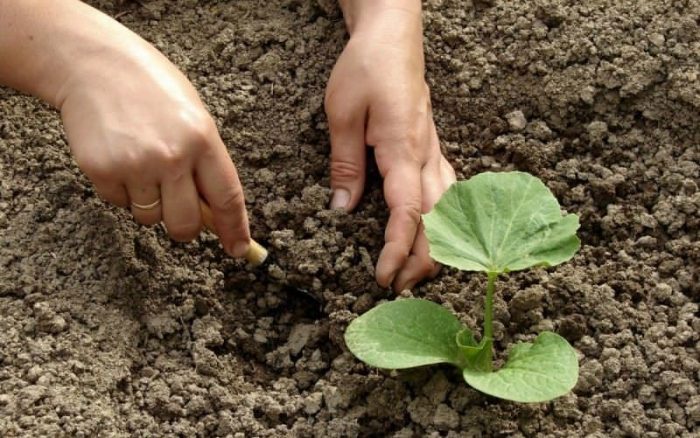
Rules for planting in open soil
How to place pumpkin bushes when planting in open ground is described above, however, in this case, the planting holes should be deeper than when sowing seeds. The holes should be of such a size that they can fully accommodate the root system of the plants at a depth of 80 to 100 mm. If in the autumn during the preparation of the site the soil was not fertilized, then during planting of seedlings in the soil in the spring, 50 grams of superphosphate, ½ a bucket of compost or humus and a couple of glasses of wood ash should be poured into each hole. In this case, the fertilizer should be thoroughly mixed with the soil. When fertilizing the soil, the holes need to be done even more.
Each hole should be shed 1-2 liters of freshly boiled water, after it is completely absorbed, the plant should be poured into it along with an earthen clod, while the voids should be filled with soil, and the earth around the bush should be well compacted. When the pumpkin is planted, the surface of the bed must be covered with a layer of mulch (dry earth or peat), thanks to this, a dense crust will not appear on the soil.
Pumpkin care
When the pumpkin seedlings are planted in the ground, they will need to be watered, weeded, thinned out, fed in a timely manner. And the bushes may need artificial additional pollination, for this you need to pick 2 male flowers no later than 11 am. Remove all the petals on them, while the anthers of both flowers must be carefully held along the stigma of the female flower, and the last of the male flowers must be left on the stigma of the female. This method of additional pollination is used if there is a threat of incomplete fertilization of the ovaries, due to which the formation of irregularly shaped fruits is observed.
How to water
Seedlings that have recently been planted in open soil need systematic watering, which is carried out every day until they take root well. Then watering should become very rare until the size of the ovaries is equal to the fist. If it rains regularly in summer, then you don't need to water the pumpkin.
After the pumpkin begins to gain weight, the bushes begin to be regularly watered again, while the volume of water must be gradually brought to 10 liters under one adult bush.
Loosening the soil
When the pumpkin is watered or it rains, it is necessary to loosen the soil surface near the bushes, while pulling out all the weeds. The first time it is necessary to loosen the soil to a depth of 60 to 80 mm after the seedlings appear.The surface of the soil between the rows must be loosened to a depth of 12 to 18 centimeters immediately before watering, thanks to which the liquid penetrates faster to the root system. When loosening the surface of the soil, huddle the bushes a little, thanks to this they will become more stable.
Thinning
If the sowing of seeds was carried out directly into open soil, then after the seedlings have formed 2 true leaf plates, they must be thinned out, while in 1 hole when growing a large-fruited pumpkin one plant should remain, and nutmeg or hard bark - 2. Re-thinning must be carried out when forming a third or fourth leaf plate in plants. However, it should be remembered that in no case should you pull out excess plants, otherwise you can easily injure the roots of the remaining seedlings. In this regard, excess plants must be cut off at the level of the surface of the site.
Feeding pumpkin
For the first time, the pumpkin is fed with a solution of manure or chicken manure (1: 4), fertilizers are applied to the soil 7 days after transplanting seedlings into open ground or 20 days after sowing seeds into the ground. The pumpkin should be fed organic 3 or 4 times every 4 weeks.
Such a culture responds well to feeding with a solution of a garden mixture (for 1 bucket of water from 40 to 50 grams), while 1 liter of nutrient solution is taken for 1 bush. It is also recommended to feed the bushes with a solution of wood ash (1 glass for 1 bucket of water). Before feeding the pumpkin for the first time, a furrow with a depth of 60 to 80 mm should be made around the bush at a distance of 10 to 12 centimeters. The nutrient solution is then poured into this groove. With subsequent top dressing, the depth of the grooves should be from 10 to 12 centimeters, while about 40 centimeters should be retreated from the bush. After the nutrient mixture has been introduced into the furrows, they should be covered with soil. If cloudy weather is established for a long time, the bushes must be treated with a urea solution (10 grams for 1 bucket of water).


Watch this video on YouTube
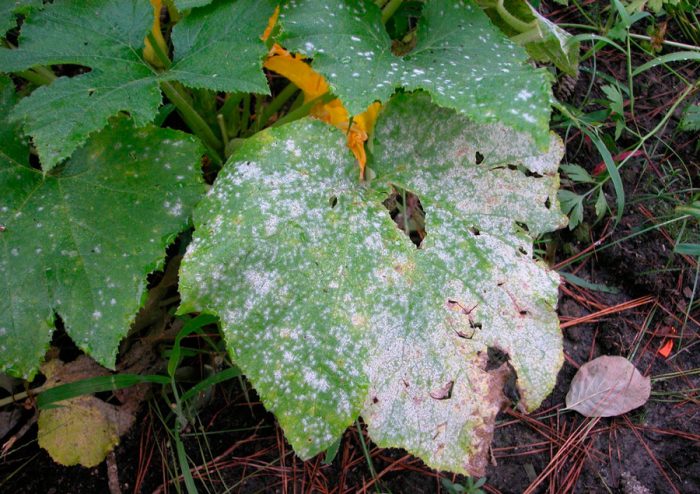
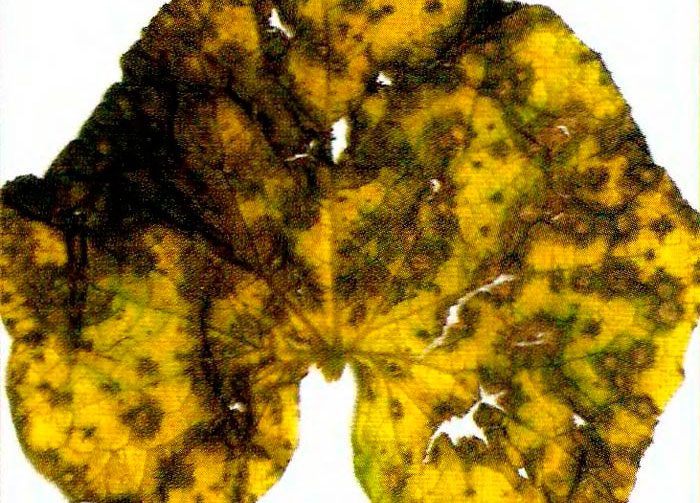
Pumpkin pests or diseases with photos and names
Diseases
Pumpkin can be affected by fungal diseases such as black mold, powdery mildew, rot, ascochitosis and anthracnose.
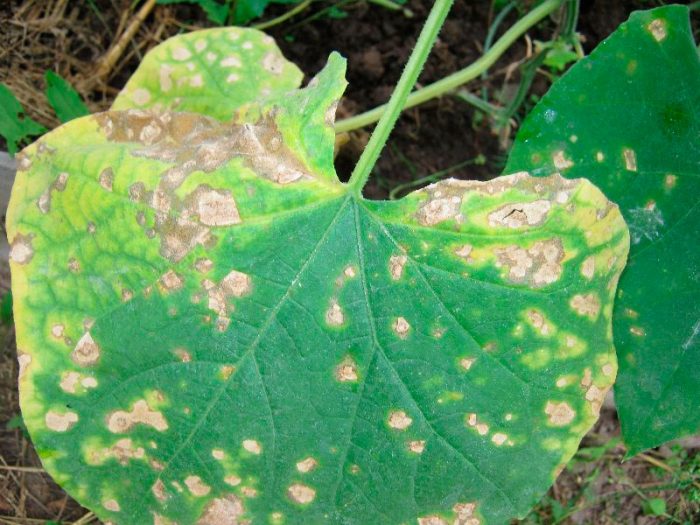
Black mold
If the bush is affected by black mold, then brownish-yellow spots form between the veins of the leaf plates; as the disease develops, a dark bloom appears on their surface, which contains fungal spores. When the spots dry up, holes form in their place. Young fruits become shriveled, and their development stops.
Ascochitosis
If the bushes are sick with ascochitis, then on the shoots, foliage and in the nodes of the stems, at first, large brownish-yellow specks form, and then light specks with chlorotic bordering are formed, and black pycnidia appear on their surface, which contain the bodies of the pathogenic fungus. The bush dries up and dies.
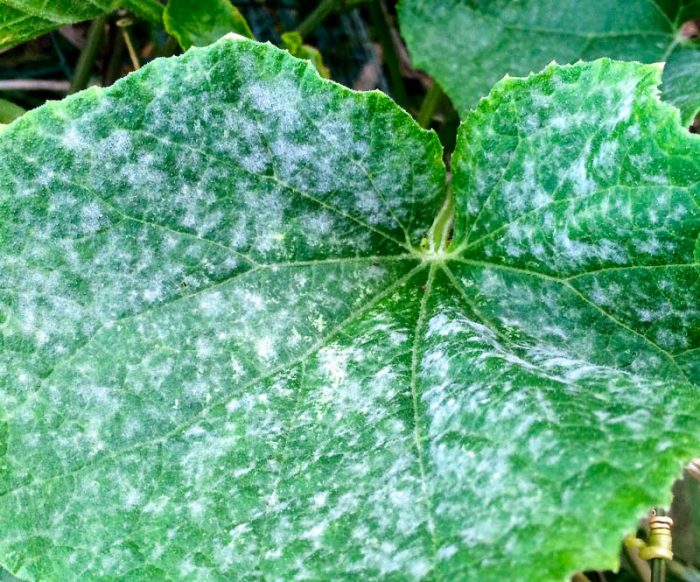
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fairly common disease. On diseased plants, a thick whitish bloom is formed, which is outwardly similar to spilled flour, while it contains fungal spores. The affected leaf plates dry out, and deformation and cessation of the development of pumpkins are also observed. The disease develops most rapidly in conditions of a sharp change in temperature and humidity.
Anthracnose
If the pumpkin is affected by anthracnose, then large watery specks of a pale yellow color are formed on the leaf plates. In too humid weather, a pink coating forms on the surface of the veins of the leaf plates. As the disease progresses, pink spots appear on the petioles, foliage, pumpkins and shoots, while the affected areas turn black by autumn. At high humidity, anthracnose develops faster.
White rot
The development of white rot is observed on all parts of the bushes, while the root system is affected, fruiting shoots dry out and yield decreases. A flocculent mold appears on the surface of a yellowed and brown pumpkin. Mucus may form on the surface of the shoots.
When the bushes are affected by gray rot, blurry specks of brown color are formed on its surface, which quickly merge with each other and affect the entire bush.
The development of wet bacterial rot is most often due to damage to ovaries or slugs by puffs or slugs or young pumpkins in overly dense plantings.
Pests
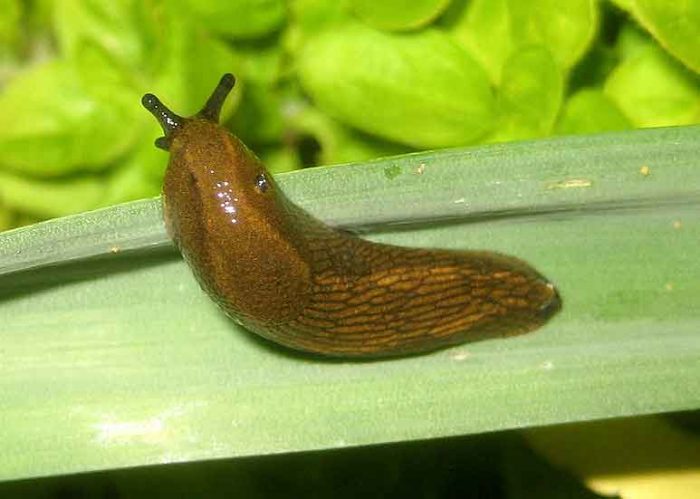
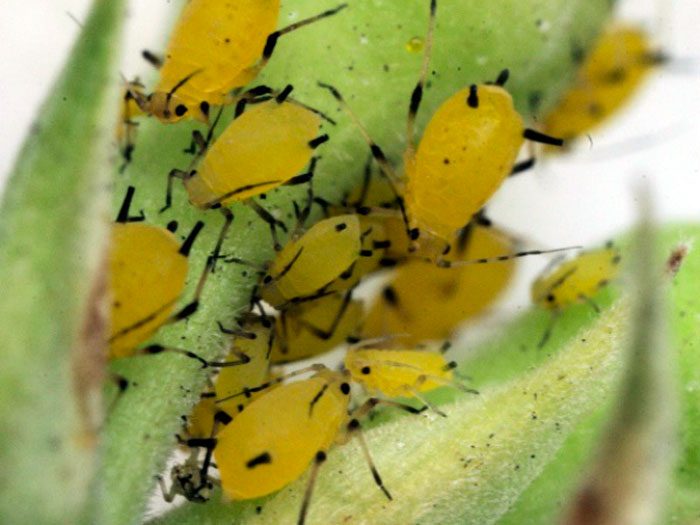
A gourd aphid, podura, or white springtails, wireworms and slugs can settle on a pumpkin.
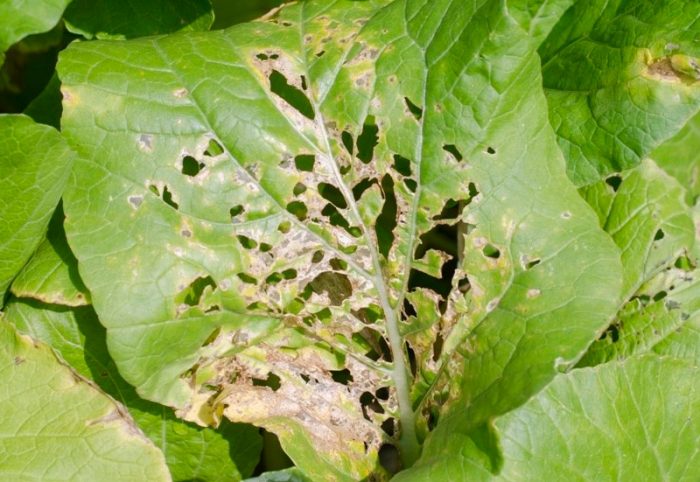
Slugs
The slugs gnaw at the foliage, leaving only a net of veins from it. With prolonged rainy weather, there are a lot of such pests. In addition, they can live and damage various crops for several years.
Melon aphid
The melon aphid is capable of injuring flowers, stems, the seamy surface of the leaf plates and the ovary. The foliage becomes wrinkled and curled.
Puffs
Podura are very small white insects, with a cylindrical body length of about 0.2 cm, they feed on underground parts of the bush, and also on seeds. Such a pest is most active in cool weather with high humidity.
Wireworms
Wireworms are click beetle larvae that damage the root collar of young bushes, which leads to their death. Such pests prefer to accumulate in wet lowlands.
Treatment
The pumpkin should be treated when there are symptoms of disease or when pests appear. It is also recommended to regularly carry out preventive treatments, since it is much easier to prevent the disease from affecting the bushes than to cure diseased bushes.
In order to prevent the defeat of pumpkin by fungal diseases, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of crop rotation and agrotechnical ones, and you should not neglect the pre-sowing treatment of the seed. If the first symptoms of the disease are noticed, then the bushes and the garden should be treated with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%) or another fungicidal preparation. Also, in spring and autumn, the site must be sprayed with Fitosporin, which is able to protect the bushes from a large number of diseases.
To get rid of slugs, you will need to collect them manually or you will need to make special traps. In several places on the site, bowls must be placed, which should be filled with beer, then they are systematically checked and crawling pests are collected.
In order to clear the area of wireworms, you will also need to make several traps. To do this, you need to dig holes half a meter deep, into which root crops (beets or carrots) cut into pieces are placed; on top, the hole must be covered with wooden shields, boards or roofing material. It is necessary to regularly check the traps, while the pests there are destroyed.
To get rid of sublevels, the surface of the soil near the bushes is powdered with wood ash. And to destroy aphids, you can use Carbofos or Phosphamide, and you can also use a soap solution (0.3 kg of soap for 1 bucket of water). You also need to remember that weakened and unkempt bushes are most susceptible to pests and diseases.
Collection and storage of pumpkin
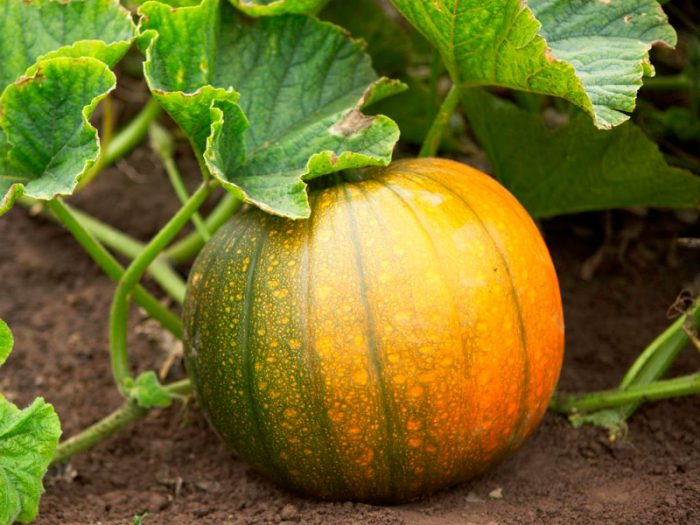
Harvesting the pumpkin is done after the pumpkin has reached biological maturity, however, before harvesting the fruit, you need to make sure that they are really fully ripe. You can understand that the pumpkin is ripe by several signs: the stalks of hard-bore varieties dry out and their corking is observed, while a clear pattern appears on the hardened bark of the nutmeg and large-fruited pumpkin.
Collecting pumpkins should be carried out in dry weather after the first frost, after which the foliage of the pumpkin will die. The pumpkins are pruned with a stalk, and then they need to be sorted by size and quality. This must be done very carefully so as not to injure the fruit. Injured or unripe pumpkins will have to be processed, and those that are intended for long-term storage must be thoroughly dried in the sun or in a warm and dry well-ventilated room for 15 days, while the stalks should be grafted and the bark should become very hard. Then the pumpkins are stored.
Until the first frost, the pumpkin can be stored for storage on a loggia, balcony or in a dry shed, while on top they are covered with a layer of rags or straw. After the air temperature drops to 5 degrees, the pumpkins should be moved to a living room, where it should be dry and warm, while the temperature should not be less than 14 degrees, in these conditions it should be stored for half a month. After that, the pumpkin must be removed to a cooler room (about 3–8 degrees), and the air humidity should be from 60 to 70 percent, if everything is done correctly, then they can lie there until spring and even until a new harvest. For storing pumpkins, you can choose an attic, dry shed or basement. If you store pumpkins in a warmer place (15 to 20 degrees), they lose about 20 percent of their weight, and there is a high probability that they will rot. If there are a lot of pumpkins, then for storage it can be placed on a rack, while its surface must be covered with straw. On them, pumpkins should be laid in 1 row, while they should not touch each other. You can also put them in boxes, while sprinkling them with dry moss. The storage must have good ventilation. Pumpkins can also be stored in the garden in dug trenches, the bottom and walls of which should be lined with straw, the layer thickness should be equal to 25 centimeters. With the first frosts, the trench must be covered with soil, while making several holes for ventilation, in severe frosts they must be closed, and during thaws they are opened. If there are not too many fruits, they can be stored in a house or apartment, while choosing a dark place, the seeds will not germinate there, and the pulp will not acquire a bitter taste. The cut pumpkin is stored on the refrigerator shelf.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of pumpkin
There are many varieties of pumpkin that are designed to be grown in open soil, as it is very difficult to grow such a large vegetable in a greenhouse. However, in a region with a cool and short summer period, such a plant can only be grown in a greenhouse. Gardeners grow three varieties of pumpkin.
Common pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo), or hard-barked
This herbaceous annual pumpkin plant is smooth and large, they have a round shape. As a rule, they are yellow in color, but there are varieties in which the fruits are painted in different colors. Fruit ripening is observed in September. The length of pale yellow or white seeds is from 30 to 40 mm, their skin is thick. If the pumpkins are stored correctly, they can last until the next harvest. The most popular varieties are:
- Spaghetti... This variety is early maturing, with the pumpkins ripening in 8 weeks. The boiled pulp of the fruit breaks down into rather long fibers, which outwardly are somewhat similar to pasta. Both cold and hot pulp are delicious.
- Gribovskaya bush 189... This early variety is very popular. The pumpkin grows as a bush, on it, as a rule, a couple of fruits, slightly ribbed at the stalk, ripen, which have a tear-shaped shape, they weigh 6-7 kilograms. Ripe pumpkins have a deep orange color with green fragments.The sweet and juicy pulp is colored deep orange.
- Almond... Medium ripening climbing variety. Round shaped orange pumpkins weigh about 5 kilograms. Juicy crunchy and sweet flesh has an orange-yellow color.
- Acorn... This early maturing variety can be climbing or bush. The pumpkins are not very large, yellow, green or almost black, outwardly in shape they are similar to an acorn. The low-sugar pulp is yellowish or almost white. This variety is also called Zheludev.
- Freckle... Pumpkins of an early bush variety are not very large mesh green in color, they weigh about 3 kilograms. The color of the pulp is yellow or orange, it is not too sweet, the seeds are small.
- Bush orange... The deep orange pumpkins weigh about 5 kilograms, the heart is sweet and soft. The fruits have good keeping quality.
- Altayskaya 47... Such an early ripening early variety for universal use is distinguished by its yield, the fruits ripen in 8 weeks. Hard-bore pumpkins are orange-yellow and weigh 2–5 kilograms. On their surface there are stripes of yellowish or brownish-yellow color. The pulp of the fruit is fibrous. The variety is characterized by cold resistance and excellent keeping quality.
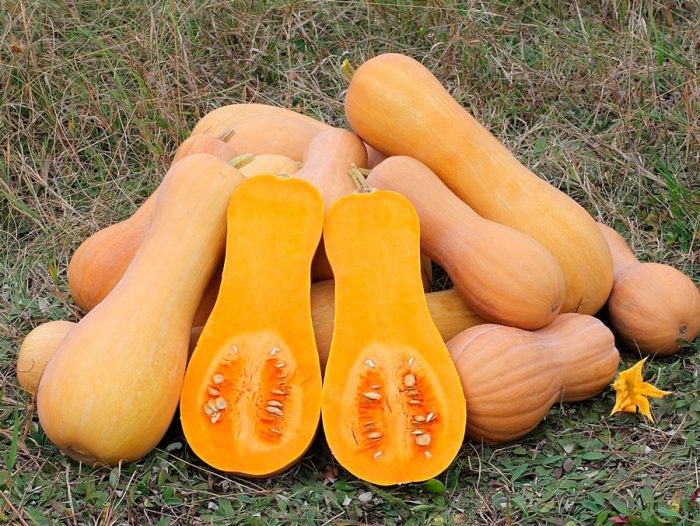
Butternut pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata)
The homeland of such a pumpkin is Central America (Mexico, Peru and Colombia). On the creeping shoots, there are alternately located long-petiolate leaf plates, on their surface there is pubescence. The pumpkins are pinkish brown or yellow, with longitudinal spots of light color on the surface. The dense, fragrant, rich orange pulp is tasty and tender. Small whitish-gray seeds along the edge are rim of a darker color. This species has a variety, which is called turban, since pumpkins have an unusual shape. The most popular varieties:
- Muscat... Long-leaved late variety with pumpkins weighing 4–6.5 kilograms. The pulp is juicy, firm and sweet, it is colored orange.
- Palav Kadu... In such a climbing late-ripening variety, rounded large pumpkins are segmented orange, their weight is about 10 kilograms. The orange juicy and sweet pulp is very tasty.
- Pearl... This late variety has a mass of dark green fruits of about 7 kilograms. The bright orange pulp is very juicy.
- Butternut... A climbing late variety with small pear-shaped pumpkins of pale orange or brownish yellow color, they weigh about 1.5 kilograms. Rich orange, fibrous, buttery flesh is sweet and nutty.
- Prikubanskaya... Climbing medium late variety. Brown-orange smooth pumpkins have a pear-shaped shape, they weigh about 5 kilograms. On their surface there are specks of orange or brown. The orange-red pulp is juicy, tender and sweet.
- Vitamin... This is a late-ripening variety that ripens in no less than 130 days. On the surface of dark green pumpkins there are stripes of yellow color, they weigh about 7 kilograms, their flesh is rich orange.
Large-fruited pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima)
This variety has the largest and most delicious pumpkins. There are varieties with a sugar content of about 15 percent, this figure is higher than that of a watermelon. The peduncle is cylindrical, rounded, the beardless stem is also rounded. Matte seeds are brown or milky white in color. In this variety, in comparison with the rest of the pumpkins, they tolerate low temperatures well and are best stored indoors.
- Zorka... The lashes of this medium early variety are long and strong. On the surface of dark gray pumpkins, there are orange spots, they weigh about 6 kilograms. The very sweet, rich orange and dense pulp contains high concentration of carotene.
- Marble... The long-leaved late variety has a high yield.The dark green lumpy pumpkins are round in shape and weigh about 4.5 kilograms. The sweet, crispy, dense, bright orange pulp contains a large amount of carotene.
- Sweetie... Climbing early variety. Orange-red, large, round fruits weigh about 2 kilograms. Juicy, sweet and firm, the pulp is dark orange in color and contains a large amount of vitamin C and sugars. This variety is frost-resistant and has a high yield.
- Volzhskaya gray... Climbing medium-ripening variety has round, slightly flattened grayish pumpkins, they weigh 7-9 kilograms. The color of the flesh ranges from rich orange to yellowish, it is characterized by medium sweetness. The variety is drought tolerant and has good keeping quality.
- Smile... The early ripening variety has good keeping quality. Round, deep orange pumpkins have whitish stripes on the surface. The orange flesh is very sweet and crunchy with a delicate melon aroma. This pumpkin is resistant to low temperatures and can be stored at home for a long time.
- Centner... Early ripening variety for universal use. Very large segmented yellow fruits can weigh 60 or 100 kilograms. Sweet white flesh. This pumpkin is intended for outdoor cultivation and is often grown to obtain seeds.
- Arina... The early ripe variety is distinguished by its unpretentiousness and resistance to diseases. The round, grayish fruits are slightly segmented, weighing about 5 kilograms. The yellow flesh is sweet and firm. The seeds contain a large amount of oil.


Watch this video on YouTube