Dill (Anethum) is a herbaceous annual plant that belongs to the monotypic genus of the Umbrella family. This genus is represented by the type of garden dill, or odorous. Under natural conditions, such a plant can be found in the southwestern or central regions of Asia, in the northern part of Africa and in the Himalayas. And this species is cultivated in all countries. Already in Ancient Egypt, man knew about the existence of dill, but such a plant began to be used as a spice in European countries only in the 16th century. Today, this plant, which is distinguished by its unpretentiousness and frost resistance, is in great demand both in medicine and in cooking.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Landing... Sowing dill seeds in open soil is necessary in early spring, then it can be sown every 15 days. If dill is grown indoors, then you can sow it at any time. Seeds of bush dill are sown on seedlings in March, and transplanted into open soil after a little over 4 weeks.
- Illumination... Shaded or sunny area.
- Priming... Well-fertilized, loose, neutral soil.
- Watering... It is necessary to water often, on hot days 2 times a day, while 2-3 buckets of water are taken per 1 square meter of the plot.
- Fertilizer... If dill is grown in pre-fertilized soil, it does not need to be fed. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers must be added to the depleted soil; for this, fermented nettle infusion is used.
- Reproduction... Generative (seed) way.
- Harmful insects... Umbrella blinds, Italian bugs (striped scinch bugs), carrot beetles and flies, melon, willow-carrot and carrot aphids.
- Diseases... Black leg, powdery mildew, fusarium, phomosis, cercosporosis and rust.
Features of dill
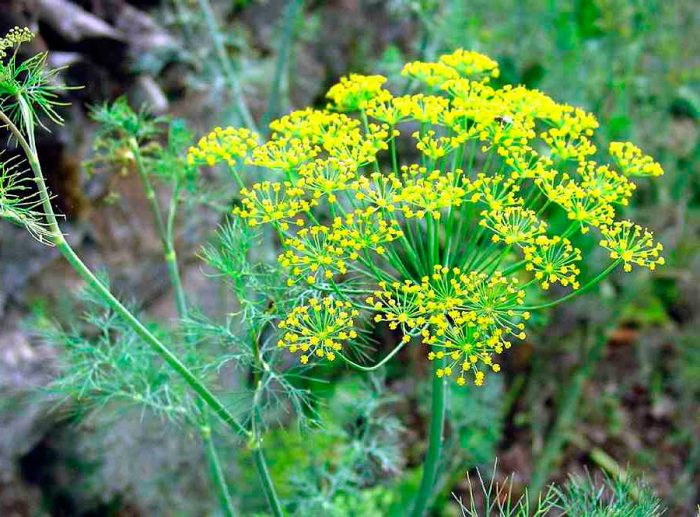
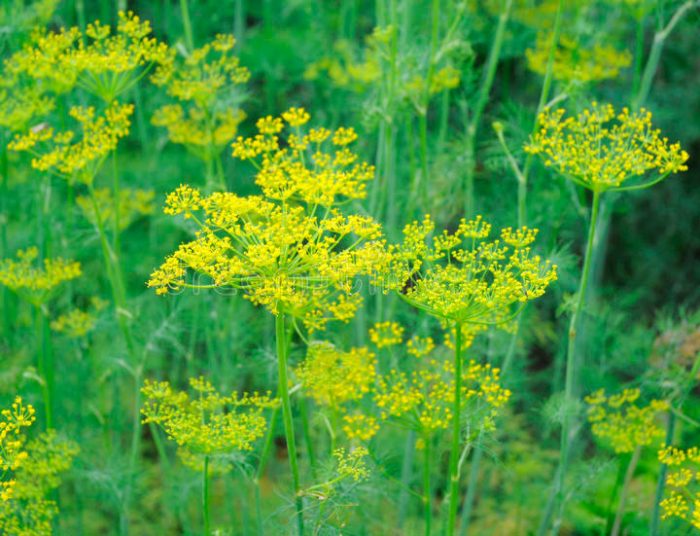
Dill is a herb that has a powerful, spicy aroma. The height of a single straight stem varies from 0.4 to 1.5 m, its dark green surface is finely grooved. The shape of the leaf plates is ovoid, they are dissected into 3 or 4 parts, the lobules of the last order are linear-filamentous or bristly.Umbrellas, reaching 20–90 mm in diameter, consist of yellow flowers, and they are collected in umbellate inflorescences with a diameter of 15–20 centimeters. The fruit is a cropped crop. The shape of the seeds is ovoid or broadly elliptical, they are up to 0.5 cm long and up to 0.35 cm thick. Flowering begins in June or July, while the fruit ripens from July to September.
Planting dill
What time to sow
The first time to sow seeds in open soil is at the beginning of the spring. In order for fresh dill to be available on the table in spring, summer and autumn, gardeners often resort to conveyor sowing, while sowing seeds should be 1 time in 10-12 days from the beginning of spring to the last days of August.
If the sowing of dill is planned for the spring, then the preparation of the site will need to be done in the fall. However, organic fertilizers (manure) are best applied under dill predecessors, and not under this crop. The best precursors to dill are beets, legumes, cabbage and cucumbers. Those areas where representatives of the Umbrella family (parsley, fennel, carrots, cumin and parsnips) were previously grown are not suitable for growing dill. This crop is not recommended to be grown next to parsley or carrots. It is best to grow garlic and dill nearby. Also, dill grows well next to potatoes.
In early spring, before sowing seeds, the soil must be loosened with a rake, and 15–20 grams of potassium salt, the same amount of urea and 20–30 grams of superphosphate per 1 square meter should be added to it.
Sowing rules
The seed material needs pre-sowing preparation, for this you need to fill it with water for 3-4 hours, during this time it must be replaced several times, this will remove substances from the seeds that slow down their germination. Then the seed is kept for a couple of hours in a solution of strong manganese potassium. After that, it must be thoroughly rinsed and dried. Then the seeds are sown in grooves, the depth of which should be about 20 mm, while the distance between them should be from 15 to 20 centimeters. It is necessary to distribute the seeds in the groove in such a way that the distance between them is from 10 to 20 mm, then the seeds need to be repaired and the garden bed watered.
Seed germination is observed at a temperature of 5 degrees, in order for the seedlings to appear as soon as possible, the surface of the site should be covered with an agrospan. The first shoots should appear after 7-14 days.
Growing dill on a windowsill
Sowing
When to sow dill indoors? In this case, you can sow dill at any time of the year. But if you want fragrant fresh greens to be there in winter, then you need to know which variety you need to sow. Early bush dill varieties such as Grenadier, Gribovsky and Richelieu are best suited for indoor cultivation.
The seeds need the same preliminary preparation as when sowing in open soil. The seeds are deepened into the substrate by 10–20 mm, and for sowing large containers are used, at the bottom of which a drainage layer is made, and on top it is covered with a moistened soil mixture, which consists of coconut fiber and vermicompost (2: 1). Then the container must be covered with film or glass, then it is removed to a darkened place. Crops must be provided with regular ventilation, and condensate must be removed from the shelter in a timely manner. The first seedlings should appear after 15 days. When this happens, the shelter is removed, and the container is moved to a well-lit place.
Room care rules
Dense shoots must be thinned out, since this plant reacts extremely negatively to tightness. It is best to have a distance of 20 to 30 mm between the plants. The room should be cool, as the seedlings can stretch out when warm. After the seedlings appear, the temperature in the room should be reduced by 2 degrees for 7 days.For this, the seedlings can be transferred to an insulated balcony. When 7 days have passed, the temperature must be increased to 15-18 degrees. This temperature is optimal for growing dill. At a time when the nights are longer than days, this plant grown on a windowsill needs additional lighting. To do this, a 40–80 W fluorescent lamp is installed above the container with dill at a distance of about 0.6 m. The seedlings must be illuminated in the early morning for 5–6 hours.
How to water
Since this culture reacts extremely negatively to chlorine, water is used for irrigation that has been separated for 24 hours, it should be at room temperature or slightly warmer. But it is best to water the plant with water passed through a magnet or melted water. It should be noted that the substrate in the container should be constantly loose and slightly damp. Water should not be allowed to stagnate in the soil mixture, as this may cause a black leg to develop. Such a plant, grown in indoor conditions, should be regularly moistened from a sprayer, especially if a container with dill is next to a heating device.
Fertilizer
Feeding the plants is carried out 1 time in 2 weeks, for this they use a solution of complex mineral fertilizer (for example, Rainbow or Ideal) in a weak concentration. Remember that if too much fertilizer is applied to the substrate, then the young dill will die. Before starting feeding, the plants are watered, and after that it is recommended to spray them with clean water, this will avoid the appearance of burns on the leaf plates. Foliar dressing can also be used to fertilize dill, but in this case the concentration of the nutrient solution should be very, very weak.
Growing dill in the open field
How to sow dill seeds in open soil is described in more detail above. This section will discuss how to properly plant the seedlings of this plant in the garden. Experts recommend growing bush varieties of dill exclusively through seedlings, and this method will also allow you to get an early harvest.
Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in March, it should be grown on a windowsill or in a greenhouse. After 4–5 weeks, the plants are transplanted into open soil, while they should develop from 3 to 5 true leaf plates. Planting is carried out on a cloudy day or in the evening, since the direct rays of the sun can harm the seedlings. In order not to thin out the dill, when planting between the bushes, a distance of 0.2 to 0.3 m should be observed, while the distance between the rows should be about the same. When the plants are planted, the soil should not be compacted very much, but the garden should be watered, after which its surface should be mulched with dry soil. It is recommended to protect the planted seedlings from direct sunlight for several days.
After the formation of flowering shoots begins, it is recommended to remove them, due to this, the growth of lateral branches will increase.
Care rules
It is very easy to grow such a crop in open soil. To do this, it is enough to water, feed, weed and thin out the plants in a timely manner, and also regularly loosen the surface of the beds. The soil on the site should be loosened to a five-centimeter depth, and this is done immediately after the seedlings are completely rooted. The next couple of loosening is carried out at an interval of 15 days, they do this after rain or watering, while the soil needs to be loosened to a depth of 10 to 12 centimeters.
While the plants are young, it is very important to remove weeds from the garden in time. After the bushes grow up and get stronger, the weed will no longer be able to inflict tangible harm on them.
How to water
Watering dill should be systematic and frequent, otherwise the bushes lose their taste, turn yellow, and sometimes lose their healing effect.On hot days, watering should be carried out 2 times a day. If you have such an opportunity, then install an automatic irrigation system. For watering 1 square meter of the garden, 2-3 buckets of water are taken.
Top dressing of dill
The bushes are fed with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer, however, it should be remembered that they can accumulate nitrates, in this regard, it is best to use an infusion of nettle fermented for 5 days as a fertilizer. Such fertilization will not only saturate the plant with nitrogen, but also destroy aphids. It is not recommended to use insecticidal preparations for processing dill, especially when less than 15 days remain before harvesting.
If necessary, then 10 to 15 grams of potassium-phosphorus fertilizer is applied per 1 square meter of the plot.
How and when to harvest dill seeds
After the seeds are dry, they will look like flat brown discs and can be easily separated from the umbrella. When this happens, they can be collected. They remain viable for 3 or 4 years. When the seeds are harvested, they should be spread out to dry in a well-ventilated dry place, they should be completely dry.
What can be grown after dill
The dill bed is suitable for growing crops such as garlic, peas, tomatoes, onions, beans and potatoes. Such a plot is not suitable for growing representatives of the Umbrella (Celery) family, since they have common harmful insects and diseases. On this site, it will be possible to sow such plants as dill only after 4 or 5 years.
Dill pests and diseases with photos and names
Dill diseases
Dill is highly resistant to diseases, but it can also suffer, especially if it is improperly looked after or if you do not adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of this culture. Bushes can get sick with powdery mildew, phomosis, rust, black leg, fusarium or cercospora.
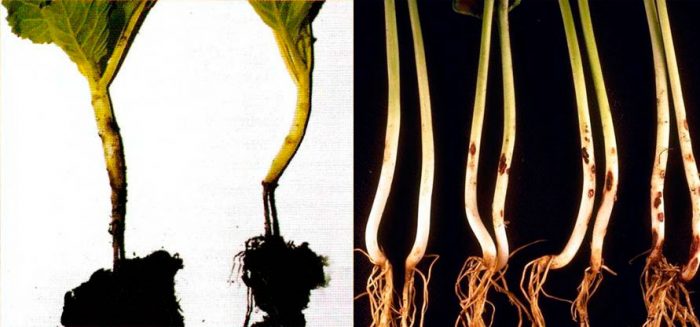
Blackleg
In young bushes with black legs, the root collar is affected, because of this it turns black, softens, becomes thin and decays. The plant falls and then withers. They usually get sick due to violations of the rules of care, for example, due to excessive watering, stagnant air, sudden temperature changes, lack of light, or when grown in a shaded place. As soon as the first symptoms of the disease are noticed, the bushes need to be sprayed with Fundazole solution.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew affects the aerial parts of the bushes, while a whitish bloom appears on them. The disease develops most actively on hot days with high humidity. Affected plants will need colloidal sulfur treatment.
Peronosporosis
Due to downy mildew (peronosporosis), chlorotic spots appear on the aerial parts of the bush, which gradually turn brown, a well-distinguishable dirty purple bloom forms on their lower surface. At the first symptoms of the disease, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%) or copper oxychloride (40 grams per bucket of water).
Fomoz
When a phomosis is damaged, brown specks form on the shoots, foliage and inflorescences, and the root system also suffers from it, on the surface of which dark stripes appear, which are arranged in rows. For prevention purposes, before sowing, it is necessary to warm up the seed for 30 minutes. in hot water, then immediately immersed in cold water, after which it should be dried to a free-flowing state. Sick bushes must be treated with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%). If necessary, dill can be sprayed with this mixture several times with a break of 10-12 days. However, the last time the bushes need to be processed no later than half a month before harvesting. Before eating or processing such dill, the greens must be thoroughly rinsed in running water.
Cercosporosis
When a plant is sick with cercosporosis, brown-yellow dirty spots appear on the surface of the inflorescences and shoots, reaching 0.6 centimeters in diameter, as the disease progresses, their middle becomes pale, while the edge remains dark brown. In order to get rid of this disease, for processing it is necessary to use the same means as when spraying the bushes from phomosis.
Fusarium wilting
The development of fusarium wilting is observed in bushes during the formation of 3-4 true leaf plates. Chlorotic spots form on the surface of plants, then they droop. The disease develops rapidly when the soil is overheated, water stagnates in it, or when the root system is injured during loosening. Bushes can be cured only at an early stage of the development of the disease, while a solution of a fungicidal preparation is used for spraying. Severely affected bushes must be pulled out and destroyed. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of dill crop rotation, and for cultivation, choose those varieties that are resistant to fusarium wilt.
Rust
When dill is damaged by rust in the first summer weeks, brownish-yellow pillows form on the underside of the foliage, petioles and shoots. For prevention purposes, before sowing, the seed must be warmed up in water heated to 50 degrees, then they must be immediately immersed in cold water, after which it is dried. Sick bushes will need several treatments with a break of 10-12 days, for this use a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%). The last time the plant must be processed no later than 2 weeks before harvest. Greens should be thoroughly rinsed in running water before processing or eating.
Dill pests
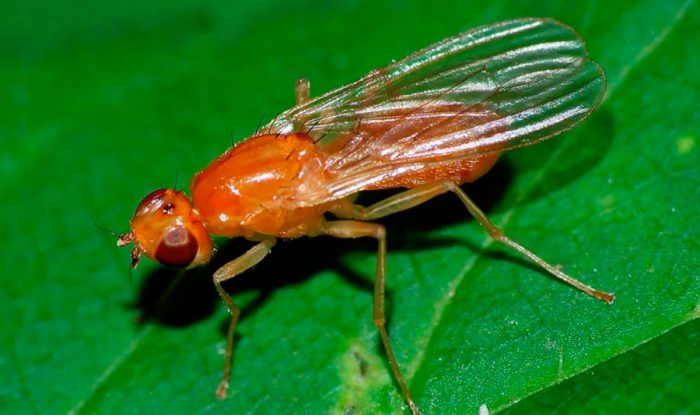
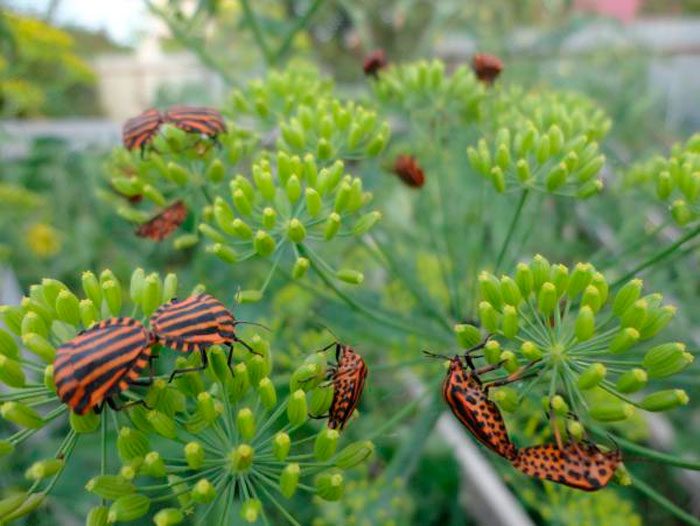
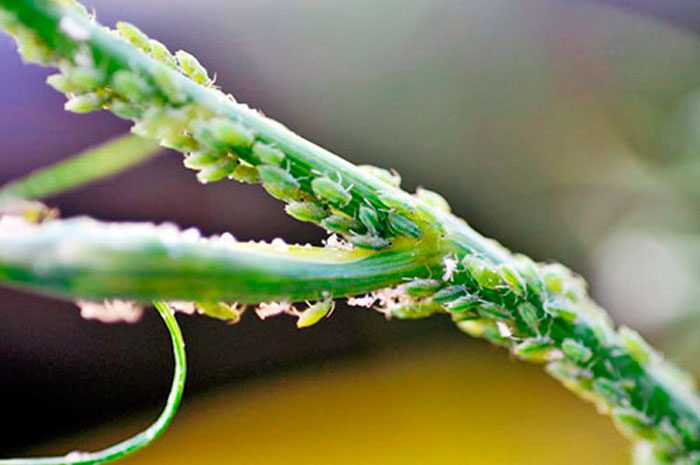
Umbrella blinds, Italian bugs, or striped bugs, carrot beetles, carrot flies, melons, willow-carrot and carrot aphids most often settle on dill.
Carrot fly
The carrot fly injures the aerial part of the bush, which is why it has a lag in development, while the foliage at the beginning turns purple-red, after which it turns yellow and dries up. Most often, pests settle on those dill bushes that are next to a garden with carrots, since such a pest is attracted by the aroma of carrot tops. To protect the bushes from such a fly, the surface of the ground along the rows must be covered with a layer of a mixture consisting of sand, to which mustard powder, dry peat, hot ground pepper or wood ash are added. If, nevertheless, a carrot fly appears, the plants must be treated with the following means: Arrivo, Vantex or Karate Zeon. In this case, the bushes must be sprayed no later than half a month before harvesting.
Umbrella Blind
Umbrella blinds are small bugs that infect all members of the Celery family, both wild and cultivated. Such a pest feeds on plant sap, which it sucks from foliage, umbrellas and stems, this leads to the death of greenery. In those beds where there are blind people, the yield of the bushes is reduced by 30-40 percent. To get rid of such pests, the bushes need to be sprayed with Fitoverm or Actellik solution.
Italian bugs
The Italian blind behave exactly like the umbrella blind and harm the same way. During one season in a warm area, such pests can give 2 generations. But such a bug can greatly harm dill only if there are a large number of individuals in the garden. In these cases, the bushes need to be sprayed with Actellik or Fitoverma solution.
Aphid
Dill can be harmed by 3 types of aphids: willow-carrot, carrot and melon. All of them feed on sap, which is sucked out of the aerial parts of the bushes, as a result, they experience stunted growth, deformation, wrinkling, yellowing and drying out.It should be remembered that such a pest is the main carrier of viral and bacterial diseases, which are currently considered incurable. To begin with, pests are removed from the bushes with a powerful stream of water, then foliar dressing is carried out using a solution of phosphorus-potassium fertilizer for this. 1 bucket of water must be combined with 3 kilograms of wood ash, when the mixture is infused for 24 hours, 1 large spoonful of liquid soap should be dissolved in it, then it must be filtered and used to spray the bushes. After 7 days, the mixture from the surface of the plants must be washed off with clean water.
Dill varieties
Experts distinguish all varieties of dill by the length, width and shape of the segments of the leaf plates, by the shape of the rosette, and by the degree of dissection and color of the foliage. Inexperienced gardeners are most often guided by the following trait - the beginning of the formation of stems, according to which varieties are divided into early, mid-ripening and late-ripening.
Early maturing varieties
- Gribovsky... This fruitful variety is easy to care for. It can be grown in open soil and indoors. This fragrant variety is very resistant to disease. The height of the bushes is about 25 centimeters.
- Further... This variety has a high yield and resistance to lodging. Such dill is grown for freezing, food, it is dried and used for making pickles and pickles. The formation of the rosette occurs 38–40 days after the seedlings appear. On the surface of the green leaf plates, there is not a very large waxy coating.
- Aurora... Such a productive variety appeared relatively recently, it is resistant to harmful insects and diseases, and ripens after 25 days. The powerful bush has a lush rosette and close internodes, rich green fragrant foliage is very juicy.
- Grenadier... Ripening of such a bush variety occurs 35-40 days after the seedlings appear. The bushes have the greatest aroma in the development phase of 3 or 4 leaf plates.
- Umbrella... This variety also appeared not so long ago, its ripening period is the same as that of the Gribovsky variety. Experts recommend using this variety for growing in a greenhouse.
Mid-season varieties
- Umbrella... The bush has thick branches and long leafy plates, such greens are eaten both fresh and used as a spice.
- Borey... Such a bush variety is distinguished by its aroma and yield. The height of the semi-raised rosettes is about 36 centimeters, and they include large green leaf plates with a bluish tint. Bushes ripen in 40-60 days from the moment of sowing, and seeds ripen after 65-105 days.
- Richelieu... This variety is decorative and resistant to diseases. The large rosettes are composed of fragrant, beautiful lacy greenish-blue leaf plates that have long lobes. During flowering, the shoots have the greatest amount of foliage.
- Kibray... This variety has a high yield and resistance to powdery mildew. It can be cultivated both in a greenhouse and in open soil. The greens ripen no more than 45 days after the seedlings appear, and the seeds ripen after 70 days. The greenish, juicy and fragrant foliage is very delicate.
- Alligator... The bush variety has leaf plates that are raised above the surface of the soil, which is very convenient during harvesting. Ripening of greens occurs 42–45 days after the seedlings appear, however, cutting greens for food can be carried out earlier.
- Lesnogorodsky... This variety, which is distinguished by its high yield and resistance to diseases, has one feature, for example, on the bushes in autumn, when the seeds are ripening, the foliage still remains large and green fragrant, and at the same time it contains a large amount of provitamin A and vitamin C ...
Late-ripening varieties
- Salute... Such a bush variety is distinguished by its yield, the bushes reach a height of about one and a half meters, and they ripen in 35–45 days. Densely leafy stem is very strong. Very fragrant foliage of a dark green color with a bluish tint, it is large and delicate. This variety is valuable because the foliage grows very quickly after cutting, and the umbrellas are formed slowly.
- Buyan... The variety is resistant to diseases, it is grown in open soil through seedlings. In succulent bushes, the shoots do not become coarse for a long time, while there is a strong waxy bloom on the surface of the fragrant foliage.
- Frost... The variety, which is distinguished by its yield, is used for conservation and freezing, as well as for fresh food. Heavily leafy plants have large umbrellas and a raised rosette, consisting of long green-bluish strongly dissected leaf plates, on the surface of which there is a waxy coating.
- Naughty... A fragrant variety, distinguished by its yield, has green-gray foliage, on the surface of which there is a waxy bloom. Most often, greens are used for fresh food, but they can also be used as a spice for dishes.
- Kutuzovsky... This variety ripens 41–44 days after the seedlings appear. Delicate fragrant and large foliage is greenish, it reaches about 20 centimeters in length, it is dissected into thread-like segments. The bushes are highly leafy. They are grown for drying, freezing, as a spice and for making brine and pickles.
Dill properties
Useful properties of dill
Dill can be eaten throughout the year. It contains such substances necessary for the human body as: nicotinic and ascorbic acids, carotene, thiamine, riboflavin, pectins, flavonoids, vitamins A, B2, B6, C, PP, as well as potassium, iron, phosphorus and calcium. The composition of the fruit contains a high concentration of fatty oil, consisting of palmetic, oleic and linoleic acids.
The essential oil, which has a characteristic aroma of dill, contains all parts of the plant. The foliage contains magnesium and iron salts in an easily digestible form, they help to enhance the processes of hematopoiesis. And the essential oil included in the composition helps to stimulate the formation of digestive and bile enzymes, and they also disinfect the organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems. A drug called Anetin is made from this plant in the medical industry, it stimulates the work of the heart muscle, and also expands the vessels of the brain and heart, as a result, their nutrition is increased several times.
This culture is very beneficial for women who are breastfeeding, as it helps to stimulate lactation. It is also recommended to use dill for hypertension, respiratory problems and visual impairment. Means from it have a diuretic, sedative and antispasmodic effect, and also an analgesic effect for stomach or duodenal ulcers. An infusion is made from dill seeds, which helps to stimulate appetite, improve digestion, and it also eliminates inflammation of the kidneys and helps get rid of insomnia. Mix 2 tbsp. freshly boiled water with 2 tsp. dill seeds, cover the container and wait 10 minutes. The infusion must be filtered and drunk at 1 tbsp. in a day. This tool has a strong anti-allergenic and anti-hemorrhoidal effect, and it is also used as an external wound healing agent.
A powder made from the seeds of this plant is also very popular, which enhances lactation. It is eaten 3 times a day, 1 gram for 30 minutes. before the meal. The infusion of foliage removes bags under the eyes, for this, cotton wool discs soaked in it must be put for 10 minutes. on the eyes. Dill oil is good for bronchitis and pneumonia, thanks to it there is a rapid separation of mucus from the walls of the bronchi.To eliminate gas formation in babies, use dill water, to prepare it, you need to combine water and dill oil in a ratio of 1000: 1. In addition, this agent helps to lower blood pressure, increase urine output, slow down intestinal motility and dilate blood vessels.
Contraindications
Everyone can eat dill, because it cannot harm anyone. At the same time, the funds from it, which help to lower blood pressure, cause weakness, blurred vision, loss of strength, and sometimes fainting in hypotensive patients. It is also contraindicated for those who have dill intolerance. It is recommended to eat such greens as rarely as possible for pregnant women and women during menstruation, but you should not completely abandon them.
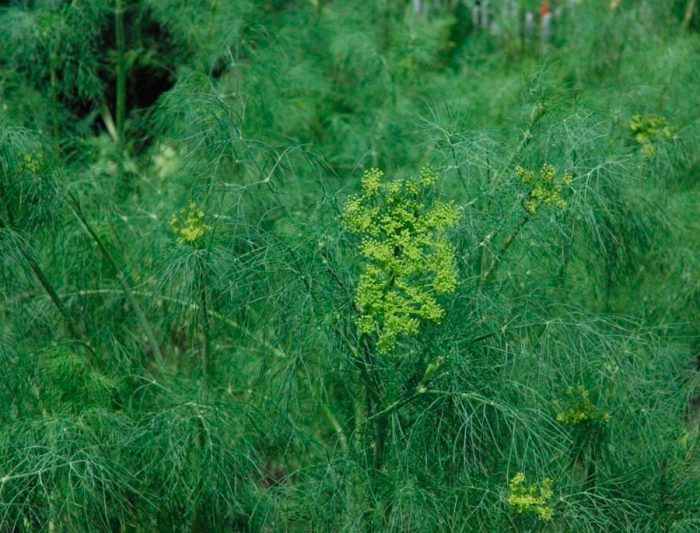
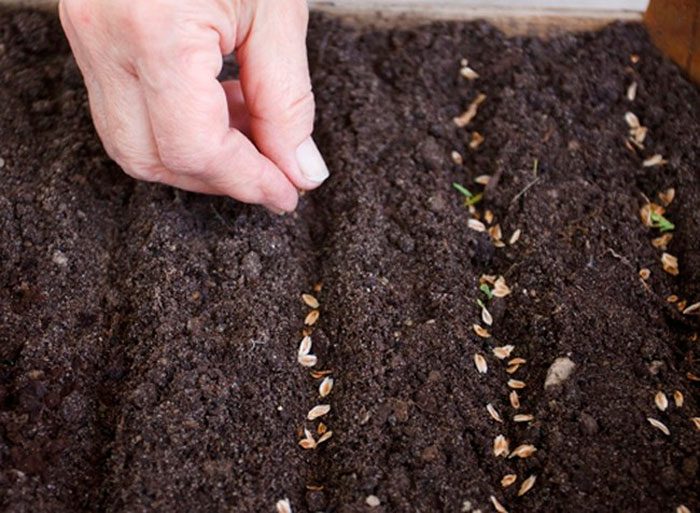
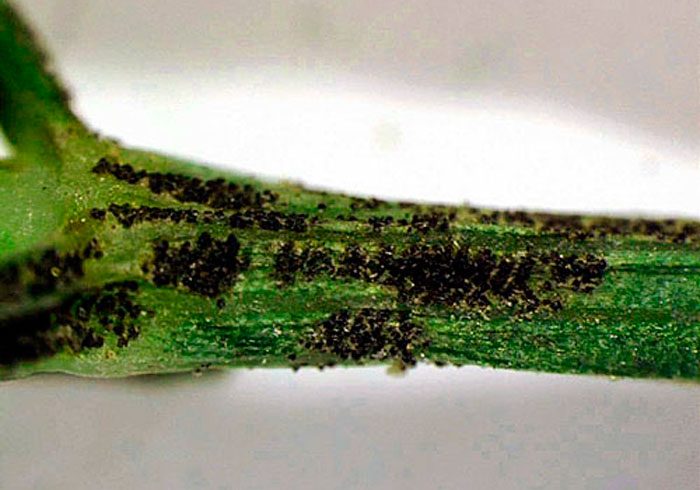
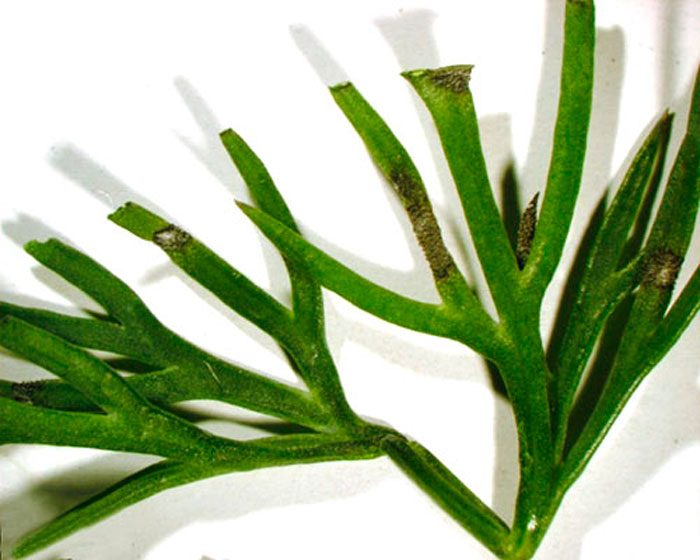









































I don't know how anyone has it, I tried 10 times to grow at least a sprig of dill) it's a pity the photo can't be attached, which I did) three sprigs the size of a match)