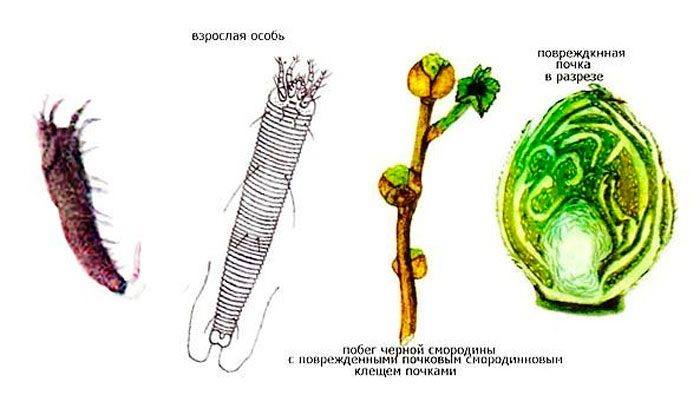
The currant bud mite (Cecidophyopsis ribis) is a microscopic four-legged insect that belongs to the genus Cecidophyopsis of the family Eriophyidae (Trombidiformes). This harmful insect is widespread in Asia, Europe and Australia. It can be found in those areas where gooseberries or currants grow.
The insect injures the kidneys, due to which the leaf mass of the shrub is significantly reduced, and the development of its stems is noticeably impaired. In addition, this pest is a carrier of a viral disease called "terry". And he is also the cause of the regeneration of the generative organs, because of which the shrub stops forming berries.
Content
Features of the kidney mite
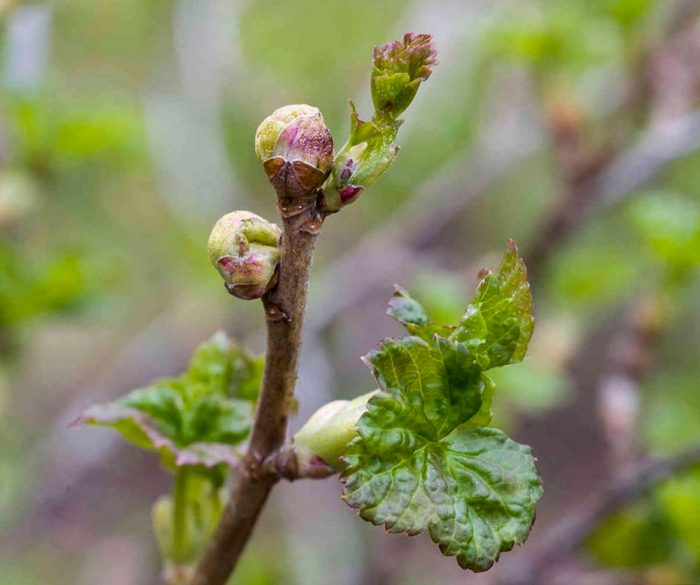
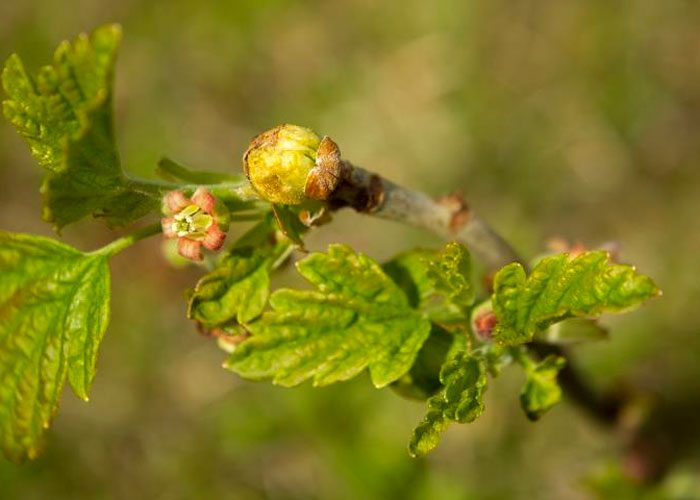
The kidney mite has a white worm-shaped body. Males reach 0.15 mm in length, females are larger - about 0.3 mm. The head ends with a mouth apparatus that is outwardly similar to a wedge-shaped proboscis. The pest has 2 pairs of legs, they have feathery bristles. Elongated-oval larvae are light in color. A kidney mite can harm gooseberries and black currants, but it can also settle on white and red currants. For the winter, ticks are taken into the kidneys. At the same time, one kidney can contain 3–8 thousand individuals, and in large buds - 8–30 thousand individuals. Those buds, inside which there are pests, look more prominent and larger. In early spring, they grow to the size of a pea and outwardly become similar to small heads of cabbage, while their deformed leaves stick out. The same kidneys, where there are not too many pests, cannot be distinguished from healthy ones, this is the main difficulty in the fight against kidney mites.
The spread of pests occurs with the wind, along with seedlings, thanks to birds and various insects. The lifespan of a female is 20–45 days, while one can lay 5–100 eggs. The duration of development of eggs is 7–15 days, and the development of larvae is 7–30 days. The appearance of the first generation of ticks is observed at the very end of flowering of currant bushes. During one season, the tick is able to give 5-6 generations of offspring: 2 in the spring and 3 in the summer-autumn period.
Kidney mite on currant
Control measures
In order to protect your garden from kidney mites, you must not forget about preventive measures. When purchasing seedlings, conduct a thorough examination of their buds to be sure that you do not bring a colony of harmful insects with them.Phytoncides, which are contained in garlic and onions, are able to scare off the pest, therefore, these crops are recommended to be planted between the rows of currants. However, in this case, the onion or garlic is not dug up in the fall, but left in the ground for the winter.
If you decide to propagate a currant bush by cutting, then cut it off from a plant that is completely healthy. Experienced gardeners recommend disinfecting the cuttings; for this, they are placed in warm water (about 45 degrees) for a quarter of an hour, to which indolylbutyric acid is preliminarily added (0.5 grams of the product per bucket of water).
If there are very few buds on the bush in which the tick lives, then they can be cut off with your hands and destroyed with fire. In the event that the pest is found in almost every bud, then the above-ground part of such a shrub is cut down and destroyed, and the stump that remains in the ground is spud. After a while, new stems will grow. In order to avoid such pruning, it is recommended to carry out a thorough examination of each bush every year in spring, during which any suspicious-looking buds are cut off and burned.
Chemicals
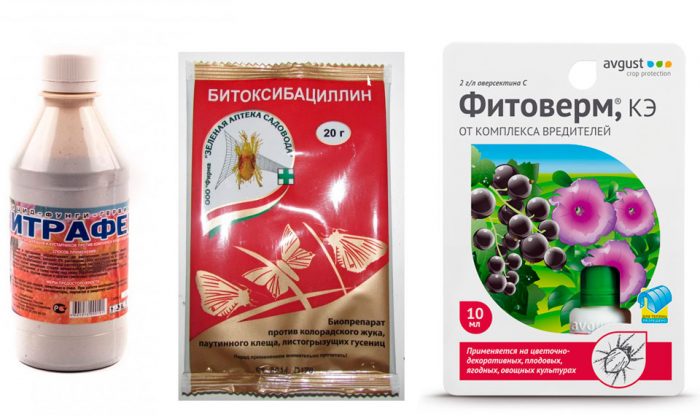
In order to get rid of a kidney mite, the fight against it must be started already in the spring. To do this, before sap flow begins, in order to prevent, currant bushes and the surface of the soil near them are sprayed with a solution of Nitrafen (for 1 liter of water 30 grams). As soon as inflorescences and foliage begin to form, they carry out 3 treatments of currants with a break of 7 days, for this they use biological pesticides from harmful insects, for example: Bitoxibacillin, Aktofit or Fitoverm. These spraying will be effective only if the air outside is warmed up to 5 degrees and above. If the weather is colder or cloudy, then it is recommended to postpone the treatment.
While the pests will move from the affected buds to healthy ones, they can be destroyed by spraying the bush with ISO (lime-sulfur broth), Karbofos, or another agent that contains sulfur. During the exposure of the buds, the bushes are sprayed with ISO solution (2%) for the first time. Re-processing is carried out after 10-12 days, or immediately, as the currants fade, but in this case the solution should be 1%. In the same way and at the same time, the bushes can be sprayed with a solution of colloidal sulfur (10 grams of the product per 1 liter of water). The following acaricidal preparations can also be used to kill the tick: Endidor, Vertimek, Oberon, Nissoran, Apollo or Neoron. When spraying, try to keep each bud and branch of the currant bush well wet with the solution.
Gooseberry bud mite
Since the gooseberry is a close relative of the currant, the kidney mite also settles on it. Both the preventive measures and the chemical preparations used in the fight against insects are the same as in the cultivation of currants, namely: inspect the seedlings before buying, at the beginning of spring, check all the buds on the bush, cut off and destroy those that aroused suspicion, plant garlic and onions between rows, and in case of total defeat by a pest, cut and burn all the stems. As for pesticides, the same means and at the same time can be used to process gooseberries as for spraying currant bushes.


Watch this video on YouTube
Folk remedies
If there are few pests on the shrub, then you can try to get rid of them using folk remedies, for example:
- Hot water... In early spring, before the buds swell, spill the bushes with quick circular motions with hot water (about 80 degrees), they must first be tied up.The result of this procedure will be the death of pests, as well as strengthening the immune system of the bush to powdery mildew and other diseases. It has also been observed that bushes doused with hot water give a richer harvest. In the spring, it is sometimes impossible to understand whether the sap flow has begun or not, which is why many gardeners carry out such treatment in the fall at the end of the leaf fall, since the buds affected by the pest can be recognized already in the last summer days.
- Garlic water... Grind 0.2 kg of garlic and combine the resulting mass with a bucket of water. The infusion will be ready after a couple of hours, it remains only to strain it and you can start processing. Instead, you can combine 150 grams of garlic husks with a bucket of hot water. Within 24 hours the infusion will be ready for use.
- Mustard infusion... Dissolve 0.2 kg of dry mustard powder in a bucket of water. Stir everything well and leave for 12 hours. Process the plants with a strained infusion.
- Dandelion infusion... Place 50 grams of fresh foliage and 200 grams of dandelion roots in a bucket of water. The product will be ready for use in a few hours.
- Tea brewing... This tool is used to get rid of mites that are on the cuttings. Add 50 grams of tea to 25 liters of freshly boiled water. After 24 hours, cuttings are immersed in the resulting infusion, which are taken out after 3-4 hours.
Kidney mite resistant currant varieties
A large number of gardeners know a way to forget forever about what a kidney mite is. To do this, they plant in their garden those varieties of currants that are resistant to this pest. For instance:
- Curiosity... This self-fertile early-ripening variety has a high yield and frost resistance. In addition, it is very resistant to both kidney mites and powdery mildew. Medium-sized fruits have an oval shape, sweet-sour taste and firm skin. The downside of this variety is that it needs frequent watering.
- Selechenskaya... A versatile early ripening variety with high productivity and resistance to frost and drought. This variety combines all the benefits of currants and gooseberries. Its large glossy black fruits with thin skin have a sweet taste and weigh about 5 grams. It is very resistant to kidney mites.
- Kipiana... This medium late variety is resistant to both powdery mildew and kidney mites. Almost black, rounded dessert fruits have a sweet-sour taste and medium size.
- Vigorous... This late-ripening highly productive variety is very popular among gardeners. The oval-shaped fruits, the size of a cherry, weigh about 8 grams, the firm flesh has a refreshingly sour taste. The variety is very resistant to both harmful insects and diseases, but at the same time it needs systematic rejuvenating pruning.
These currant varieties are usually quite easy to care for. In addition, most often they are resistant to other harmful insects.


Watch this video on YouTube