The common raspberry shrub (Rubus idaeus) is a member of the genus Rubus of the pink family. This genus unites about 600 species. Most of these species were already known in the Ancient World, for example, the first mention of the existence of wild raspberries is in the 3rd century BC manuscripts. BC. For the first time, raspberries were cultivated in Western Europe in the 16th century. Under natural conditions, such a shrub prefers to grow along river banks and in forests. For many centuries, this plant has been one of the most popular berry crops grown in gardens. Today this plant can be found in almost every garden plot. The fragrant and very tasty fruits of raspberries are also appreciated for their usefulness, as they contain minerals, acids and vitamins necessary for the human body. This culture is distinguished by its unpretentiousness. Such a plant is able to grow well and give good yields even when neglected. If properly cared for, raspberries will be protected from infection by various diseases and pests, and will also yield rich yields.
Content
Features of raspberries
Today raspberries are very popular among gardeners from different countries, such as currants, strawberries, gooseberries, strawberries, blueberries and other very useful and simply delicious garden crops. Very often, gardeners grow raspberries not only for themselves, but also for sale. In this regard, the gardener tries to get a rich harvest of good quality berries.
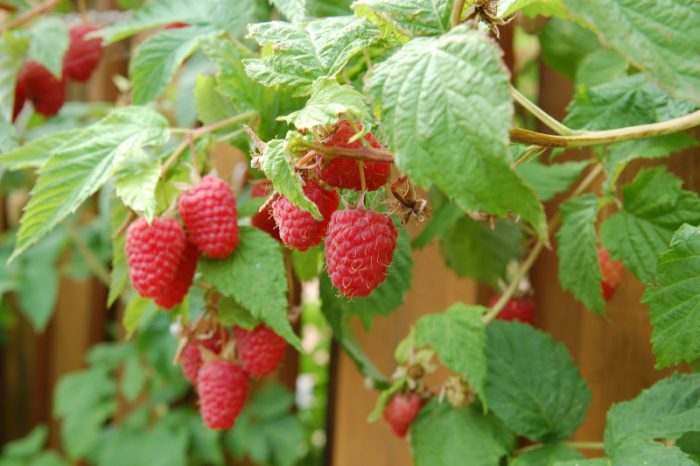
Common raspberry is a deciduous shrub, the height of which can vary from 150 to 250 centimeters. Such a plant has a woody root, around which a large number of adventitious roots grow. This leads to the formation of a strong branched root system. The stems are erect. Herbaceous young shoots are very juicy green in color, on their surface there is a bluish bloom and many small thorns. Already in the second year, the stems lignify and turn brown.When fruiting ends, such stems dry out, but in the next season they are replaced by new young shoots. Alternately oval-shaped leaf plates have petioles, they are complex, there are 3-7 ovoid leaflets. The front surface of the leaves is dark green, and the back is whitish in color, because there is pubescence on it. Axillary apical racemose inflorescences consist of white flowers, which reach about 10 mm in diameter. As a rule, the berries grow in the second year of the stems' life. The berries are small hairy drupes that have grown into a complex fruit, they can be painted in a variety of shades of crimson, and there are also burgundy-black (in varieties that are blackberry-like) or yellow fruits. Thanks to the selection work carried out, remontant raspberries were born, their fruiting begins in the first year of growth, and 2 crops are removed from it during the season. Kumanik and blackberry are raspberry species that form long stems, with which they cling to the support due to the thorns located on their surface. Bony and prince are herbaceous species of raspberries. It is quite simple to grow raspberries, but in order to get a bountiful harvest, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of this crop, as well as to properly care for it.
Planting raspberries in open ground
What time to plant
Planting raspberries in open soil can be done both in spring and autumn (from September to October). The area suitable for planting should be sunny. In the event that this culture is grown in a shaded place, then due to a lack of light, young shoots sometimes stretch out so much that they shade the fruiting stems. Different varieties of raspberries have different soil preferences. However, most of them grow well on light nutritious soils; loam and black soil are also suitable for this plant. The required soil pH for raspberries should be between 5.7 and 6.5. In lowlands and in places with uneven relief, this shrub cannot be grown, because there is stagnation of water in them. Also, steep slopes are not suitable for planting, as well as elevated areas, in this case the raspberries will suffer from a lack of moisture. For planting such a crop, it is recommended to choose a flat or slightly sloped site. In one and the same place without transplanting such a shrub can be grown for 7-10 years, after which it will need a transplant, because the soil will be very depleted. And on this site, it will be possible to plant raspberries again only after at least 5-7 years. Where nightshades (potatoes, tomatoes, peppers) were grown, this berry culture should never be planted. But the area after cereals or legumes for planting raspberries is very suitable.
Planting raspberries in spring
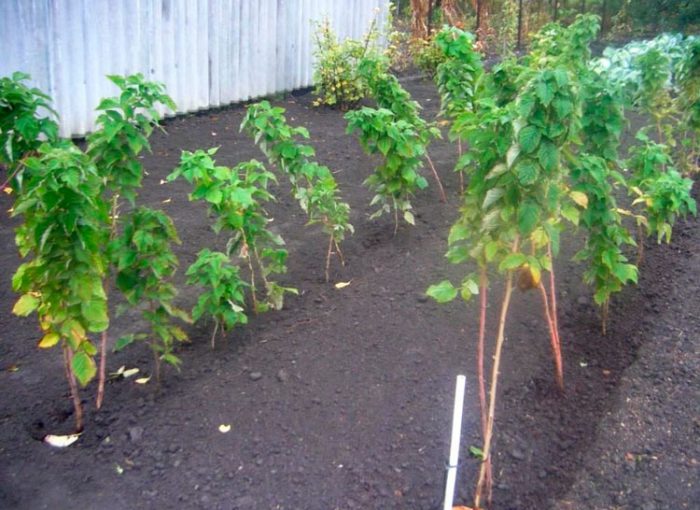
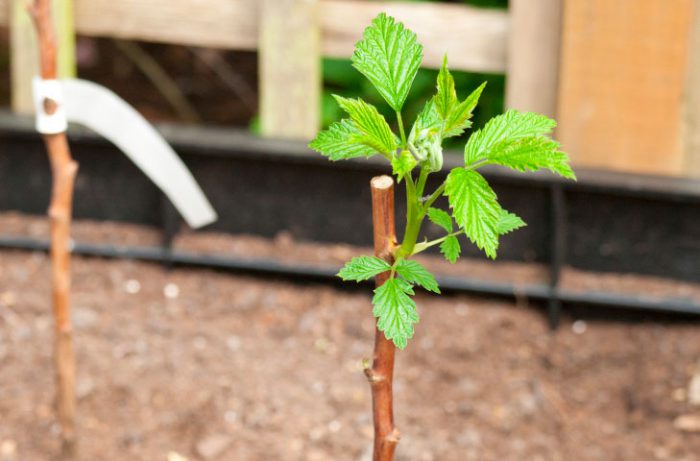
Spring and autumn planting differ only in the method of preparation for this procedure, but otherwise they are absolutely the same. At the beginning of the spring period, you need to prepare a hole, the size of which should be 0.5x0.4x0.4 m, while the upper nutrient layer of the soil should be thrown back separately. The distance between the specimens in the garden should be about 0.5 m, while the row spacing should be at least 1.5 m.The upper nutrient layer of the soil must be combined with 50 grams of potassium sulfate, with 100 grams of granular superphosphate, with 10 kilograms of humus or compost and with 0.4 kilograms of wood ash. Part of the resulting soil mixture must be poured into the hole, and the rest must be poured with a slide near it. If, before you start planting, the soil mixture in the hole is compacted, it will need to be loosened. Then the seedling should be placed in the hole so that the replacement bud is located just below the ground level. After the roots are carefully spread out, the hole should be filled with soil.It is tamped, and then a not very deep hole is made around the plant, which should be filled with water. After the liquid is completely absorbed, the surface of the hole must be mulched with sawdust, humus or dry straw. The seedling is shortened to 0.3 m above the soil level. If the weather is dry for several days after planting raspberries, then the plants will need repeated watering. In spring, planting raspberries is worse than in autumn, because there is a high probability of being late due to unfavorable weather, as a result of which the seedlings will take root much worse. In the spring, planting material purchased in a special store or nursery is planted, or one that was harvested in the autumn (it is placed in the refrigerator for wintering).
Planting raspberries in autumn
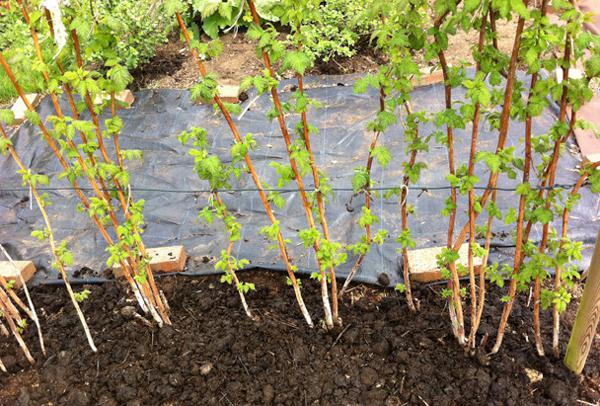
In the autumn, the preparation of the landing pit should be known 6 weeks before the day of disembarkation. The site is dug to the depth of a shovel bayonet, while all the roots of the weeds are selected and 0.2–0.4 kg of superphosphate, from 2 to 3 buckets of rotted manure and 100–200 grams of potassium sulfate per 1 m2 plot. If you fertilize the soil before planting, then the raspberries will not need phosphorus and potassium fertilizers for about 5 years. If the soil is peat, then for every 1 m2 plot you need to add four buckets of sand. It is best to do the planting of raspberries in the last days of September or the first in October. In the fall, both experts and experienced gardeners recommend planting this culture, because in this case it will be possible to slowly prepare a site for planting, and the plants themselves take root well before winter, and in spring they begin to grow actively.
Raspberry care
Spring raspberry care
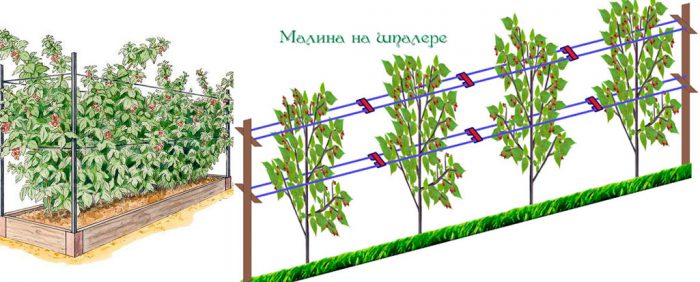
Immediately after all the snow on the site has melted, it will need to be freed from the leaves that fell last year, because they may contain pathogens or pests that were hiding there from winter frosts. This dwarf shrub needs support, therefore, in the springtime, you should tie raspberries to the trellis. If the plant is tied to a trellis, then as a result of this it will be evenly illuminated by the sun's rays, the maturation and growth of young basal shoots will accelerate, and such bushes are relatively easier to care for. If you decide to make trellises, then you will need to dig at the end and at the beginning of each row on both sides powerful posts reaching 150 centimeters in height. Between these pillars, it is necessary to stretch the wire in 2 rows: the lower row should be located at a height of 0.6-0.7 m from the surface of the site, and the upper one at a height of 1.2 m. To avoid the wire sagging, it is necessary every 5 m into the ground stick a wooden stake. Place the stems of the bushes along the wire in a fan-like manner, and then secure them by tying them with twine. After a couple of years, additional rows of wire must be stretched between the pillars: the first - at a height of 0.3 m from the surface of the site, and the other - at a height of 1.5 m.
The rest of the time it will be very easy to care for this culture. So, it needs to be systematically weeded, fed, watered, loosened near the bushes to a shallow depth, after which its surface is covered with a layer of mulch. What is used to feed this crop in the spring? In the event that all the necessary fertilizers were applied to the soil before planting, then raspberries will not need potassium and phosphorus for 5 years. However, it is necessary to feed the plants with nitrogen-containing fertilizers every year. Prepare the following nutrient solution for feeding: Combine 10 liters of water with 1 shovel of cow droppings and 5 grams of urea or saltpeter. This mixture is poured under each plant in the last days of March or the first in April. If you decide to use a different nitrogen-containing fertilizer, then for every 1 m2 the site will need to take from 20 to 25 grams of the substance.Then the surface of the soil will need to be loosened.
Raspberry care in autumn
When in the autumn time all the fruits from the bushes are collected, you need to start preparing raspberries for the upcoming winter. This procedure must be approached with all responsibility, since it depends on this how abundant the harvest will be in the next season. The surface of the site must be freed from the old mulch layer, which should be destroyed, since it can contain various pests or pathogens. Then the soil is carefully dug to a depth of no more than 8-10 centimeters. Once every couple of years, it is recommended to add wood ash and compost to the soil for digging. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers for feeding raspberries in autumn are not used, because they can cause active growth of young shoots, their leaves will fly around late, which increases the likelihood of frost damage. In the event that a dwarf shrub needs phosphorus and potash fertilizers, then they should be applied in not very deep (from 15 to 20 centimeters) grooves, which should be located at a distance of at least 0.3 m from the plants.No more than 1 bush is taken 40 grams of potassium salt and 60 grams of superphosphate. In plants fed in this way, the laying of flower buds will improve, which will have a positive effect on the future harvest.
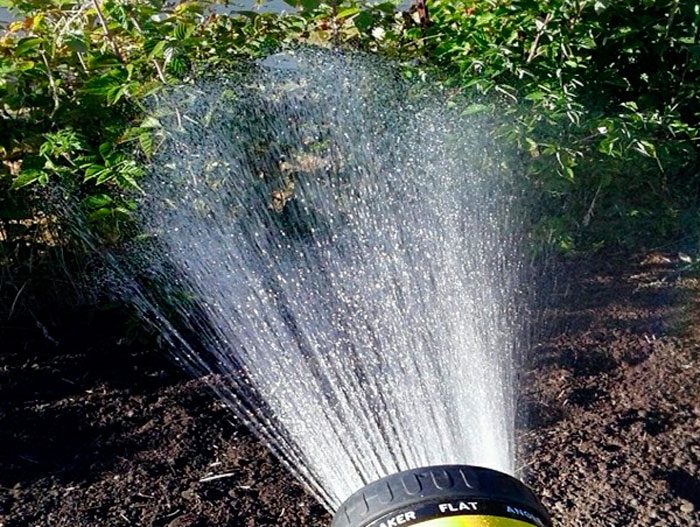
Watering raspberries
Watering raspberries in spring and summer is only necessary if there is a prolonged drought. If it rains systematically, then it will not need watering. In a hot and dry period, the plant will need abundant watering, while the water should soak the topsoil by 0.3–0.4 m. In addition, this shrub needs mandatory watering in May before it blooms, as well as during time of active growth and ripening of fruits. Podwinter watering for such a culture is of great importance, since in the autumn time it sets buds of growth in the root system. At the same time, try to soak the soil to the maximum possible depth, then the wintering of raspberries will be more than successful. Most of all, the drip method is suitable for watering this plant, because it has a number of advantages:
- water saving - less liquid is consumed compared to sprinkling or ditch irrigation;
- warm water - in no case should it be watered with cold water, and with this method of irrigation, the liquid is already comparatively warm to the root system;
- uniform soaking of the soil.
If you want to significantly reduce the number of waterings in the summer, then the surface of the site should be covered with a layer of mulch.
Raspberry transplant
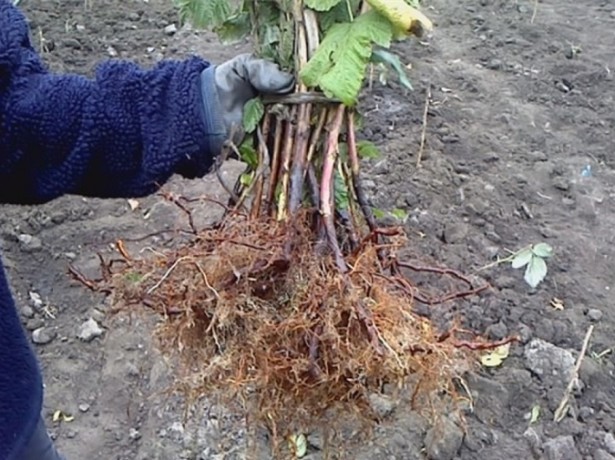
When transplanting such a plant, you must adhere to the same principles as when it was first planted. This shrub is prone to strong growth. Its roots are located close enough to the soil surface, and a large number of offshoots grows during the summer. If desired, using a shovel, they can be separated from the mother bush and, having dug up along with the roots, planted in a new permanent place. If the specimen is overgrown and old, then using a shovel, you can cut off the youngest part from it along with the root system and a lump of earth, while taking into account that the diameter of its shoots should not be less than 10 mm. In such a "delenka" it is necessary to shorten the shoots to 0.25 m, and then it is planted in another place. You can transplant raspberries at any time, except for the winter period. However, experienced gardeners recommend doing this procedure in the spring. To prevent the uncontrolled growth of such a plant, the area where it grows must be fenced; for this, sheets of iron or slate are dug into the ground around the perimeter.
Reproduction of raspberries
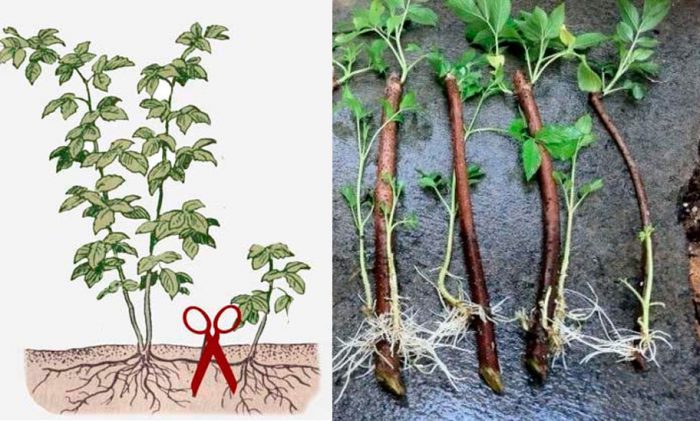
Propagating raspberries is very simple, easy and quick.How to reproduce it by offspring was described in detail above. Cuttings are also used for propagation of this plant. Cuttings are cut in June on a cloudy day; for this, two-year or three-year-old root suckers are chosen. The length of the cuttings should be from 10 to 12 centimeters, and they should have 2 or 3 leaf plates. The cuttings are immersed for 12 hours in an agent that stimulates the growth of roots, after which they are planted in containers with a volume of 0.5 liters, which must be filled with sand mixed with peat. The containers are removed under the film, while it should be borne in mind that the air humidity required for rooting of the cuttings should be about 90 percent, and the temperature should be from 22 to 25 degrees. After 4 weeks, the cuttings should start growing. When this happens, they are carefully transferred together with a lump of earth into a more spacious container: its height should be at least 14 centimeters, and its volume should be 1.5 liters. After the cuttings have taken root, they must be hardened, for this they are taken out for a while in fresh air. Hardened cuttings are planted on a training bed, they will need shading from the scorching sun's rays, which is removed only when the plants take root and start growing. In autumn, they are transplanted to a permanent place. Cuttings harvested in autumn must be treated with a fungicide, which will protect them from fungal diseases. Then the cuttings must be covered with peat and stored in a cellar, basement or other cool place. Thus, before the onset of the spring period, the cuttings will undergo stratification; it is important not to forget to systematically moisten the peat. In spring, the cuttings are immediately planted on the garden bed, while its surface must be covered with a layer of mulch.
There are types of raspberries, for which the rooting of the tops (like in blackberries) is used for reproduction. So, they include purple and black raspberries. In the first autumn weeks, the grown shoot begins to lean towards the soil, while the leaves located on its top become smaller, and the shoot itself acquires a loop-like shape - at this time and make its rooting. This shoot should be separated along with the "handle", while it must be rooted in the same way as described above.
Pruning raspberries
Pruning raspberries in spring
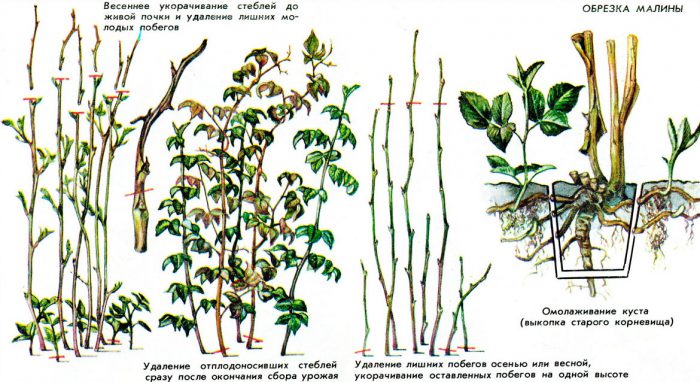
In spring, all stems affected by frost should be cut off from raspberries to a healthy bud, and also injured, diseased and underdeveloped branches should be cut out. If you follow the rules of agricultural technology for this culture, then 10-15 shoots should fall on 1 running meter of the plot. In this regard, all shoots should be cut out on the bush, leaving only those that started growing first, they must be shortened by 15–20 centimeters. As a result of such thinning pruning, the quality of the fruit will improve, as well as they will be larger. Such pruning can be carried out if desired in the autumn, but still, with the onset of spring, all the stems injured and frost-damaged by the bushes will need to be cut out from the bushes. And according to I.V. Kazakov, cut bushes in the spring will give a richer harvest.
Pruning raspberries in autumn
In the fall, after harvesting, you need to remove all two-year-old stems, since in the next season they will not bloom and bear fruit. Of course, they can be cut out in spring, but in this case they will take away the nutrients from the plant that are so necessary for it in winter. All stems that have borne fruit in the current season should be cut. If the raspberries you are growing are not remontant, then you can prune them earlier, and it is not at all necessary to wait for late autumn. Experts recommend carrying out a similar procedure immediately after the entire crop from the bushes has been harvested, in this case all the forces of the raspberry will be directed to the growth and development of young shoots, namely, they will bear fruit in the next season.If remontant varieties are grown, then they should be cut off at the end of the second fruiting. It is recommended to destroy all cut stems, as pathogenic microorganisms and various pests can settle on them.
Wintering raspberries
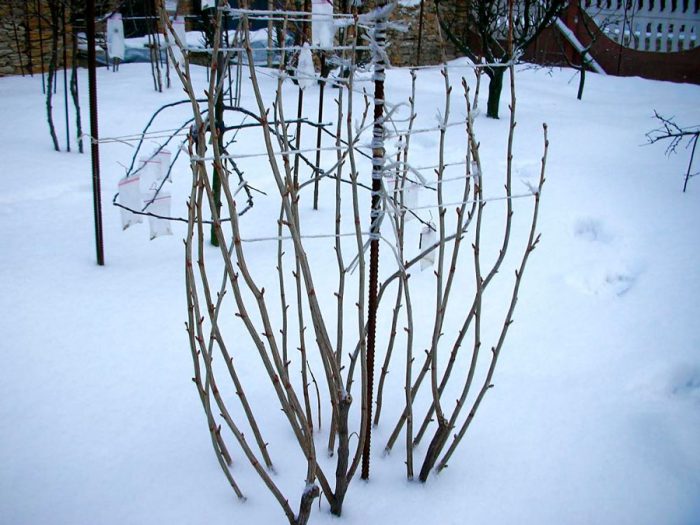
It is very important to properly prepare the raspberries for wintering. It is a very common opinion among gardeners that raspberries need to be tied up for the winter and left in a standing position. However, this should not be done in any case, because flower buds not covered with snow can freeze out. The bushes are bent as close as possible to the soil surface and fixed in this position, tying trellis to the lowest wire. All foliage must be removed from the stems; for this, put on mittens and run along the shoot from the bottom up. Be careful, because if you pull off the foliage by running your hand from top to bottom, this can lead to the removal of flower buds. Try to keep the shrub completely covered with snow during the winter. Therefore, if necessary, the raspberry tree will need to be covered with snow.
It is also very important to remember that wintering plants need air; therefore, the ice that appears on the snow cover must be pierced. If the winter is not very snowy, in this case the raspberry tree will need to be covered with a covering material. In the springtime, the shelter must be removed from the site. Look at all the stems and remove those affected by frost. The remaining shoots can be lifted and tied to the trellis.
Raspberry diseases and their treatment
Raspberries turn yellow
Many gardeners are interested in why the raspberry foliage turns yellow and flies around? In the event that the foliage on the bush has changed its color to yellow, then this means that this specimen is infected with root cancer, rust or chlorosis. You can find out that a plant hurts such an incurable disease as root cancer by the swelling that appears on the surface of the roots, the stems grow too short, the fruits have no taste, and the leaf plates turn yellow and fly around. Infected plants should be removed from the ground and destroyed, while the area on which they grew should not be used for planting for at least 8 years. If the plant is infected with rust, then it will begin to appear in May. Drying, yellowing and flying around the foliage will begin, ulcers of a dark color will appear on the surface of the stems. Such a disease can be cured only at the initial stage of development; for this, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture (1%). If the disease is already running and the bushes are very badly affected, then they must be dug up and destroyed. The main carrier of such a viral disease as chlorosis is aphids. In this regard, in order to protect raspberries from chlorosis, it is necessary to take all the necessary measures to combat aphids. In infected specimens, leaf plates become smaller and deformed, the stems stop developing, the fruits dry out and lose their taste. In some cases, the development of chlorosis can be caused by the use of cold water for irrigation, a strong alkaline reaction of the soil, an insufficient amount of trace elements in the ground, or stagnant water in the soil. Try to find out what exactly caused the development of this disease, and eliminate it as soon as possible.
Raspberries dry
This culture is among the moisture-loving, so if the plants do not get moisture, then the foliage will begin to dry out. However, if the bushes are always watered on time and in sufficient volume, then you need to take a good look at the dried leaves. If you see thickenings on their surface, this means that the raspberries are affected by gall midge. This pest lays its larvae on the surface of raspberry leaf plates, as a result of which such thickenings appear, called galls. All infected shoots must be cut to the root, while there should be no stumps left, then they are burned.If this shrub is affected by purple spot, which is a fungal disease, then specks of brown-red color will first appear on its leaf plates, and over time they dry out. After all the fruits have been collected from the affected bushes, they need to be sprayed with Zircon. Cut out all the dried stems to the root immediately after it becomes clear that the plant is sick, but you do not need to wait until autumn comes.
Raspberry anthracnose
The fungal disease anthracnose actively develops in wet, rainy weather in summer. In the affected bush, gray spots with a red border appear on the surface of the leaf plates, the fruits dry up, and the ends of the shoots die off. In order to prevent planting, varieties that are resistant to this disease should be chosen, and all infected parts of raspberries should be cut and burned. Also, the affected specimen must be treated with Nitrafen solution.
Raspberry pests and control
The following pests can settle on raspberry bushes: aphids, spider mites, shoot and stem raspberry gall midges, weevil, raspberry nutcracker, raspberry beetle and raspberry stem fly. During the flowering period, a brown-yellow raspberry beetle can settle on this half-shrub. This pest feeds on the buds, flowers and foliage of the plant, while the females in the flowers arrange their egg-laying. The larvae hatching from the eggs eat the fruits. After the snow melts, the affected bushes must be sprayed with Nitrafen, and during the cherry blossoms they are treated with Fitoverm. The raspberry stem fly makes its oviposition in the axils of the apical leaf plates, the larvae that are born eat the stems from the inside. Raspberry gall midges and stem gall midges, as well as shoot gall midges, lay their eggs in young shoots, when the larvae hatch, they will eat them. If aphids have settled on the bush, then honeydew can be found on the surface of the stems and leaf plates, and the deformation of the shoots and twisting of the foliage also occurs. In addition, this pest is the main carrier of various dangerous diseases. Spider mites, settling on raspberries, suck out its juice, while they are carriers of viral diseases and gray rot. In the flower buds, the female weevil makes its oviposition, while gnawing at the pedicels. One individual can harm a large number of flowers (up to 50). To get rid of all the described pests, you need to treat the bushes with Karbofos or Aktellik in early spring and after all the fruits have been collected. And most importantly, remember that if you adhere to the rules of agricultural technology, then you will not have problems with pests.
Raspberry varieties with photos and descriptions
Many varieties of raspberries are divided into large-fruited, traditional and remontant. Traditional varieties are distinguished by their reliability, they quickly adapt to climatic conditions and are undemanding to the soil, but it will not be possible to collect a rich harvest from them. The stems of large-fruited varieties branch relatively strongly, due to which they are distinguished by high yields, their fruits are large and fragrant. Repaired varieties give 2 crops per season, while they stop bearing fruit only with the onset of very strong frosts. Also, these varieties differ from each other in color and quality of taste of fruits, ripening period, and also in the degree of resistance to diseases and harmful insects.
Early maturing varieties
- Cascade... A medium-sized variety that reacts negatively to drought and is prone to spotting. The height of the slightly thorny bush reaches 200 cm. The shape of the dark red fruits is blunt-conical, they weigh about 3.5 g, the taste is sweet-sour.
- Cumberland... The variety has moderate frost resistance and resistance to pests and diseases. Black fruits weigh about 2 g.The bush can reach a height of 200 cm, the stems are arched, does not give root suckers.
- Golden Giant... This large-fruited variety is resistant to frost and high yields. Large yellow fruits weigh 8-14 grams.
- Vega... The frost-resistant variety is resistant to fungal diseases. The height of the bush is about 250 cm, a lot of spiny shoots grows. The shape of the raspberry fruit is blunt-conical, weighing about 4 grams, the taste is sweet and sour.
- Glen Ample... The variety was created in England. It is resistant to frost, diseases and pests, has a very high yield (up to 15 tons of berries are harvested from 1 hectare). The height of a strong bush is about 350 cm, the stems branch well. The deep red dense fruits are round-conical and weigh about 4 grams.
Late-ripening varieties
- Ruby... The frost-resistant variety is susceptible to anthracnose attack. Plant height about 1.8 m, on the surface of the shoots there are many short thorns of dark purple color. The shape of the rich red fruits is blunt-conical, they weigh about 3.5 grams.
- Mirage... The variety is resistant to pests and diseases. On the surface of medium-sized bushes there are small, short and rather soft thorns of a dark red color. The shape of large red fruits is elongated, weighing about 6 grams.
- Stolichnaya... The variety is resistant to diseases and frost, differ in yield (up to 4 kilograms of fragrant fruits are harvested from 1 bush). The height of an upright compact bush is about 200 centimeters. Large red fruits weigh about 8 grams.
Repaired varieties
- Orange Miracle... The variety is resistant to pests and fungal diseases. Orange glossy fruits have high taste, they are elongated and weigh from 7 to 9 grams. The taste of berries is sweet and sour.
- Apricot... The fruit is golden in color with a delicate scent Their shape is blunt-conical, and they weigh about 3.5 grams.
- Mulatto... The variety is high-yielding, highly resistant to fungal diseases and pests. The sweet-sour, round, glossy fruits, colored in dark cherry color, weigh about 4 grams.
- Brilliant... The variety has a high yield, about 3 kg of fruits are harvested from 1 bush. Large ruby-colored fruits have a bright shine and conical shape, weigh about 7 g. Sweet-sour, dessert taste.
Raspberry properties
Raspberries include fructose, organic acids - citric, malic, tartaric, ascorbic, formic, nylon, as well as vitamins and trace elements - magnesium, iron, potassium, calcium and phosphorus. For a long time, raspberries have been used as a cure for colds, for example, tea is prepared with dried berries, jam is made, or fresh fruits are ground with granulated sugar. Raspberry differs from other berries in that after heat treatment, all of its beneficial properties are preserved. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from the foliage of the plant, used for sore throat and cough. And the infusion made from foliage and flowers is used to treat hemorrhoids and gynecological diseases. Preparations made from berries, flowers and foliage have antipyretic, antioxidant, anti-sclerotic and anti-inflammatory effects; they are used in the treatment of colds, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, anemia, heart rhythm disturbances, and kidney diseases. In oriental medicine, impotence and infertility are treated with similar drugs.
An infusion made from foliage is used for acne, erysipelas of the skin, eczema and rashes, while rubbing the surface of the epidermis. Lotions are made from it for conjunctivitis and blepharitis. A decoction is prepared from the roots, which is used to treat purulent otitis media and stop hemorrhoidal and nosebleeds.
Recently, research has been conducted at Clemson University regarding raspberries.Experimental animals with cancerous tumors were given raspberry extract, which led to the death of 90 percent of the cancer cells. This result cannot be repeated by more than one antioxidant known to science. At the same time, all varieties of raspberries have this effect.
Raspberries have a number of contraindications. It is not recommended to use it during an exacerbation of gastritis, stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers. It is also contraindicated for people suffering from nephritis, gout and amyloidosis.