The herbaceous perennial plant horseradish (Armoracia rusticana), either village horseradish or horseradish, is a member of the Horseradish genus of the Cabbage family (Cruciferous). Under natural conditions, such a plant can be found in the Caucasus, Siberia and Europe, while it prefers to grow in damp places along the banks of various reservoirs and rivers. Horseradish is cultivated in all countries, including Greenland. Already in ancient times in Greece and Rome, people began to eat it. The first written sources where there is a mention of horseradish date back to the 9th century AD, according to scientists, it was at this time that it began to be grown in Russia. It was used as a seasoning for meat and fish dishes, it was added grated to kvass, as well as to various pickles. In Western Europe, or rather, in Germany, such a culture began to be grown again only in the 16th century, they began to season various dishes with it, and also used it as an additive in beer and schnapps. After that, it began to be cultivated in Scandinavia, France and England, where it was also called "horse radish". At this time, horseradish was already used, not only adding to various dishes, but also as a folk remedy with powerful healing properties.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Landing... In the last days of March or in the first days of April.
- Illumination... Needs the bright light of the sun.
- Priming... Sandy loam, loamy or chernozem soil, which must be nutritious.
- Watering... It is necessary to water systematically, while 1 to 2 buckets of water should go per 1 square meter of the plot. If it rains regularly in the summer, then horseradish can do without watering.
- Fertilizer... The first time they are fed after the formation of the first true leaf plates, for this they use a solution of complex mineral fertilizer. After 15–20 days, re-feeding is carried out, for this they use organic matter, or rather, a mullein solution.
- Reproduction... Vegetatively (parts of the rhizome), less often the seed method is used.
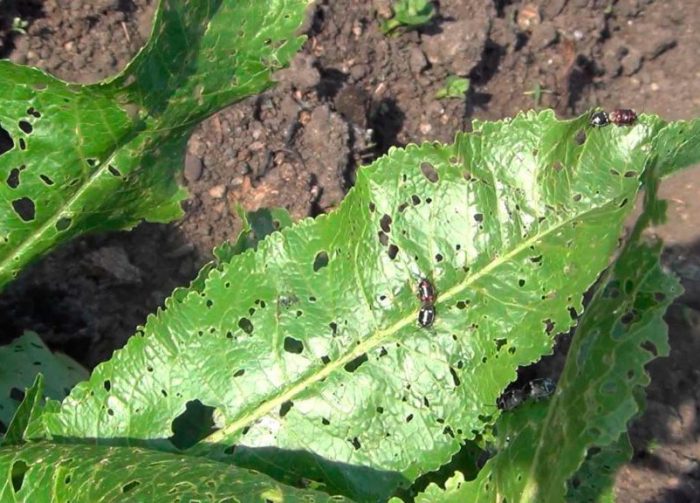
- Harmful insects... Cruciferous fleas, rapeseed bugs and flower beetles, cabbage bugs and moths.
- Diseases... White rot, leucorrhoea, verticillosis and viral mosaic.
Horseradish features
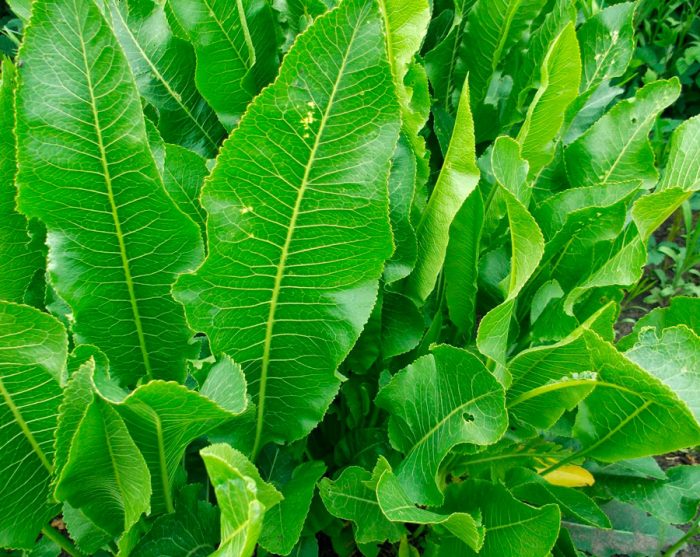
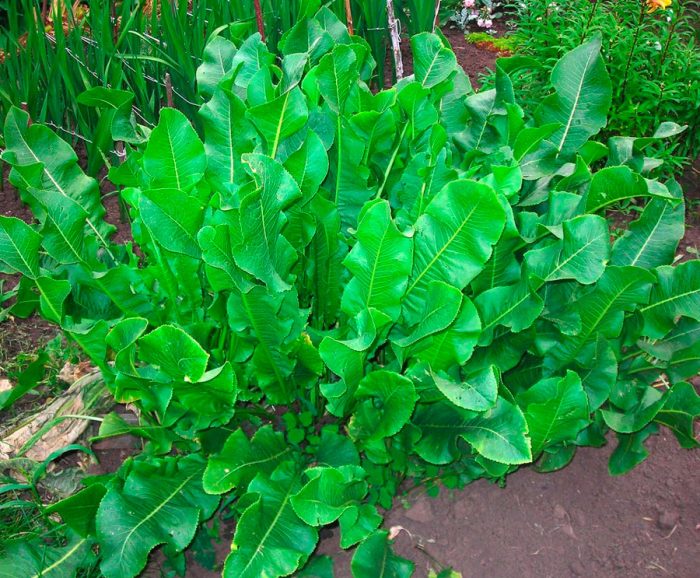
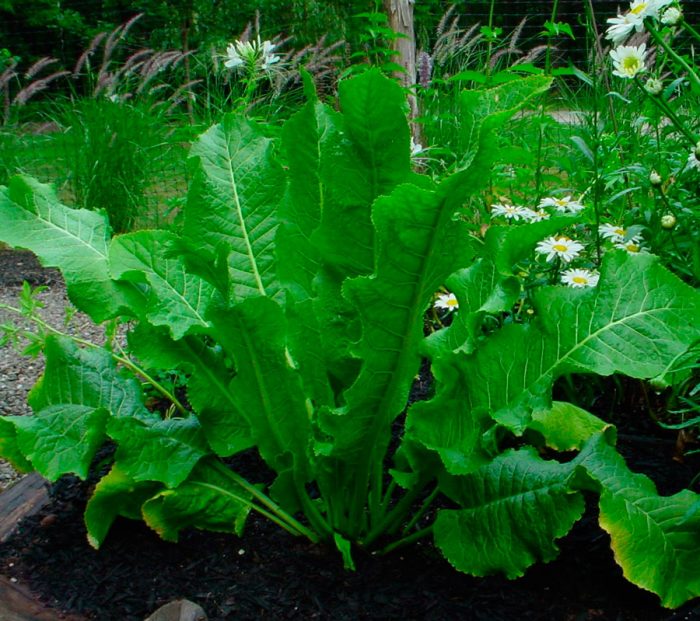
Horseradish forms a fleshy and thick root crop. The stem is straight and branched, its height can vary from 0.5 to 1.5 meters. Very large crenate basal leaf plates have an oblong-oval shape, while at the base they are cordate.The upper leaf plates are whole-edged linear, while the lower ones are pinnately separate. In white flowers, the length of the petals reaches 0.6 cm. Fruits are swollen pods of an oblong-oval shape, the length of which is 0.5-0.6 cm, on the surface of the valves there is a reticular-vein pattern. Inside the pods, there are nests containing 4 seeds. This perennial plant is distinguished by its amazing unpretentiousness and frost resistance. Having planted it once, it will be impossible to get rid of it, since it behaves extremely aggressively, akin to weed grass.
Each part of the bush contains an essential oil that has a pungent smell and taste. The root juice of such a plant contains ascorbic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, carotene, starch, carbohydrates, fatty oil, resinous substances and protein lysozyme, which has a powerful antimicrobial effect. The root vegetable contains mineral salts of calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur, phosphorus, copper and iron. Official medicine has known for a long time that horseradish has powerful healing properties, so it helps to improve intestinal activity, has a choleretic, antiscorbutic and expectorant effect. It is used in the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract, liver and bladder, colds, gout and rheumatism.
Planting horseradish in open ground
What time to plant
Horseradish planting in open soil is carried out in early spring, or rather, in the last days of March (if it is warm) or in April. This culture is not afraid of any frost or cold snap. A small, well-lit area located near the fence is perfect for planting such a plant.
The most popular is the vegetative way of horseradish propagation by parts of the rhizome. However, it is quite possible to grow it from seeds, but this method is relatively labor-intensive, for which gardeners do not like it.
Horseradish soil
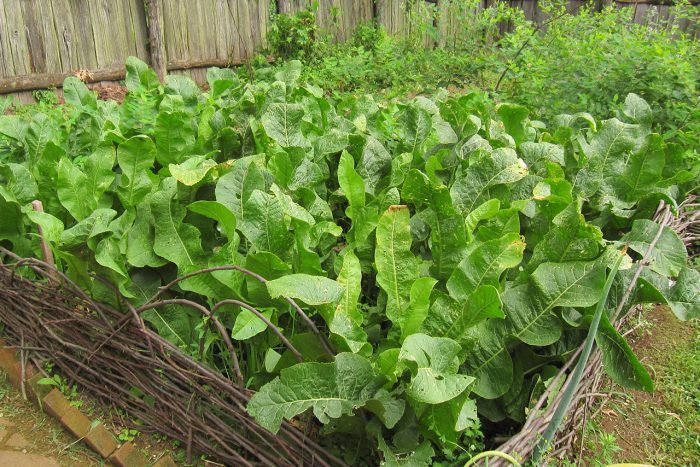
This culture grows well in nutritious soil, which can be black soil, loam or sandy loam. If you properly prepare clay soil, then such a plant will develop and grow on it within normal limits. To do this, in the autumn months, during the digging of such a site, sand, peat, and manure should be added to the soil (per 1 square meter from 10 to 12 kilograms). At the same time, minerals are introduced into the soil in the spring: 30 grams of superphosphate, potassium salt and ammonium nitrate per 1 square meter of the plot. If, for the cultivation of such a root crop, a site with a suitable soil for it is chosen, then organic fertilizers are recommended to be applied under the previous crop, for example: legumes or cereals.
Landing rules
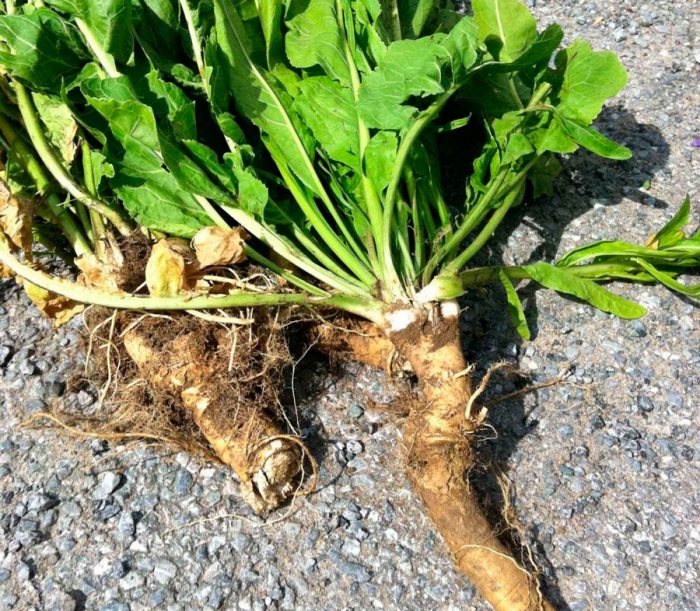
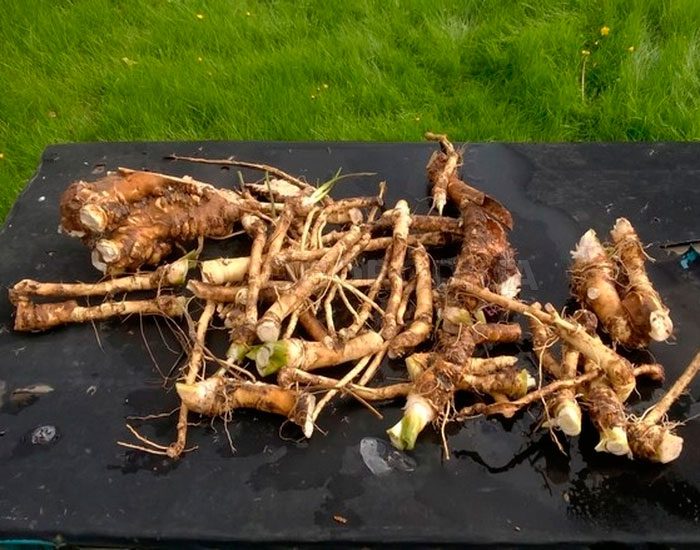
Harvesting of root cuttings should be carried out in the autumn along with the harvest. They are stored for storage in a cellar or basement, buried in dry sawdust or sand. Harvesting of root cuttings can also be carried out at the beginning of the spring, before leaf plates appear on the bushes. When 10-15 days remain before planting in the ground, the cuttings should be taken out of storage and, covered with a damp cloth, removed to a warm place. This is necessary in order for the buds to germinate.
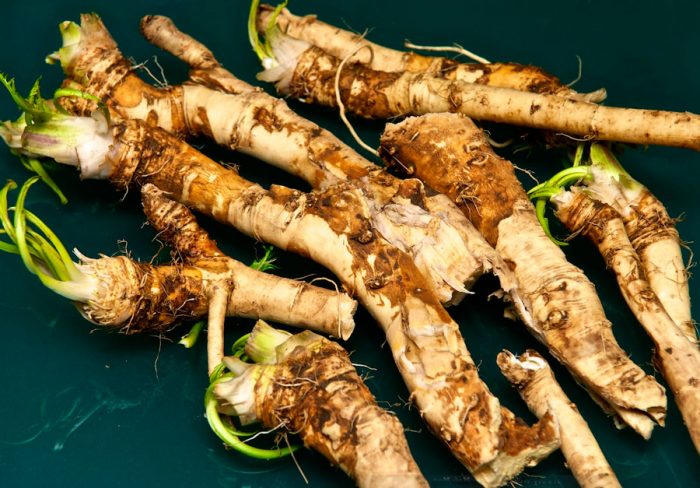
Before proceeding with planting, the lateral processes must be separated from the main root, the length of which should not be more than 25 centimeters, and in diameter they should reach up to 1.2 centimeters. If the stalk is very long, then it must be divided into parts, while the lower cut should be oblique, and the upper cut horizontal. Then they are planted on a previously prepared site, while it should be borne in mind that there should be no more than 4-6 bushes on 1 square meter. When planting cuttings, the distance between them should be from 0.3 to 0.4 m, and the width between the rows must be kept within the range from 0.65 to 0.7 m. To harvest a rich crop of even root crops, the cuttings must be prepared before planting.To do this, take a coarse tissue and rub the middle part of the cutting with it, as a result you will remove excess buds from it, while leaving only the upper buds for the formation of foliage and the lower ones for the formation of the root system. When planting such a vegetable in order to obtain planting material, it is not necessary to remove sprouted buds from the cutting, in which case the root of the bush will be very branched and a large number of cuttings can be obtained.
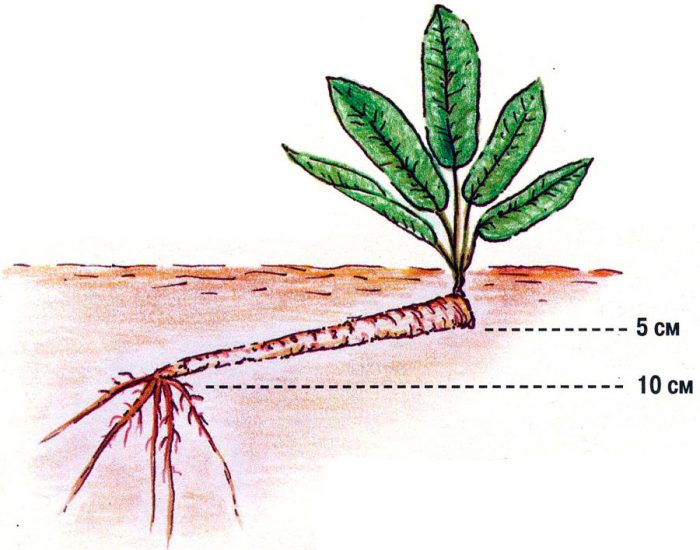
It is necessary to plant cuttings in open soil at an angle, while their top is buried only 50 mm into the ground, and the lower part - 100 mm. For the propagation of such a vegetable, small pieces of roots are also suitable, the thickness of which should be no more than 25 mm, and the length up to 80 mm, they must be planted horizontally in the soil, while it is not necessary to remove the buds from them.


Watch this video on YouTube
Planting horseradish before winter
This plant is planted in the ground in the autumn in the same way as in the spring. In this case, it is recommended for him to choose a site on which tomatoes or potatoes were previously grown, while all the necessary organic matter must be introduced into the soil before planting such crops. All weeds and plant debris must be removed from the site, and when it is dug up, you can start planting horseradish. It is best to plant horseradish before winter in mid-October.
Horseradish care
After horseradish sprouts appear from the soil, they must be thinned out. During this procedure, it is necessary to remove all weak and poorly developed shoots, leaving the most powerful ones. In July, lateral branches are trimmed from the root crop, for this it should be carefully excavated and all existing side roots removed from its upper part (up to 0.25 m). When all the rhizomes have been processed, they are again carefully covered with soil, which is then thoroughly compacted and watered. At the same time, try to avoid voids near the rhizome. The rest of the care of such a plant is very simple, it must be watered, weeded, loosened up the soil surface near the bushes in a timely manner, and also provide protection from various harmful insects and diseases.
Watering
Throughout the growing season, watering such a vegetable should be systematic. During such a procedure, 1–2 buckets of water should be consumed per 1 square meter of the plot. Particular attention is paid to watering during prolonged drought. If it rains systematically in the summer, then horseradish can do without watering at all, since if liquid stagnates in the soil, then rot may appear on the roots, which will cause the loss of the entire crop.
Fertilizer
After the first leaf plates appear, the bushes should be fed with a mineral complex, for this, 8 grams of superphosphate, 5 grams of ammonium nitrate and the same amount of potassium salt are taken per 1 square meter of the garden. If the growth and development of the bushes is very slow, then 15–20 days after the first fertilization, they must be fed with a mullein solution (1:10).
Horseradish pests and diseases
Horseradish is more resistant to diseases than other crops belonging to the Cruciferous family. If such a plant is poorly looked after or does not provide optimal conditions for growth, then the bushes can be affected by linen, mosaics, white rot or verticillosis. Cruciferous fleas, rapeseed bugs and flower beetles, cabbage bugs and moths can harm such a root crop.
To date, viral diseases are considered incurable, so if horseradish strikes a mosaic or verticillary wilting, then such bushes must be dug up and destroyed. If the plant is affected by white rot or linen, which are fungal diseases, then they can be cured only at the very beginning of the development of the disease.To do this, they are treated with a solution of the drug containing copper (for example: copper sulfate, Tiovit Jet, Bordeaux liquid, Oxychom or another similar agent).
In order to prevent the appearance of harmful insects on the plants, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of this crop: observe the rules of crop rotation, remove weeds from the site in time, when the harvest is collected, the site must be cleaned of plant residues, and then it is deeply digged. Insecticidal preparations can also help in pest control. If bugs and fleas have settled on the bushes, then they need to be sprayed with a solution of Foksim or Aktellik, fireflies and flower beetles are destroyed with Etaphos, Tsimbush or Zolon.
Please note that all chemical treatments should be stopped 20 days before harvest. It should be remembered that bushes weakened by improper care most often get sick, and harmful insects also prefer to settle on them. And if you look after horseradish correctly and adhere to the rules of agricultural technology, then you will be able to protect it from many diseases and pests.
Horseradish cleaning and storage
Already in August, they begin to cut horseradish foliage, it is used as a spice during the canning of tomatoes, cucumbers and other vegetables. At the same time, remember that if you cut off all the leaf plates from a bush, then this will have an extremely negative effect on the development of the rhizome. Foliage pruning should be carried out at a height of 10 to 15 centimeters from the surface of the soil, in this case both the apical bud and the leaf will remain unharmed.
Mass harvesting of root crops is carried out in the last days of October or the first - November before the frost begins, at which time the foliage turns yellow and begins to dry out. When planting large cuttings, harvesting is carried out in the same season. If relatively small root cuttings were planted, then normal root crops from them will grow only in the next season. Before you start harvesting, you need to cut off all the foliage from the bushes, then dig the rhizome with a shovel and pull it out of the soil. Remember that if at least a few pieces of small roots remain in the ground, then next year they will look more like weeds. As soon as the roots are removed from the soil, they need to be removed to a cool room without tightening. Then, soil residues and side branches are removed from them, the cuts must be coated with iodine. To dry, horseradish is removed in a warm, well-ventilated place for 24 hours.
For storing root crops, wooden boxes are used, on the bottom of which a layer of soil must be poured, while they are laid out on it in rows so that their surfaces do not touch each other. After the row of horseradish has been laid, it should be sprinkled with clean sand. When the vegetable is placed in boxes, it is stored in the cellar or basement. For storage, the root crop can also be put on a refrigerator shelf, but in this case its length should not exceed 0.3 m, while each of them must be wrapped with cling film, in which do not forget to make several holes for ventilation. Horseradish retains its properties on a refrigerator shelf for vegetables for about 20 days. In frozen form, it can be stored for up to 6 months, for this, the skin is removed from the root crop and cut into cubes, after the moisture that has come out from them is removed (you can use napkins) they are poured into a plastic bag and put into the freezer.
Horseradish can be dried if desired. To do this, the root should be cut into small slices, which are laid out on a baking sheet in 1 layer, after which it is removed in the oven for 90 minutes. the temperature should be no more than 60 degrees. The dry and hardened root is crushed, for this you can use several devices: a grater, a coffee grinder or a mortar. The resulting powder must be poured into a porcelain or glass container, which is closed with a lid.Before using the ready-made powder for its intended purpose, it must be mixed with water to soak it. The shelf life of dried horseradish is no more than two years.
Such a vegetable can be pickled. To do this, take 1 kilogram of root vegetables that need to be peeled and rinsed. They are rubbed on a grater or passed through a meat grinder, and the resulting mass is tightly placed in a glass jar, which must be sterilized in advance, after which the marinade is poured into the container. For its preparation in 1 tbsp. put boiling water on 1 large spoonful of salt and granulated sugar, when the marinade is removed from the stove, add ½ tbsp. apple cider vinegar (6%). If desired, 1 large spoonful of citric acid can be used to replace the vinegar. The freshly boiled marinade is poured into a horseradish jar, which is rolled up with a pre-sterilized metal lid. The pickled vegetable retains its properties for several years.
Types and varieties of horseradish
Below, those horseradish varieties that are considered the best will be described in detail:
- Atlas, or Wild... This medium-ripening variety is resistant to drought, frost and moisture. The length of the root crop can vary from 0.2 to 0.5 m, it reaches 40-50 mm in diameter, and it weighs 190-380 grams. The color of not too juicy dense pulp is milky white.
- Valkovsky... This late variety is resistant to diseases and cruciferous midges. The cylindrical root crop of a pale yellow color reaches 0.5–0.6 m in length and 20–30 mm in diameter. On average, the root weighs about 150 grams.
- Suzdal... An even root crop has no lateral branches, its length is about 0.3 m, and in diameter it reaches 30 mm. Its white flesh is juicy and very pungent.
- Tolpukhovsky... Root crops of such a late variety in length reach from 25 to 35 centimeters, and they weigh 65-250 grams.
In addition to these varieties of horseradish, the following are popular among gardeners: Riga, Jelgavsky, Latvian, Rostovsky, Volkovsky, Marune, Boris Yeltsin, etc.
The gardeners also cultivate the katran plant, which is a relative of horseradish and is distinguished by its unpretentiousness, nutritional value and resistance to frost. This plant is also used as a medicinal plant, it contains a large amount of minerals and vitamins. Despite all the advantages, it is not cultivated as widely as horseradish, although on top of that it does not grow on the site like an aggressive weed. Katran has large greenish leaf plates with a blue tint. They are boiled and served as a side dish for meat and fish dishes.


Watch this video on YouTube




















I read the article about horseradish with interest. It describes in detail how to breed horseradish on the plot, watering, soil, etc. We have horseradish growing without any care. It can be seen in the fields as a weed. It is difficult to get rid of it at the dacha. Of course, when preparing, you cannot do without horseradish.
And as an independent preparation, it's also good for the winter. You only need
make sure that it does not occupy the whole garden. And all the same, there is a great benefit from horseradish. I advise you to read the article about horseradish