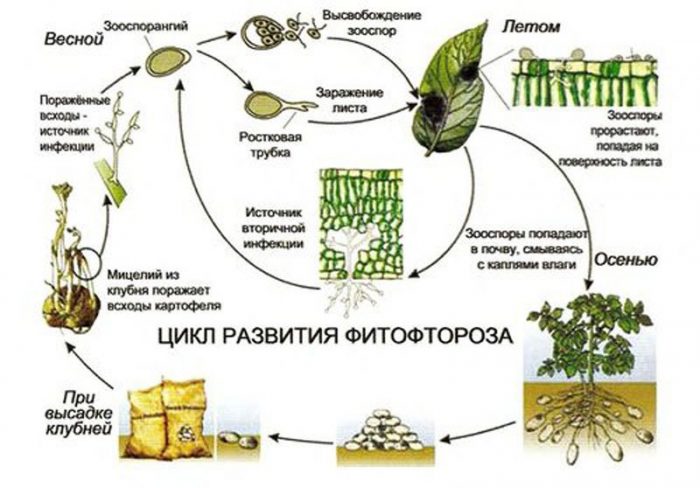
Phytophthora (Phytophthora) is a genus of mushroom-like microorganisms that cause late blight disease. More than 70 species of late blight have been described by experts, but there are about 500 more varieties that have not yet been described. The name "late blight" is derived from two Greek words that translate as "plant" and "destroy". Most often, this disease affects plants belonging to the Solanaceae family: tomatoes, peppers, potatoes and eggplants.
Content
Features of late blight (late blight)
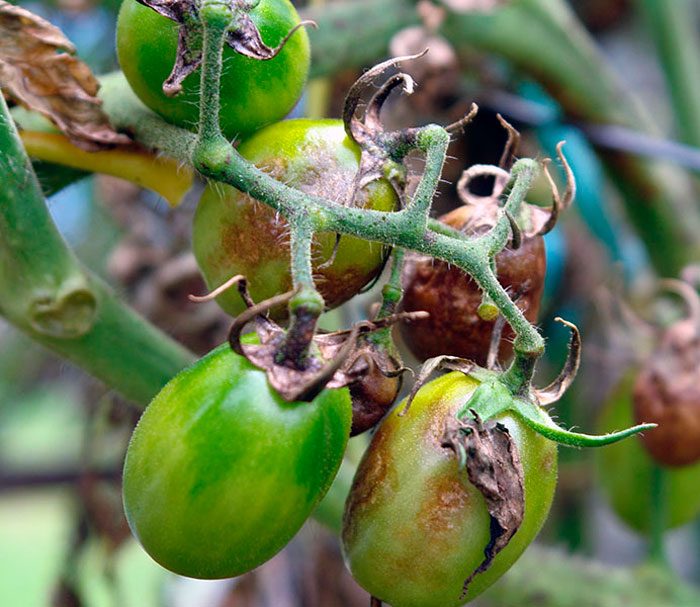
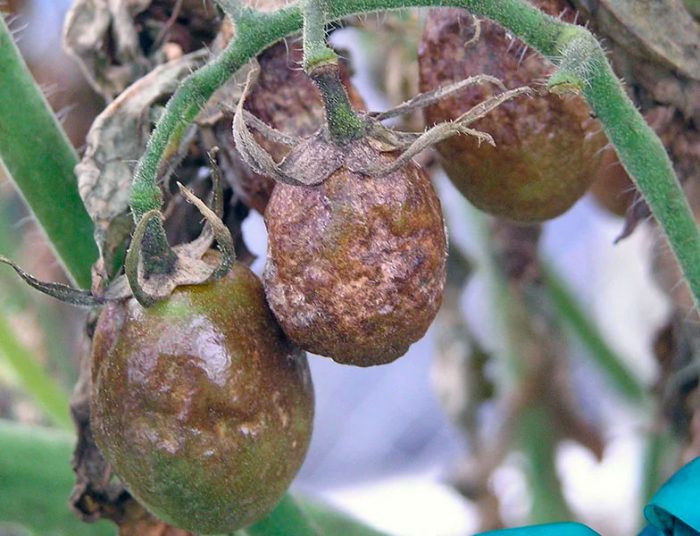
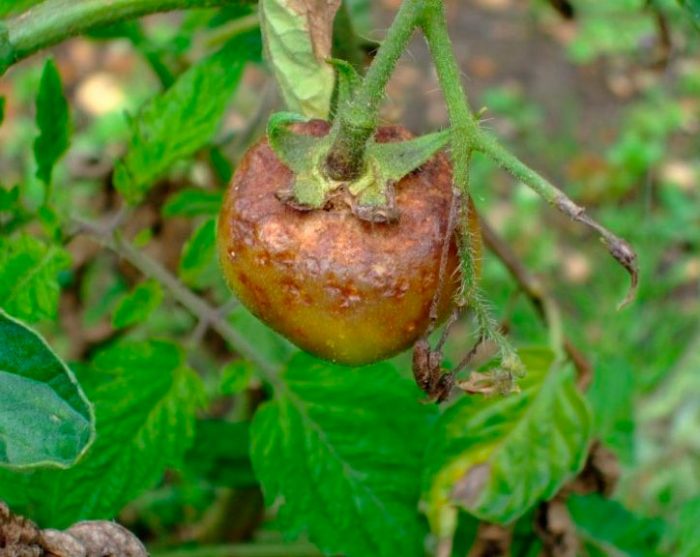
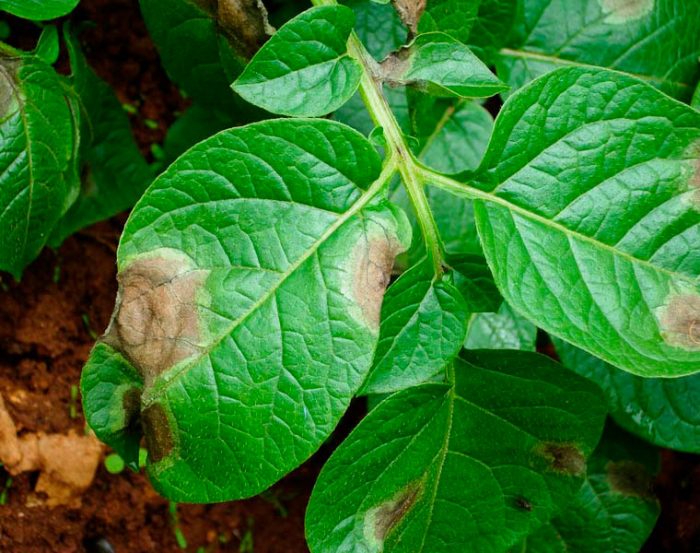
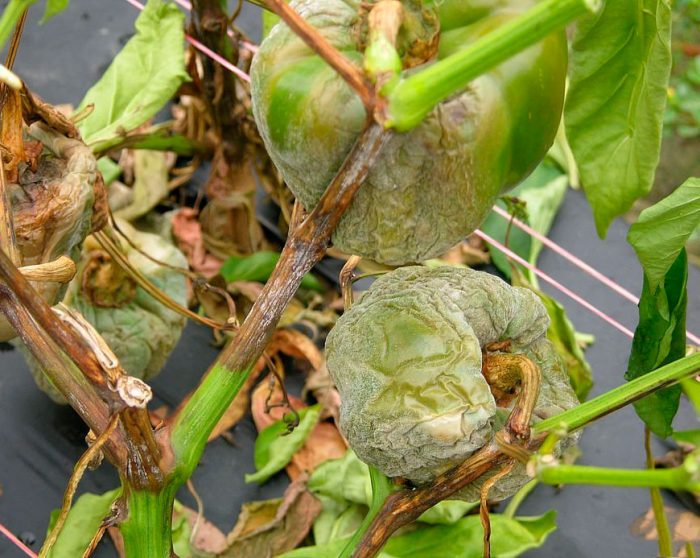
The disease late blight (brown rot), as a rule, manifests itself in the second half of the summer period. It can destroy up to 70 percent of the potato and tomato crop. The simplest fungus Phytophtora infestans is the causative agent of such a disease, it has the ability to multiply rapidly, for which it is called an "infectious plant eater." Most often, the lower leaf plates are affected first, but then the disease gradually spreads to the entire plant. With increased air humidity, brown specks form on the foliage, which are covered from below by a fluffy white coating, consisting of fungal spores. Dark brown stripes appear on the affected shoots. When the air humidity rises, the spots and stripes begin to rot, but when the weather is dry, then they begin to dry out. Over time, the affected foliage becomes similar to a dry crust. Rotting and decaying areas of a dark color appear on the surface of the skin of the affected tubers. And even seemingly completely healthy tubers stored in storage can begin to rot after a while.
Late blight spots can also form on fruits, and they increase both in depth and in width. Both mature and green fruits get sick with late blight. And if you plucked absolutely healthy peppers and tomatoes from diseased bushes, they will still turn black over time.
Fight against late blight
Prevention measures
In order to prevent the appearance of late blight on your site, you must definitely adhere to the preventive measures that are recommended by experts.Thus, preventive spraying of crops from late blight with solutions of special preparations is among the preventive measures.
The main agricultural techniques that will help protect the site from late blight:
- For cultivation, it is recommended to choose those varieties that are resistant to late blight.
- Remember the rules of crop rotation.
- Plants belonging to the Solanaceae family are not recommended to be grown close to each other. For example, if the symptoms of late blight are noticed on potatoes, then after only 1-2 weeks, eggplants, peppers or tomatoes will already be affected by this disease.
- Landings should not be thickened. Remember that insufficient ventilation and cramped conditions contribute to the rapid spread of late blight.
- Also, sudden changes in temperature at night and during the day can contribute to the development of the disease. Because of this, experts advise that planting seedlings in open ground only after all returnable spring frosts have passed or the seedlings can be covered with something at night.
- Try not to allow a strong increase in the level of humidity. For this, the surface of the site can be covered with a layer of mulch, and water during irrigation is not recommended to be poured directly onto the plants.
- Do not overfeed the plants, and especially carefully apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers to the soil.
- Collect fruits after they have reached the technical ripeness stage. Do not wait until the fruits are overripe.
- All foliage that grows below the fruit must be cut off, the same is done with flowers that do not give ovaries.
- All fruits and bushes affected by late blight are removed from the site and must be destroyed by fire.
- At the beginning of the development of the disease, you can try to defeat it with folk remedies that are time-tested and safe for both humans and animals, and for plants. However, if they are not effective enough, then you will have to resort to treating the plants with fungicidal preparations, which can be purchased at a specialized store.
Treatment with pesticides of plants
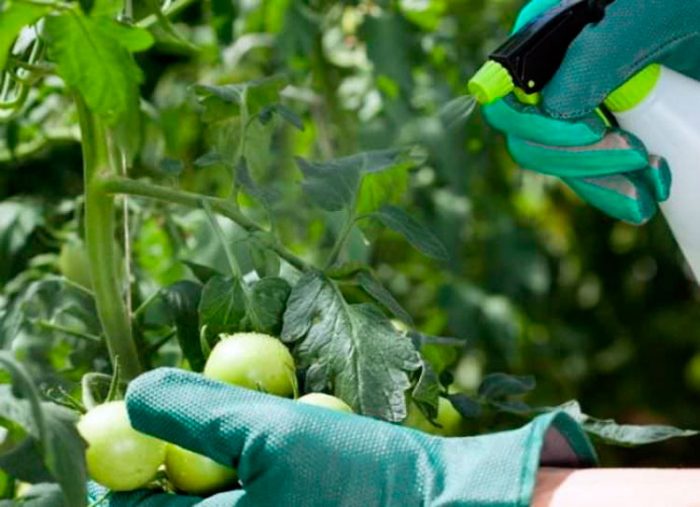
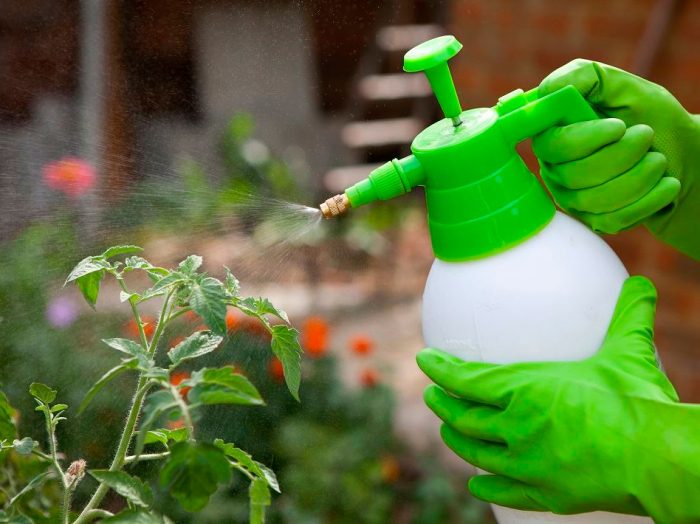
To cope with late blight, sometimes agricultural techniques alone are not enough, and the gardener has to treat crops with pesticides. To combat this disease, many chemicals have been created, but it should be remembered that late blight can very quickly get used to them. To prevent this from happening, the plants are treated with various means, alternating them.
For the first time, in order to prevent, the plants need to be sprayed in the spring, immediately after transplanting seedlings into open ground. Most experts advise that the timing of subsequent spraying of crops from late blight should be correlated with the growth of simple mushrooms in the forest: it is necessary to carry out treatments for fungal diseases at the time when forest mushrooms begin to grow, even if there are no signs of late blight on the plants. The bushes are sprayed from morning to noon, and they choose a sunny, dry and calm day.
Tillage
To clear the soil from phytophthora spores, microbiological preparations and fungicides are used. In order to prevent, the introduction of fungicidal preparations into the soil is carried out in early spring, at least 4 weeks before planting potatoes or planting seedlings in open ground. As for microbiological agents, they can be applied to the ground at any time during the entire growing season, except for the flowering time of plants, since this drug can harm bees.
Chemicals containing copper are quite effective in the fight against late blight, for example: copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid, Fitosporin-M, Trichodermin and Ordan. For example, for soil treatment, you can use a solution of copper sulfate (2-3%), after which the site is digged.Then the soil is spilled with a solution of Fitosporin (for 1 bucket of water 1 tbsp. L. Means), and 10 liters of the mixture should go to 1 square meter of the plot. Those areas that are intended for growing strawberries and flowers are spilled with a solution of Ordan or Alirin, the same funds can still be used for prophylactic spraying of grapes.
The greenhouse for this disease is treated in autumn and early spring; for this, special sulfur bombs are burned in it. During processing, do not forget about safety rules and stay away from the smoke emitted by the checkers.
Phytophthora on tomatoes: how to fight
Prevention measures
Many gardeners prefer not to allow late blight to develop on tomatoes, resorting to agrotechnical methods, than then fight this disease for a long time and intensely. It should be borne in mind that it is completely very difficult to get rid of late blight. Basic preventive measures:
- before planting seedlings, the soil on the site must be treated from phytophthora;
- when the seedlings are planted, the surface of the site is covered with a layer of mulch;
- timely tear off stepsons and lower leaf plates from the bushes;
- experts advise planting peas, corn or curly beans around the perimeter of the plot with tomatoes.
Immediately after the seedlings are transplanted into the open ground, they are sprayed with a solution of Trichodermin or Fitosporin-M for prevention purposes.
Fight against late blight on seedlings
If tomato seedlings were affected by late blight, then it is recommended to remove all diseased bushes, and then spill the soil mixture with Fitosporin-M solution. You can also dissect the seedlings into separate cups using fresh sterilized soil mixture that is spilled with Fitosporin. The same tool is used for soil treatment in the area where tomatoes will be planted. Remember that after processing the soil in the garden with a fungicidal preparation, at least 30 days should pass, only then it will be possible to plant tomatoes in it. If you do not have that much time, then it is better to use Alirin for processing the soil on the site.
Tomato processing
If it often rains in summer, then in order to cure late blight-affected tomatoes, they are treated at least 4 or 5 times with an interval of 1-1.5 weeks. The last time to spray plants with pesticides from phytophthora is necessary no later than 20 days before harvesting. In order to increase the resistance of tomatoes to diseases and strengthen their immunity, they are treated with the growth regulator Oxygumat (100 milligrams per bucket of water) or Exiol (1 milligram per 3 liters of water).
Phytophthora can affect both those plants that grow in open ground and those grown in a greenhouse. If tomatoes growing in greenhouses are affected by the disease, then the gardener can lose almost the entire crop. To combat this disease in the greenhouse, the same chemicals are used as when processing bushes in the open field. However, in no case should you neglect the safety rules, since it is much easier to poison yourself with pesticides in the greenhouse than when processing tomatoes in the open field.
Remember that all bushes need to be treated for late blight at once, because a single treatment will be ineffective. And in general, this disease cannot be completely defeated, and all the means used for treatment only suppress its development.


Watch this video on YouTube
Preparations for phytophthora
Late blight on tomatoes is treated with such means as: Bordeaux mixture, Ridomil Gold, Tatu, Quadris, Baikal EM and Radiance. Before preparing the medicinal solution, it is imperative to study the manufacturer's instructions, which is on the package. To suppress the disease on the bushes, you can only after a few treatments with a break of 1-1.5 weeks.Remember that causative agents of the disease quickly get used to drugs, so do not forget to alternate them. Try to use a more powerful treatment with each subsequent treatment than the previous one.
Late blight on potatoes
Treatment for late blight
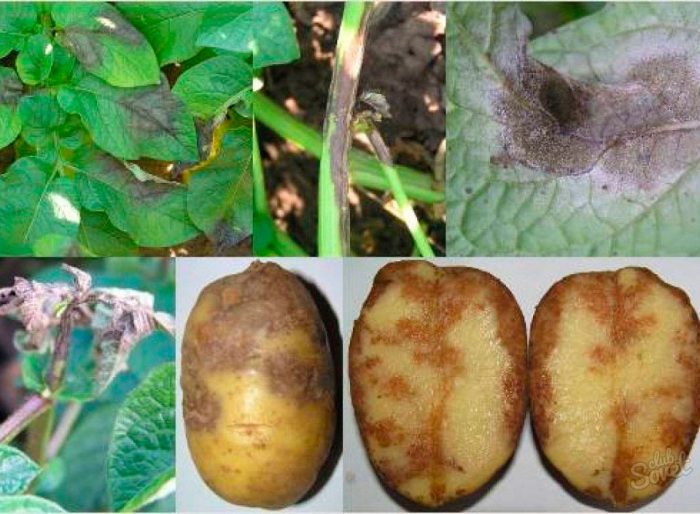
Symptoms of late blight of tomatoes and potatoes are very similar to each other: specks form on the foliage, which rapidly spread throughout the bush, as the disease develops, the leaf plates curl and dry out. If the tubers are affected by the disease, then hard spots can be found on their surface.
In order to prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to the following scheme for processing bushes:
- The first time the treatment with a systemic fungicidal preparation is carried out after the height of the tops is 25-30 centimeters. You can spray potatoes with the following means: copper sulfate (0.2 grams per 1 liter of water), Bordeaux liquid (1%) or copper sulfate (2 grams per 1 liter of water).
- Shortly before flowering, the bushes must be sprayed with such means as: Oxygumate, Epin or Exiol. But if the weather conditions are unfavorable for the development of late blight, then treat the plants only with a resistance inductor, for example, Krezacin or Silk: after 1-2 weeks, the bushes are sprayed with a contact fungicide, for example, Ditan M-45 or Efal, and you can also use copper oxychloride ( strictly follow the manufacturer's instructions), with preventive treatment, the dosage is reduced by 2 times. If the potato is very badly affected, then it is sprayed with Ridomil MC, Oxykhom or Ridomil Gold MC, after 1.5–2 weeks, they are re-sprayed with the same means. When the bushes have faded, they can be sprayed with a solution of Bravo, and after 1-1.5 weeks, the treatment is repeated with this preparation.
- During the ripening of tubers for treatment against late blight, it is recommended to use Alufit.
Processing is best done on a cloudy but dry and calm day. If it rains after spraying, the bushes will have to be processed again. Spraying the tops should be carried out until it completely dies out.
Prevention measures
To protect potatoes from late blight, you need to choose the most suitable place for planting it, and for growing it is best to use those varieties that are most resistant to this disease. Also, do not forget to process plants in time for prevention purposes. It is recommended to grow this crop in leveled areas. If you choose a lowland or a wet area for this, then this can cause the development of fungal diseases. The soil must be light and drained, and the site itself must be well lit and blown by the wind. If possible, choose an area for growing potatoes that is located away from other plants belonging to the Solanaceae family.
Potatoes will grow best in areas where perennial grasses, beets, winter crops, corn and flax were previously grown. And the worst predecessors of this plant are nightshades. After peppers, potatoes, tomatoes and eggplants, you can grow them again in the same area only after 4-6 years. If you do not have the opportunity to adhere to a full-fledged crop rotation, then it is recommended to grow potatoes on the site at least once every 2 years, while during the break it is sown with mustard or radish, which must be mowed and buried in the ground. Thanks to radish and mustard, the risk of potato damage by late blight or other fungal disease is reduced by 3 times.
Before proceeding with planting, it is recommended to process the soil on the site (how to do this is described in detail above). Also, experts recommend using only absolutely healthy planting material for growing.In order to understand which tubers are affected by late blight, it is recommended to keep them at a temperature of 15 to 18 degrees for 15 days. As soon as it becomes clear which tubers are sick, they should be removed, and the remaining planting material is treated with Fitosporin-M or Agatom-25K.


Watch this video on YouTube
Processing before planting
In order not to constantly worry whether your potatoes will be hit by late blight or not, it is recommended to choose varieties resistant to this disease for cultivation, for example: Lazar, Arina, Rosara, Visa, Verb, etc. Also, for preventive purposes, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied to the soil until planting potatoes or during it. And after the formed tubers begin to gain weight, the potassium component is increased by 1.5 times. If there is too much nitrogen in the soil, then this will cause a delay in the development of tubers, as a result of which their susceptibility to late blight increases. After the tuber mass gain is completed, the surface of the soil is loosened, and the tops are mowed, due to this, the process of increasing the density of the peel by the tubers is accelerated. And soil treatment on the site with a solution of Reglon Super can also help. And also do not forget to dig up and destroy plants affected by the disease in a timely manner, remove weeds from the site, and do not water the bushes by sprinkling if the weather is cool, dry.
Late blight on various crops
Above, it was described in detail how to deal with late blight on tomatoes and potatoes. However, this disease can also affect other plants. Peppers and eggplants are also affected by late blight nightshade. Symptoms of the disease on these crops are similar to those observed when potatoes or tomatoes are affected by late blight. And the preventive measures and methods of combating the disease in this case are the same as those used for tomatoes. But for the treatment of eggplant patients with late blight, experts advise using agents such as: Antracol, Consento or Quadris. When 8-10 days pass after transplanting seedlings into open ground, they are first sprayed with Quadris or Antracol. Then, every 12-14 days, repeated treatments are carried out regularly, and fungicidal preparations must be alternated, otherwise the fungi may develop addiction to them. Peppers affected by late blight are recommended to be sprayed with a Barrier, Oxychom or other fungicidal agents. Most importantly, remember that the bushes cannot be sprayed with the same agent twice or three times in a row. In some cases, late blight affects cucumbers grown in greenhouses, but only folk remedies can be used to process them (more on them below).
Preparations for phytophthora
In the fight against late blight, gardeners most often use the following pesticides:
- Fitosporin-M, Trichodermin and Alirin... These are microbiological fungicidal preparations of a wide spectrum of action, which are created on the basis of a natural bacterial culture.
- Antracol, bordeaux liquid and copper sulfate... These broad-spectrum contact fungicides are very effective.
- Quadris and Bravo... These systemic fungicidal preparations are used both for greenhouses and for open ground. They are distinguished by curative, protective and eradicating action.
- Ridomil Gold, Tattoo, Oxyhom and Ordan... These are fungicidal agents of contact and systemic action.
- Baikal EM... This biofertilizer helps to accelerate the growth of bushes and ripening of fruits.


Watch this video on YouTube
Folk remedies for phytophthora
Today, many gardeners are trying, if possible, to abandon the use of pesticides on their site.If the disease has just begun to develop, then it is quite possible to try to cope with it with folk remedies. Below will be described those folk methods for late blight, which are most popular with gardeners.
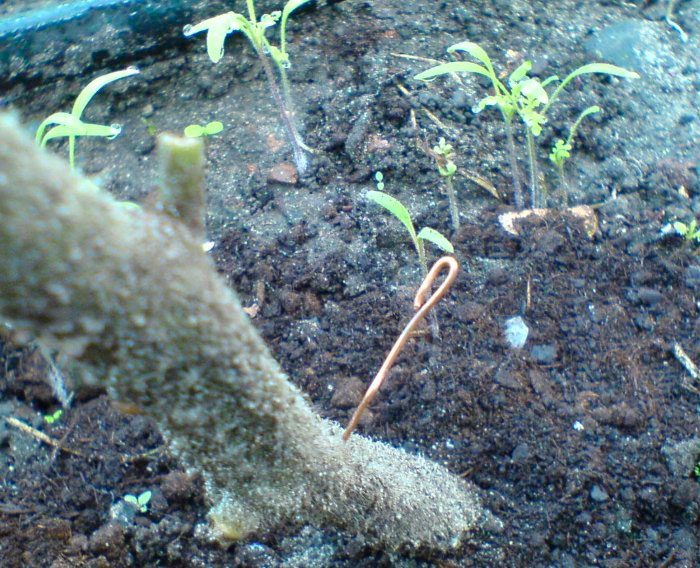
Copper wire
This method using copper wire was patented by German scientists. It lies in the fact that before planting in open ground, the root system of the seedlings is wrapped with a thin copper wire. There is another method of using copper wire for the prevention of fungal diseases. In this case, the stalk of pepper, eggplant or tomato is pierced with copper wire (the length of the segment is from 30 to 40 mm). Next, a piece of wire is pushed through the stem, after which its ends are lowered down and pressed against the plant. In this case, the culture constantly receives microdoses of copper, which stimulates its respiration, stabilizes the production of chlorophyll and enhances oxidative processes. Thanks to this, the plant's resistance to fungal diseases increases. Remember that you can wire the stem only when it gets stronger. Do not forget to prepare the copper wire, for this it is calcined over a fire and cleaned with sandpaper. Then it is cut into small pieces and introduced into the stem of the bush at a height of about 10 centimeters from the soil surface. Wire ends should not be wrapped around the stem.
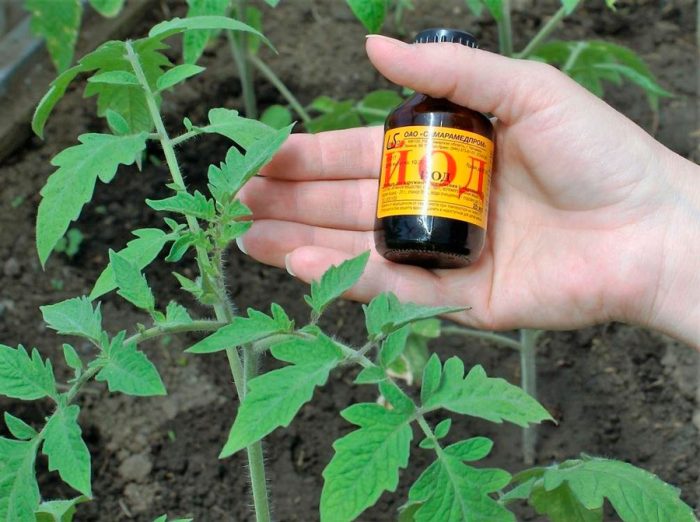
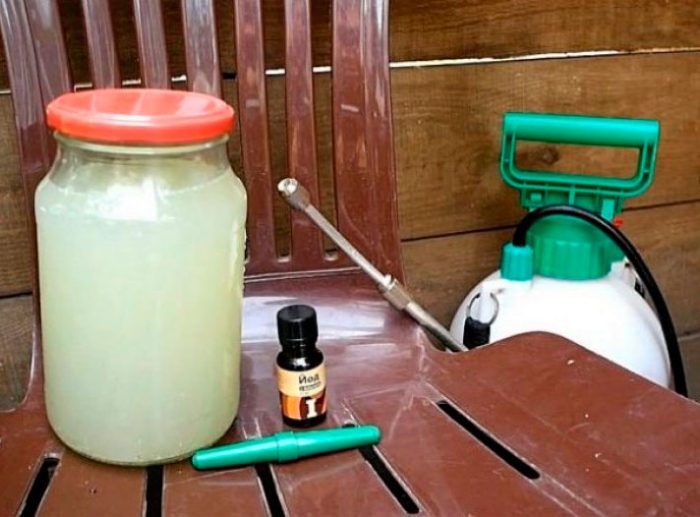
Iodine
The fact that iodine has antimicrobial properties has been known for a long time. It has long been used to protect the foliage of potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes and peppers. For late blight, iodine is used as follows: a bucket of water is combined with 1 liter of low-fat milk and 20 drops of iodine, everything is mixed well. With this mixture, seedlings are treated half a month after transplanting them into open ground, and then the plants are sprayed with them regularly once a week.
Serum
Whey is quite effective in the fight against late blight, which is combined with water in a 1: 1 ratio. A thin film appears on the surface of a plant sprayed with such a composition, which does not allow pathogenic fungi to penetrate into the bush. The microflora contained in the serum is destructive for the causative agent of late blight. However, the film formed after treatment is very quickly destroyed, in this regard, the bushes should be sprayed systematically. The first spraying with serum is carried out in July, and then they are repeated every day.


Watch this video on YouTube
Kefir
A bucket of water is combined with 1 liter of kefir (fermented for 2 days) or yogurt, treat the bushes with a mixture. The first spraying with such a composition can be carried out 15 days after transplanting the seedlings to the garden bed.
Salt
Saline solution is also quite effective in combating late blight. He, getting on the fruits, foliage and shoots, forms a film on them, which does not allow pathogens to penetrate the plant through the stomata. But such a solution is used only to protect plants from late blight, and not for treatment.
Garlic
Garlic has a detrimental effect on fungal spores. The first garlic treatment is carried out shortly before the formation of the ovaries, then it is repeated twice: after 1.5 weeks and half a month after the second spraying. To prepare the infusion, pour 1.5 tbsp into a bucket of water. garlic pulp (finely chopped heads and stems), after 24 hours, filter the agent and combine with 1.5-2 grams of manganese potassium. Mix everything well and you can start spraying the bushes.
Wood ash
Combine a bucket of water with 5 liters of wood ash, the infusion will be ready after three days, but do not forget to stir it periodically. Gently drain the infusion and add such an amount of water to it so that the final volume is 30 liters.Add 35 grams of household or liquid soap crushed on a grater to the solution, mix everything thoroughly. Plants are treated with this agent 3 times during the season: one and a half weeks after transplanting the seedlings to the garden bed, shortly before flowering and immediately after the formation of the first ovaries begins.
Tinder fungus
Regularly, once every 1.5 weeks, early in the morning in calm and calm weather, the bushes are sprayed with a composition that is able to restrain the development of late blight. To prepare it, 100 grams of fresh tinder fungus is crushed, dried, and then passed through a meat grinder. After that, it is combined with 1 liter of boiling water, the container is covered with a lid and wait until the mixture has completely cooled down. With the strained infusion, the bushes are sprayed for the first time when the ovaries appear, and after half a month they are re-treated.


Watch this video on YouTube