The herbaceous perennial plant garlic (allium sativum) is a species belonging to the genus Onion of the Amaryllidaceae family. His homeland is Central Asia. It was first cultivated in the mountains of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, in the northern part of Iran, in Afghanistan and Pakistan. Scientists have proven that garlic originated from long-pointed onions. Garlic is popular in all countries and is valued for its pungent taste and unusual pungent odor. However, it is popular not only among cooks, it is also used in medicine, since it has long been known that this plant has medicinal properties.
Content
Brief description of cultivation
- Landing... Garlic cloves are planted in open soil at the beginning of the spring, after the soil warms up to 5-7 degrees.
- Illumination... Needs lots of bright sunlight.
- Priming... Suitable nutritious cultivated loamy or sandy loam soil of neutral reaction.
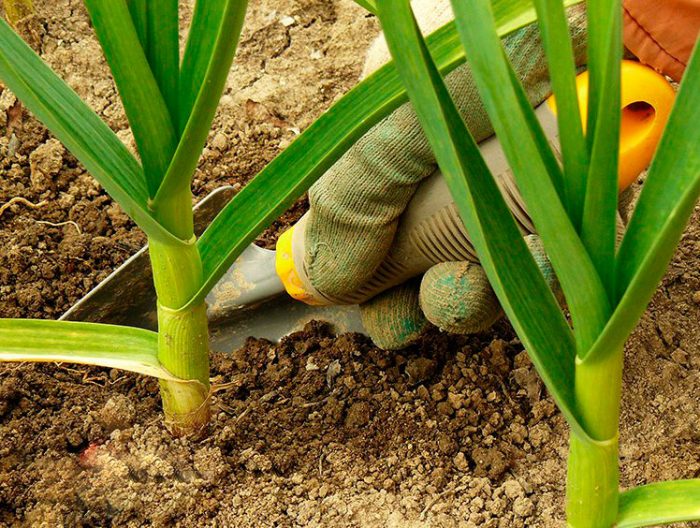
- Watering... During the active growth of the aboveground part of the garlic, it is watered often and abundantly. From the middle to the end of the growing season, watering is reduced to moderate, and if it rains regularly, then the garden may not be watered at all.
- Fertilizer... The first feeding is carried out at the beginning of foliage growth, and the second one - after half a month, and for this, a nitrogen-containing fertilizer is used, for example, a solution of bird droppings (1:12) or mullein (1:10), you can also take an infusion of grass. During the formation of cloves, which is observed in the last days of June or the first days of July, the plants are fertilized with wood ash. It is not recommended to feed garlic with a large amount of mineral fertilizers. In mid-August, all feeding is stopped.
- Reproduction... Vegetative (teeth).
- Harmful insects... Onion flies, thrips, moths, lurkers, hoverflies, stem nematodes, root mites, and quadrupeds garlic mites.
- Diseases... Black mold, fusarium (bottom rot), downy mildew (downy mildew) and white rot.
Features of spring garlic
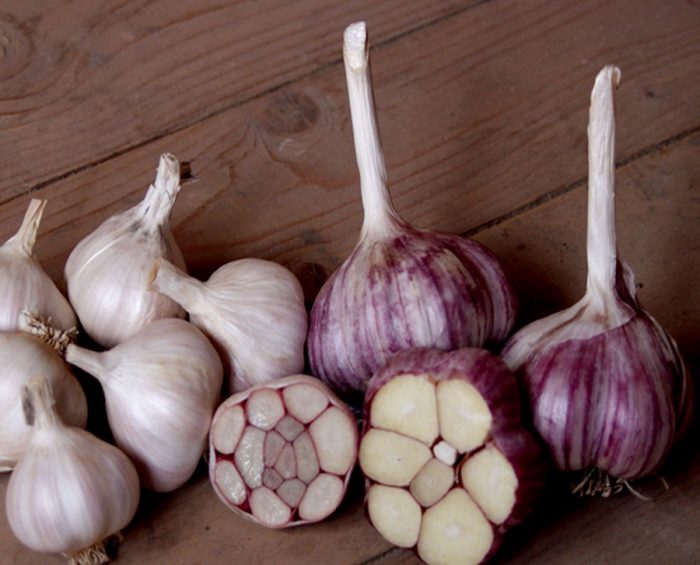
Garlic has a slightly flattened rounded bulb, which has a complex structure: 2-50 children are formed in the axils of the scales, which are covered with hard leathery scales. These children are popularly called slices or teeth. The oblong teeth have a triangular cross-section, they thicken towards the center and have a convex outer surface.Covering scales at the lobules can be pale yellow, white, dark purple or violet-pink. Narrow grooved sheet plates have a lanceolate elongated shape, from the seamy side they are keel-shaped. The leaves are pointed towards the top, they can be erect or drooping, their width can be up to 10 mm, and the length varies from 0.3 to 1 meter. The false stem of such a plant is strong enough, it is formed due to the fact that the next leaf grows from the sinus of the previous leaf plate. The height of the flower arrow varies from 0.6 to 1.5 m, at the top it twists into a spiral and ends with an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, and before flowering begins, it is covered with a film. The composition of the spherical inflorescence includes sterile flowers of a pale lilac or white color, a dense bedspread and bulbs. The fruit is a box, inside of which airy bulbs-bulbs ripen, in this regard, garlic cannot be propagated by seed, since it does not form seeds at all. However, in ornamental species, as well as in perennial garlic, widely cultivated in Central Asia, which does not form an onion, seeds are formed.
Planting spring garlic outdoors
What time to plant
For reproduction of spring garlic, only its cloves are used; they are planted in open ground at the beginning of the spring period immediately after the soil on the site warms up to 5-7 degrees. Formation and growth of the root system and foliage is observed at a temperature of 4-10 degrees. If the garlic is planted later than necessary, this will have a negative impact on the yield. The fact is that when the air and soil warms up to higher temperatures, then because of this, the bushes stop developing, and the bulbs stop forming. If you care for your garlic correctly and provide it with the right conditions for growth, then growing it will be quite simple.
Site preparation
For the cultivation of such a plant, a cultivated nutrient neutral loamy or sandy loam soil is suitable. The site must be sunny and well protected from the cold north wind. Low-lying areas, where the snow cover does not melt for a long time and water stagnation is observed, are the least suitable for growing garlic.
They begin to prepare a site for planting such a culture in the autumn. To do this, the soil is dug to the depth of the shovel bayonet, while 3 tbsp is added to it. wood ash, 5 liters of compost or humus and 10-15 grams of complex mineral fertilizer per 1 square meter of land. In springtime, before starting planting, the surface of the bed must be leveled with a rake.
Best predecessors
Garlic grows best in those areas where cabbage, cucumbers, squash, squash and other pumpkin, cereals and legumes, as well as herbs were grown before it. The worst areas for growing garlic are areas where potatoes or carrots were previously cultivated. And those areas where onions or garlic grew can be used for growing this crop no earlier than after 3 or 4 years.
Since garlic is able to scare away slugs, borers, weevils and other harmful insects, it is recommended to place a garden bed with it next to roses, gladioli, tulips, strawberries, potatoes, black currants, onions, tomatoes, cucumbers and gooseberries. Remember that if spring garlic is planted near peas, cabbage or beans, then it will oppress these crops.


Watch this video on YouTube
Landing rules
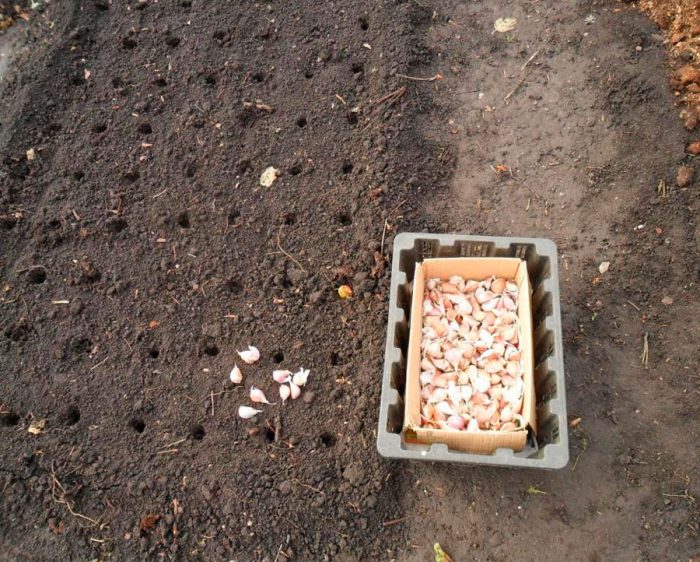
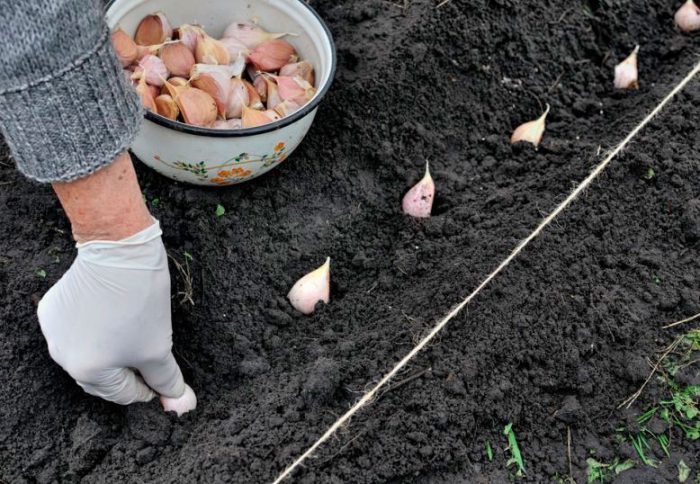
Immediately before planting, the cloves must be separated from the bulb. At the same time, it is recommended to plant only medium (3–6 grams) and large (more than 6 grams) slices, you cannot peel them.Planting material should not be taken from the bulbs on which only 2 or 3 slices are formed, since this is a degenerating garlic that is not suitable for reproduction. Examine all lobules, they should be elastic and not injured.
When there are 30 to 40 days left before planting, whole garlic heads should be dug into the snow or put on the refrigerator shelf intended for vegetables. Before planting, the prepared cloves are placed in a disinfectant solution of potassium manganese (1%) or copper sulfate (1%) for half a day. Instead, the cloves can be placed in a very warm place (40 to 42 degrees) for 8-10 hours. Ash liquor can also be used to disinfect the planting material, for the preparation of which it is necessary to combine a liter of water with 200 g of ash, the mixture is boiled for half an hour. When the lye has cooled, the teeth are immersed in it for a couple of hours.
In order for the first sprouts to appear as soon as possible, it is recommended to germinate garlic cloves for a start in room conditions. Scaled teeth should be wrapped in a damp cloth and placed in a polyethylene bag for two or three days.
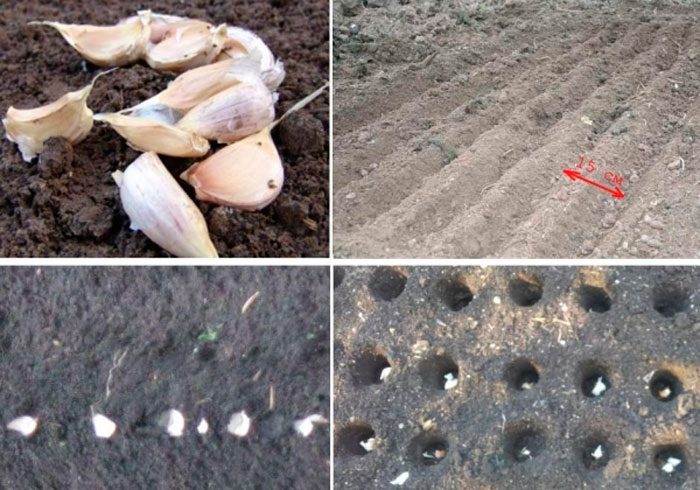
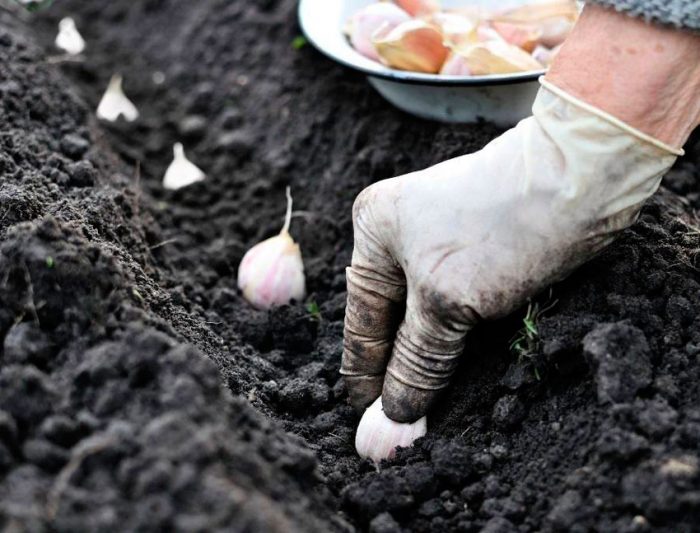
It is necessary to plant garlic in a pre-moistened soil. The surface of the bed must be leveled, and then grooves are made on it with a depth of 30 to 40 mm, while the width between them should be from 25 to 30 centimeters. Then the teeth are distributed in them, while the distance between the middle slices should be at least 8 centimeters, and between the large ones - about 10-12 centimeters. You should not press the slices into the soil, because this has a bad effect on the growth and development of the root system.
Spring garlic care
In spring garlic, seedlings are very frost-resistant, and their appearance is observed at a temperature of 3-4 degrees. It is very easy to grow such a culture on your site; for this, the bushes must be weeded, watered, fed and regularly loosened the soil surface. To reduce the number of weeding and watering, it is recommended to cover the bed surface with a two or three centimeter layer of mulch (peat, humus or rotted manure).
How to water
Remember to water such a plant correctly throughout the growing season. In the first half of the growing season, the bushes experience intensive growth of the aboveground part, and at this time they need to be watered often and abundantly. If the tops of the leaf plates turn yellow or dry out, then this indicates excessively rare or poor watering. From the middle to the end of the growing season, watering should be reduced to moderate, if at this time the soil is oversaturated with moisture, this can cause bulbs to dry out or be affected by diseases. If it rains regularly at this time, then you can not water the garden with such a plant at all. When it rains or the area is watered, the next day the soil surface is necessarily loosened.
Fertilizer
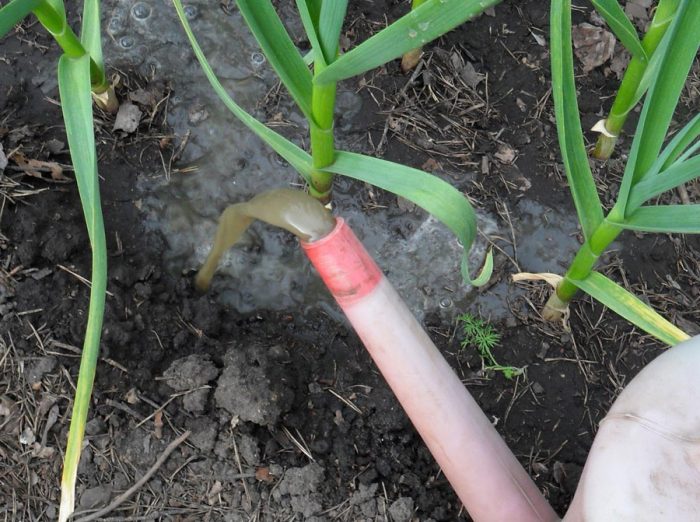
After the first sprouts appear in the garden, the garlic will need feeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizer. For this purpose, you can use an infusion of grass, humus, a solution of bird droppings (12: 1) or mullein (10: 1), and you can also take mineral fertilizers. You cannot feed such a crop with fresh manure. Re-feeding is carried out half a month after the first, using a liquid nutrient solution for this.
The formation of lobules is observed in the last days of June or the first days of July. At this time, the bushes need phosphorus and potassium, therefore it is recommended to use ash infusion for feeding. During all dressings, garlic must be watered. Fertilization ends in mid-August. Do not feed the garlic with a large amount of mineral fertilizers, as this can lead to the accumulation of substances harmful to the human body in the bulbs.


Watch this video on YouTube
Diseases and pests of spring garlic
Possible problems
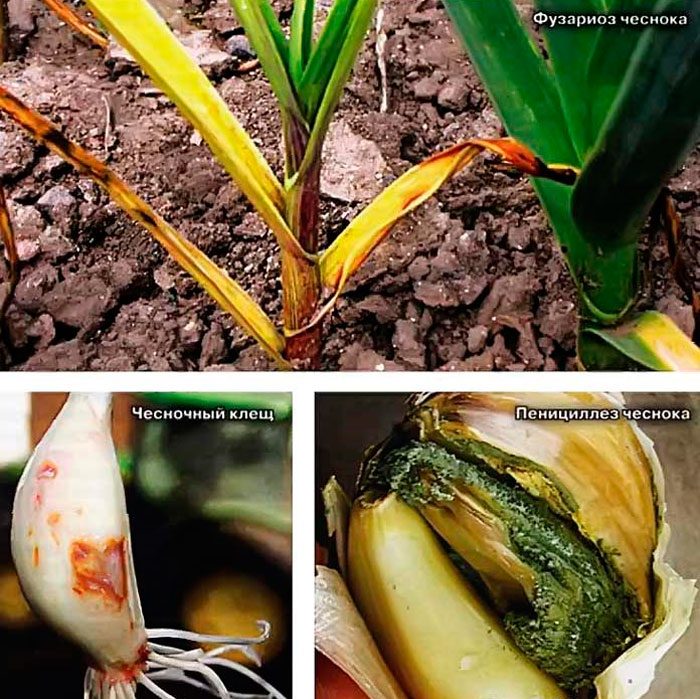
Garlic has a fairly high resistance to harmful insects and diseases, but problems can still arise with it. So, it can be damaged by such harmful insects as: onion flies, thrips, moths, lurkers, hoverflies, stem nematodes, root mites and a four-legged garlic mite. It can also suffer from black mold, fusarium or bottom rot, peronosporosis or downy mildew and white rot. It is necessary to control the condition of the bushes immediately after the emergence of sprouts.
Treatment
In order to prevent the appearance of harmful insects, such a plant is fed with ammonium sulfate. Re-feeding is carried out in mid-June. All bushes that have been damaged by pests or affected by diseases must be carefully dug up, then their root system is examined. Avoid thickening the plantings and thin out if necessary.
You can understand that the bush is affected by a fungal disease by the following signs: the formation of yellow spots on the foliage, the appearance of a plaque on the bottom of the bulb or between the scales, the color of the leaf plates changes to yellow, and they dry, the roots die off. If the appearance of rot is associated with a bacterial disease, then brown ulcers form on the bulbs, the color of the scales changes and the smell of decay is felt. To cure the bushes affected by a fungal disease, they are sprayed with agents such as Gamair-TM or Alirin-B.
To get rid of ticks, thrips and other harmful insects, the garden bed should be sprayed with a solution of the biological product Bitoxibacillin or Lepidocide. If a stem nematode settles on the garlic, it will be extremely difficult to get rid of it. It is a small worm that feeds on plant sap, because of this, the roots dry out in the affected bushes, and cracks appear on the bulb. In order to prevent the appearance of nematodes in the aisles of garlic, it is recommended to plant chicory or calendula.
In order for garlic to be affected by diseases and damaged by pests as rarely as possible, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the agrotechnical rules of such a culture and not forget about preventive measures. Also remember that planting material and soil on the site needs mandatory pre-sowing preparation.


Watch this video on YouTube
Harvesting and storage of spring garlic
Spring garlic is harvested from mid to late August after 2/3 of its leaf plates turn yellow and fall. It is impossible to delay harvesting, because because of this, the scales on the bulbs will crack, the cloves will begin to disintegrate, and new roots will appear on the bottom.
When half a month is left before harvesting, you need to stop watering the garlic altogether. Carefully scrape off the soil from the bulbs, in this case they dry out and ripen much faster. The crop is harvested on a fine day, for this the bushes are dug with a pitchfork. Remove soil residues from the bulbs and spread them out to dry. For this, the garlic can be spread directly on the garden bed, where it will dry for 5 days. If it starts to rain, the bulbs should be moved to a dry and well-ventilated area or under a canopy. The crop is dried along with foliage and roots. After the bulbs are well dry, their roots are shortened to a maximum of 3 mm, the foliage is removed, and the shoots are cut off, leaving about 10 centimeters. Then the bulbs are sorted by size, after which they can be stored. For this, a dry and ventilated room is chosen, while the air temperature can vary from 16 to 20 degrees or from 2 to 4 degrees. Garlic is tied in bunches or braided into braids, or you can simply place it in a nylon stocking or a mesh bag, and store it in a suspended state. Also, for storage, the crop can be poured into boxes from boards or into wicker baskets. If the garlic is stored in glass or plastic containers, it is recommended to sprinkle it with coarse salt, which perfectly absorbs moisture.


Watch this video on YouTube
Types and varieties of spring garlic
Distinguish between winter and spring garlic. In both varieties, the structure is similar, however, in winter varieties, large cloves are arranged in 1 row, and in spring varieties, small slices are located in several rows. In addition, in winter garlic, after ripening, a part of the flower arrow remains in the bulb, which is a dividing rod, and cloves are already placed around it; in spring varieties, such a rod is absent, because they do not shoot. Winter garlic can also be planted in the ground in spring, however, in this case, its bulbs will not divide into cloves, since they will not have enough time, therefore it is recommended to plant it in autumn. Both bulbs and slices are used for breeding winter varieties.
In order for the harvest of spring garlic to be rich, one must carefully consider the choice of the variety. Since this plant reacts negatively to a sharp change in climatic conditions, then zoned varieties should be chosen for planting. All varieties are divided into early ripening, medium ripening and late ripening. And they are also divided into shooting and non-shooting, but this division is conditional, for example, in warm climates, non-shooting varieties can throw out the arrow, and shooting varieties grown in cool climates may not form a peduncle. Most often, arrowhead varieties are cultivated as winter crops.
The most popular among gardeners are the following varieties of spring garlic:
- Gulliver... This medium-ripening, versatile variety has high yields, disease resistance and long shelf life. This spring variety is the largest, the weight of its bulbs can reach an average of 95-115 grams, but sometimes they can weigh up to 250 grams. The head is covered with gray scales, inside of which 4 or 5 large lobules with a sharp taste are formed.
- Aleisky... This spring variety is the best of those that have been released for cultivation in the middle latitudes. However, it grows well in warm mild climates. It is quite fruitful, one of its bulbs has an average weight of about 25 grams. The cloves have a pungent taste. This variety is not resistant to fusarium.
- Yelenovsky... Such a mid-season variety was born relatively recently. It is a fruitful universal non-shooting and is resistant to disease and frost. Dense bulbs weigh about 35 grams and include 7-9 lobules. If you store the crop correctly, it will retain its properties and taste for a couple of years.
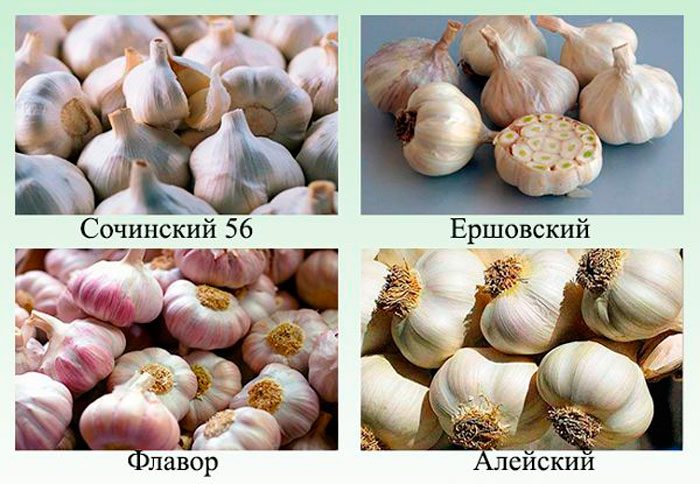
- Sochi 56... This early variety gives a stable yield and is resistant to frost and disease. The bulb is covered with dense white scales, and its mass can reach 45 grams. The cloves contain sucrose, which makes them very tasty. The harvested crop retains its qualities for one and a half years.
- Permyak... The variety is non-shooting with an average ripening period, it is zoned for cultivation in the northern regions. One onion has an average weight of about 35 grams and includes 15-16 cloves. They contain a lot of essential oils, so they taste very pungent. The harvested crop will be stored for no longer than 10 months.
- Victorio... The medium ripening variety is distinguished by its yield and semi-sharp taste. It is recommended for growing in gardens. The heads weigh about 40 grams and contain up to 13 lobules. The harvest of such garlic is able to maintain its qualities for 8 months.
- Abrek... Medium ripening, the variety has a very pungent taste. The bulb weighs about 25 grams and contains 13 to 16 cloves. You can store the crop for no longer than 7 months.
- Moscow... A medium-ripening non-shooting variety with a slightly pungent taste and high yield. The shape of the multi-toothed bulbs is round, their average weight is about 14 grams, they are distinguished by good keeping quality.
- Ershovsky... This non-shooting variety is semi-sharp and disease resistant.The heads weigh on average about 35 grams, and they can contain up to 12 lobules. You can store the crop for no longer than seven months.
- Degtyarsky... The variety was created by the Ural breeders. The head weighs about 38 grams and contains 15 to 18 teeth. The pale red outer scales are covered with purple streaks. The color of leathery scales is pink. The white pulp of the lobules has a pungent taste. The crop is stored for no longer than 10 months.
There are also foreign varieties of spring garlic that grow well in mid-latitudes. The best ones are:
- Kledor... This elite, high-yielding medium-ripening variety was created by French breeders; it is resistant to both bacterial and fungal diseases. In diameter, the bulb reaches 4.5–5.5 cm, and it includes 16–20 large lobules, which are covered with a pink shell.
- Flavor... This medium-ripening French variety is widespread in Western Europe and has a medium-sharp flavor. The bulbs weigh on average about 80 grams, and are covered with glossy pinkish scales. One head contains 15–20 teeth arranged in 2 rows, they are small and painted in a pastel cream shade. If stored correctly, such garlic will last until the next harvest.


Watch this video on YouTube